|
|
|
The Bulgars, a Central Asian Turkic tribe, merged with the local Slavic inhabitants in the late 7th century to form the first Bulgarian state. In succeeding centuries, Bulgaria struggled with the Byzantine Empire to assert its place in the Balkans, but by the end of the 14th century the country was overrun by the Ottoman Turks. Northern Bulgaria attained autonomy in 1878 and all of Bulgaria became independent from the Ottoman Empire in 1908. Having fought on the losing side in both World Wars, Bulgaria fell within the Soviet sphere of influence and became a People's Republic in 1946. Communist domination ended in 1990, when Bulgaria held its first multiparty election since World War II and began the contentious process of moving toward political democracy and a market economy while combating inflation, unemployment, corruption, and crime. The country joined NATO in 2004 and the EU in 2007.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
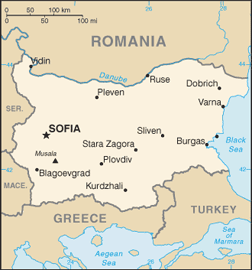
Southeastern Europe, bordering the Black Sea, between Romania and Turkey
|
|
|
|
|
43 00 N, 25 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 110,879 sq km
country comparison to the world: 104
land:
108,489 sq km
water:
2,390 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly larger than Tennessee
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,808 km
border countries:
Greece 494 km, Macedonia 148 km, Romania 608 km, Serbia 318 km, Turkey 240 km
|
|
|
|
|
354 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone:
24 nm
exclusive economic zone:
200 nm
|
|
|
|
|
temperate; cold, damp winters; hot, dry summers
|
|
|
|
|
mostly mountains with lowlands in north and southeast
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Black Sea 0 m
highest point:
Musala 2,925 m
|
|
|
|
|
bauxite, copper, lead, zinc, coal, timber, arable land
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 29.94%
permanent crops:
1.9%
other:
68.16% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
5,880 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
19.4 cu km (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 6.92 cu km/yr (3%/78%/19%)
per capita:
895 cu m/yr (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
earthquakes; landslides
|
|
|
|
|
air pollution from industrial emissions; rivers polluted from raw sewage, heavy metals, detergents; deforestation; forest damage from air pollution and resulting acid rain; soil contamination from heavy metals from metallurgical plants and industrial wastes
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
strategic location near Turkish Straits; controls key land routes from Europe to Middle East and Asia
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7,204,687 (July 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 13.8% (male 509,544/female 484,816)
15-64 years:
68.5% (male 2,426,060/female 2,508,772)
65 years and over:
17.7% (male 518,711/female 756,784) (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 41.4 years
male:
39.2 years
female:
43.6 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
-0.79% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 231
|
|
|
|
|
9.51 births/1,000 population (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
|
|
|
|
|
14.31 deaths/1,000 population (July 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
-3.11 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 71% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
-0.3% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.68 male(s)/female
total population:
0.92 male(s)/female (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 17.87 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 115
male:
21.28 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
14.25 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 73.09 years
country comparison to the world: 111
male:
69.48 years
female:
76.91 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.41 children born/woman (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
|
|
|
|
|
less than 0.1% (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
|
|
|
|
|
346 (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
|
|
|
|
|
100 (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Bulgarian(s)
adjective:
Bulgarian
|
|
|
|
|
Bulgarian 83.9%, Turk 9.4%, Roma 4.7%, other 2% (including Macedonian, Armenian, Tatar, Circassian) (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Bulgarian Orthodox 82.6%, Muslim 12.2%, other Christian 1.2%, other 4% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Bulgarian 84.5%, Turkish 9.6%, Roma 4.1%, other and unspecified 1.8% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
98.2%
male:
98.7%
female:
97.7% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 14 years
male:
13 years
female:
14 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
4.5% of GDP (2005)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Bulgaria
conventional short form:
Bulgaria
local long form:
Republika Balgariya
local short form:
Balgariya
|
|
|
|
|
parliamentary democracy
