|
|
|
The Italians supplanted the Ottoman Turks in the area around Tripoli in 1911 and did not relinquish their hold until 1943 when defeated in World War II. Libya then passed to UN administration and achieved independence in 1951. Following a 1969 military coup, Col. Muammar Abu Minyar al-QADHAFI began to espouse his own political system, the Third Universal Theory. The system is a combination of socialism and Islam derived in part from tribal practices and is supposed to be implemented by the Libyan people themselves in a unique form of "direct democracy." QADHAFI has always seen himself as a revolutionary and visionary leader. He used oil funds during the 1970s and 1980s to promote his ideology outside Libya, supporting subversives and terrorists abroad to hasten the end of Marxism and capitalism. In addition, beginning in 1973, he engaged in military operations in northern Chad's Aozou Strip - to gain access to minerals and to use as a base of influence in Chadian politics - but was forced to retreat in 1987. UN sanctions in 1992 isolated QADHAFI politically following the downing of Pan AM Flight 103 over Lockerbie, Scotland. During the 1990s, QADHAFI began to rebuild his relationships with Europe. UN sanctions were suspended in April 1999 and finally lifted in September 2003 after Libya accepted responsibility for the Lockerbie bombing. In December 2003, Libya announced that it had agreed to reveal and end its programs to develop weapons of mass destruction and to renounce terrorism. QADHAFI has made significant strides in normalizing relations with Western nations since then. He has received various Western European leaders as well as many working-level and commercial delegations, and made his first trip to Western Europe in 15 years when he traveled to Brussels in April 2004. The US rescinded Libya's designation as a state sponsor of terrorism in June 2006. In January 2008, Libya assumed a nonpermanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2008-09 term. In August 2008, the US and Libya signed a bilateral comprehensive claims settlement agreement to compensate claimants in both countries who allege injury or death at the hands of the other country, including the Lockerbie bombing, the LaBelle disco bombing, and the UTA 772 bombing. In October 2008, the US Government received $1.5 billion pursuant to the agreement to distribute to US national claimants, and as a result effectively normalized its bilateral relationship with Libya. The two countries then exchanged ambassadors for the first time since 1973 in January 2009.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Egypt and Tunisia
|
|
|
|
|
25 00 N, 17 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,759,540 sq km
country comparison to the world: 17
land:
1,759,540 sq km
water:
0 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly larger than Alaska
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4,348 km
border countries:
Algeria 982 km, Chad 1,055 km, Egypt 1,115 km, Niger 354 km, Sudan 383 km, Tunisia 459 km
|
|
|
|
|
1,770 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
note:
Gulf of Sidra closing line - 32 degrees, 30 minutes north
exclusive fishing zone:
62 nm
|
|
|
|
|
Mediterranean along coast; dry, extreme desert interior
|
|
|
|
|
mostly barren, flat to undulating plains, plateaus, depressions
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Sabkhat Ghuzayyil -47 m
highest point:
Bikku Bitti 2,267 m
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, natural gas, gypsum
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 1.03%
permanent crops:
0.19%
other:
98.78% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
4,700 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
0.6 cu km (1997)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4.27 cu km/yr (14%/3%/83%)
per capita:
730 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
hot, dry, dust-laden ghibli is a southern wind lasting one to four days in spring and fall; dust storms, sandstorms
|
|
|
|
|
desertification; limited natural fresh water resources; the Great Manmade River Project, the largest water development scheme in the world, is being built to bring water from large aquifers under the Sahara to coastal cities
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Law of the Sea
|
|
|
|
|
more than 90% of the country is desert or semidesert
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,310,434
country comparison to the world: 105
note:
includes 166,510 non-nationals (July 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 33% (male 1,064,866/female 1,019,790)
15-64 years:
62.7% (male 2,033,478/female 1,920,755)
65 years and over:
4.3% (male 133,092/female 138,453) (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 23.9 years
male:
24 years
female:
23.8 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.17% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
|
|
|
|
|
25.15 births/1,000 population (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
|
|
|
|
|
3.45 deaths/1,000 population (July 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 214
|
|
|
|
|