|
|
|
|
|
name: Sofia
geographic coordinates:
42 41 N, 23 19 E
time difference:
UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
28 provinces (oblasti, singular - oblast); Blagoevgrad, Burgas, Dobrich, Gabrovo, Khaskovo, Kurdzhali, Kyustendil, Lovech, Montana, Pazardzhik, Pernik, Pleven, Plovdiv, Razgrad, Ruse, Shumen, Silistra, Sliven, Smolyan, Sofiya, Sofiya-Grad, Stara Zagora, Turgovishte, Varna, Veliko Turnovo, Vidin, Vratsa, Yambol
|
|
|
|
|
3 March 1878 (as an autonomous principality within the Ottoman Empire); 22 September 1908 (complete independence from the Ottoman Empire)
|
|
|
|
|
Liberation Day, 3 March (1878)
|
|
|
|
|
adopted 12 July 1991
|
|
|
|
|
civil and criminal law based on Roman law; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Georgi PARVANOV (since 22 January 2002); Vice President Angel MARIN (since 22 January 2002)
head of government:
Prime Minister Boyko BORISSOV (since 27 July 2009);
Deputy Prime Ministers Simeon DJANKOV and Tsvetan TSVETANOV (since 27 July 2009);
cabinet:
Council of Ministers nominated by the prime minister and elected by the National Assembly
elections:
president and vice president elected on the same ticket by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held 22 and 29 October 2006 (next to be held in 2011); chairman of the Council of Ministers (prime minister) elected by the National Assembly; deputy prime ministers nominated by the prime minister and elected by the National Assembly
election results:
Georgi PARVANOV reelected president; percent of vote - Georgi PARVANOV 77.3%, Volen SIDEROV 22.7%; Sergei STANISHEV elected prime minister, result of legislative vote - 168 to 67
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National Assembly or Narodno Sabranie (240 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held 5 July 2009 (next to be held mid-2013)
election results:
percent of vote by party - GERB 39.7%, BSP 17.7%, MRF 14.4%, ATAKA 9.4%, Blue Coalition 6.8%, RZS 4.1%, other 7.9%; seats by party - GERB 116, BSP 40, MRF 38, ATAKA 21, Blue Coalition 15, RZS 10
|
|
|
|
|
independent judiciary comprised of judges, prosecutors and investigating magistrates who are appointed, promoted, demoted, and dismissed by a 25-member Supreme Judicial Council (consists of the chairmen of the two Supreme Courts, the Chief Prosecutor, and 22 members, half of whom are elected by the National Assembly and the other half by the bodies of the judiciary for a 5-year term in office); three levels of case review; 182 courts of which two Supreme Courts act as the last instance on civil and criminal cases (the Supreme Court of Cassation) and appeals of government decisions (the Supreme Administrative Court)
|
|
|
|
|
ATAKA (Attack Coalition) (coalition of parties headed by the Attack National Union); Attack National Union [Volen SIDEROV]; Agrarian National Union or ANU [Stefan LICHEV]; Blue Coalition (a coalition of center-right parties dominated by UDF and DSB); Bulgarian New Democracy [Borislav RALCHEV]; Bulgarian Socialist Party or BSP [Sergei STANISHEV]; Citizens for the European Development of Bulgaria or GERB [Tsvetan TSVETANOV]; Coalition for Bulgaria or CfB (coalition of parties dominated by BSP) [Sergei STANISHEV]; Democrats for a Strong Bulgaria or DSB [Ivan KOSTOV]; Gergyovden [Petar STOYANOVICH]; Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization or IMRO [Krasimir KARAKACHANOV]; Liberal Initiative for Democratic European Development or LIDER [Khristo KOVACHKI]; Movement for Rights and Freedoms or MRF [Ahmed DOGAN]; Movement Forward (LIDER, IMRO, ANU, Gergyovden); National Movement for Stability and Progress or NDSV [Simeon SAXE-COBURG-GOTHA] (formerly National Movement Simeon II or NMS2); New Time [Emil KOSHLUKOV]; Order, Law, Justice or RZS [Yane YANEV]; Union of Democratic Forces or UDF [Martin DIMITROV]; Union of Free Democrats or UFD [Stefan SOFIYANSKI]; United Agrarians [Anastasia MOZER]
|
|
|
|
|
Confederation of Independent Trade Unions of Bulgaria or CITUB; Podkrepa Labor Confederation
other:
numerous regional, ethnic, and national interest groups with various agendas
|
|
|
|
|
ACCT, Australia Group, BIS, BSEC, CE, CEI, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EIB, EU, FAO, G- 9, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM (guest), NATO, NSG, OAS (observer), OIF, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, SECI, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNWTO, UPU, WCL, WCO, WEU (associate affiliate), WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Latchezar PETKOV
chancery:
1621 22nd Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 387-0174
FAX:
[1] (202) 234-7973
consulate(s) general:
Chicago, Los Angeles, New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Nancy McELDOWNEY
embassy:
16 Kozyak Street, Sofia 1407
mailing address:
American Embassy Sofia, US Department of State, 5740 Sofia Place, Washington, DC 20521-5740
telephone:
[359] (2) 937-5100
FAX:
[359] (2) 937-5320
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of white (top), green, and red