NA (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 78% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
2.2% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.06 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.96 male(s)/female
total population:
1.05 male(s)/female (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 21.05 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 102
male:
23.21 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
18.78 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 77.26 years
country comparison to the world: 57
male:
74.98 years
female:
79.65 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.08 children born/woman (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
|
|
|
|
|
0.3% (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
10,000 (2001 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Libyan(s)
adjective:
Libyan
|
|
|
|
|
Berber and Arab 97%, other 3% (includes Greeks, Maltese, Italians, Egyptians, Pakistanis, Turks, Indians, and Tunisians)
|
|
|
|
|
Sunni Muslim 97%, other 3%
|
|
|
|
|
Arabic, Italian, English, all are widely understood in the major cities
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
82.6%
male:
92.4%
female:
72% (2003 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 17 years
male:
16 years
female:
17 years (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
2.7% of GDP (1999)
country comparison to the world: 152
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
conventional short form:
Libya
local long form:
Al Jamahiriyah al Arabiyah al Libiyah ash Shabiyah al Ishtirakiyah al Uthma
local short form:
none
|
|
|
|
|
Jamahiriya (a state of the masses) in theory, governed by the populace through local councils; in practice, an authoritarian state
|
|
|
|
|
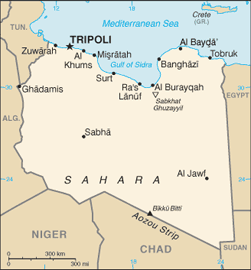
name: Tripoli (Tarabulus)
geographic coordinates:
32 53 N, 13 10 E
time difference:
UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
|
|
|
|
|
25 municipalities (baladiyat, singular - baladiyah); Ajdabiya, Al 'Aziziyah, Al Fatih, Al Jabal al Akhdar, Al Jufrah, Al Khums, Al Kufrah, An Nuqat al Khams, Ash Shati', Awbari, Az Zawiyah, Banghazi, Darnah, Ghadamis, Gharyan, Misratah, Murzuq, Sabha, Sawfajjin, Surt, Tarabulus, Tarhunah, Tubruq, Yafran, Zlitan; note - the 25 municipalities may have been replaced by 13 regions
|
|
|
|
|
24 December 1951 (from UN trusteeship)
|
|
|
|
|
Revolution Day, 1 September (1969)
|
|
|
|
|
none; note - following the September 1969 military overthrow of the Libyan government, the Revolutionary Command Council replaced the existing constitution with the Constitutional Proclamation in December 1969; in March 1977, Libya adopted the Declaration of the Establishment of the People's Authority
|
|
|
|
|
based on Italian and French civil law systems and Islamic law; separate religious courts; no constitutional provision for judicial review of legislative acts; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal and technically compulsory
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: Revolutionary Leader Col. Muammar Abu Minyar al-QADHAFI (since 1 September 1969); note - holds no official title, but is de facto chief of state
head of government:
Secretary of the General People's Committee (Prime Minister) al-Baghdadi Ali al-MAHMUDI (since 5 March 2006)
cabinet:
General People's Committee established by the General People's Congress
elections:
national elections are indirect through a hierarchy of people's committees; head of government elected by the General People's Congress; election last held March 2006 (next to be held March 2009)
election results:
NA
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral General People's Congress (760 seats; members elected indirectly through a hierarchy of people's committees)
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court
|
|
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
other: Arab nationalist movements; anti-QADHAFI Libyan exile Movement; Islamic elements
|
|
|
|
|
ABEDA, AfDB, AFESD, AMF, AMU, AU, CAEU, COMESA, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OAPEC, OIC, OPCW, OPEC, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCL, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Ali Suleiman AUJALI
chancery:
2600 Virginia Avenue NW, Suite 705, Washington, DC 20037
telephone:
[1] (202) 944-9601
FAX:
[1] (202) 944-9060
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Gene A. CRETZ
embassy:
off Jaraba Street, behind the Libyan-Swiss clinic, Ben Ashour
mailing address:
US Embassy, 8850 Tripoli Place, Washington, DC 20521-8850
telephone:
[218] 91-220-3239
|
|
|
|
|