note:
the national emblem, formerly on the hoist side of the white stripe, has been removed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bulgaria, a former Communist country that entered the EU on 1 January 2007, has experienced strong growth since a major economic downturn in 1996. Successive governments have demonstrated a commitment to economic reforms and responsible fiscal planning, but have failed so far to rein in rising inflation and large current account deficits. Bulgaria has averaged more than 6% growth since 2004, attracting significant amounts of foreign direct investment, but corruption in the public administration, a weak judiciary, and the presence of organized crime remain significant challenges.
|
|
|
|
|
$93.98 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
$88.66 billion (2007 est.)
$83.48 billion (2006 est.)
note:
data are in 2008 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$49.9 billion (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
6% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
6.2% (2007 est.)
6.3% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$12,900 (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
$12,100 (2007 est.)
$11,300 (2006 est.)
note:
data are in 2008 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 7.3%
industry:
30.5%
services:
62.2% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.67 million (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 7.5%
industry:
35.5%
services:
57% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
6.3% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
7.7% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
14.1% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3%
highest 10%:
25.5% (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
30.7 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 109
26.4 (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
33.4% of GDP (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $22.24 billion
expenditures:
$20.74 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
14.1% of GDP (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
41.9% of GDP (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
12.3% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 171
9.8% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.77% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 111
4.58% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
10.86% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 85
10% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$14.29 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 40
$15.58 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$19.67 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 42
$17.03 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$32.04 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 52
$25.18 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$8.858 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 68
$21.79 billion (31 December 2007)
$10.32 billion (31 December 2006)
|
|
|
|
|
vegetables, fruits, tobacco, wine, wheat, barley, sunflowers, sugar beets; livestock
|
|
|
|
|
electricity, gas, water; food, beverages, tobacco; machinery and equipment, base metals, chemical products, coke, refined petroleum, nuclear fuel
|
|
|
|
|
1.5% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|
|
40.25 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
|
|
|
|
|
31.08 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|
|
8.441 billion kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.097 billion kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3,357 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
|
|
|
|
|
124,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
76,570 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
189,000 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
|
|
|
|
|
15 million bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|
|
300 million cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
|
|
|
|
|
3.4 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008)
country comparison to the world: 198
|
|
|
|
|
3.1 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
|
|
|
|
|
5.663 billion cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
|
|
|
|
|
-$12.65 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
-$8.716 billion (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$22.71 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 69
$18.58 billion (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
clothing, footwear, iron and steel, machinery and equipment, fuels
|
|
|
|
|
Greece 9.9%, Germany 9.2%, Turkey 8.9%, Italy 8.5%, Romania 7.2%, Belgium 5.9%, France 4.1% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$35.64 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
$28.65 billion (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment; metals and ores; chemicals and plastics; fuels, minerals, and raw materials
|
|
|
|
|
Russia 14.6%, Germany 11.8%, Italy 7.9%, Ukraine 7.3%, Romania 5.6%, Turkey 5.5%, Greece 5.4%, Austria 4.1% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$17.93 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
$17.54 billion (31 December 2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$51.46 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
$42.62 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$42.91 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
$33.91 billion (31 December 2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.292 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
$559 million (31 December 2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
leva (BGN) per US dollar - 1.3171 (2008 est.), 1.4366 (2007), 1.5576 (2006), 1.5741 (2005), 1.5751 (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
| Communications ::Bulgaria |
|
|
|
2.258 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 55
|
|
|
|
|
10.633 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 59
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: an extensive but antiquated telecommunications network inherited from the Soviet era; quality has improved; the Bulgaria Telecommunications Company's fixed-line monopoly terminated in 2005 when alternative fixed-line operators were given access to its network; a drop in fixed-line connections in recent years has been more than offset by a sharp increase in mobile-cellular telephone use fostered by multiple service providers; the number of cellular telephone subscriptions now greatly exceeds the population
domestic:
a fairly modern digital cable trunk line now connects switching centers in most of the regions; the others are connected by digital microwave radio relay
international:
country code - 359; submarine cable provides connectivity to Ukraine and Russia; a combination submarine cable and land fiber-optic system provides connectivity to Italy, Albania, and Macedonia; satellite earth stations - 3 (1 Intersputnik in the Atlantic Ocean region, 2 Intelsat in the Atlantic and Indian Ocean regions) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 31, FM 63, shortwave 2 (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
39 (plus 1,242 repeaters) (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
.bg
|
|
|
|
|
706,648 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 45
|
|
|
|
|
2.647 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 63
|
|
|
|
|
| Transportation ::Bulgaria |
|
|
|
212 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|
|
total: 132
over 3,047 m:
2
2,438 to 3,047 m:
18
1,524 to 2,437 m:
15
under 914 m:
97 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 80
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
6
under 914 m:
73 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
3 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 2,926 km; oil 339 km; refined products 156 km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4,294 km
country comparison to the world: 38
standard gauge:
4,049 km 1.435-m gauge (2,880 km electrified)
narrow gauge:
245 km 0.760-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 40,231 km
country comparison to the world: 89
paved:
39,587 km (includes 331 km of expressways)
unpaved:
644 km (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
470 km (2008)
country comparison to the world: 83
|
|
|
|
|
total: 74
country comparison to the world: 59
by type:
bulk carrier 37, cargo 14, chemical tanker 5, container 6, liquefied gas 2, passenger/cargo 2, petroleum tanker 3, roll on/roll off 4, specialized tanker 1
foreign-owned:
65 (Germany 63, Ireland 1, Russia 1)
registered in other countries:
31 (Comoros 2, Malta 5, Panama 3, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 15, Slovakia 6) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Burgas, Varna
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bulgarian Armed Forces: Ground Forces, Naval Forces, Bulgarian Air Forces (Bulgarski Voennovazdyshni Sily, BVVS) (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
18-27 years of age for voluntary military service; as of May 2006, 67% of the Bulgarian Army comprised of professional soldiers; conscription ended January 2008; Air Forces and Naval Forces became fully professional at the end of 2006 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,701,979
females age 16-49:
1,691,092 (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,351,312
females age 16-49:
1,381,017 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 38,263
female:
36,374 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.6% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Bulgaria |
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
major European transshipment point for Southwest Asian heroin and, to a lesser degree, South American cocaine for the European market; limited producer of precursor chemicals; vulnerable to money laundering because of corruption, organized crime; some money laundering of drug-related proceeds through financial institutions (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
|