plain green; green is the traditional color of Islam (the state religion)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Libyan economy depends primarily upon revenues from the oil sector, which contribute about 95% of export earnings, about one-quarter of GDP, and 60% of public sector wages. The expected weakness in world hydrocarbon prices throughout 2009 will reduce Libyan government tax income and constrain Libyan economic growth in 2009. Substantial revenues from the energy sector coupled with a small population give Libya one of the highest per capita GDPs in Africa, but little of this income flows down to the lower orders of society. Libyan officials in the past five years have made progress on economic reforms as part of a broader campaign to reintegrate the country into the international fold. This effort picked up steam after UN sanctions were lifted in September 2003 and as Libya announced in December 2003 that it would abandon programs to build weapons of mass destruction. UN Sanctions against Libya were lifted in September 2003. The process of lifting US unilateral sanctions began in the spring of 2004; all sanctions were removed by June 2006, helping Libya attract greater foreign direct investment, especially in the energy sector. Libyan oil and gas licensing rounds continue to draw high international interest; the National Oil Company set a goal of nearly doubling oil production to 3 million bbl/day by 2012. Libya faces a long road ahead in liberalizing the socialist-oriented economy, but initial steps - including applying for WTO membership, reducing some subsidies, and announcing plans for privatization - are laying the groundwork for a transition to a more market-based economy. The non-oil manufacturing and construction sectors, which account for more than 20% of GDP, have expanded from processing mostly agricultural products to include the production of petrochemicals, iron, steel, and aluminum. Climatic conditions and poor soils severely limit agricultural output, and Libya imports about 75% of its food. Libya's primary agricultural water source remains the Great Manmade River Project, but significant resources are being invested in desalinization research to meet growing water demands.
|
|
|
|
|
$87.72 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
$82.83 billion (2007 est.)
$78.44 billion (2006 est.)
note:
data are in 2008 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$89.92 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.9% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
5.6% (2007 est.)
5.9% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$14,200 (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
$13,700 (2007 est.)
$13,300 (2006 est.)
note:
data are in 2008 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 1.7%
industry:
70.9%
services:
27.4% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.64 million (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 17%
industry:
23%
services:
59% (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
30% (2004 est.)
country comparison to the world: 180
|
|
|
|
|
7.4% (2005 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%:
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
9.3% of GDP (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $58.04 billion
expenditures:
$35.22 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4% of GDP (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
8.8% of GDP (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
10.4% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
6.3% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 125
4% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
8.41% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 132
6% (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$26.66 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 30
$18.04 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.264 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 73
$3.192 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2008)
$NA (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
wheat, barley, olives, dates, citrus, vegetables, peanuts, soybeans; cattle
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, iron and steel, food processing, textiles, handicrafts, cement
|
|
|
|
|
6.2% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
|
|
|
|
|
23.98 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
22.17 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
|
|
|
|
|
104 million kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
77 million kWh (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.875 million bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|
|
273,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
|
|
|
|
|
1.542 million bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
|
|
|
|
|
575.3 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 196
|
|
|
|
|
43.66 billion bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
|
|
|
|
|
15.9 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
|
|
|
|
|
5.5 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
|
|
|
|
|
10.4 billion cu m (2008)
country comparison to the world: 20
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 163
|
|
|
|
|
1.54 trillion cu m (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
|
|
|
|
|
$37.39 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
$28.45 billion (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$64.5 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
$46.97 billion (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
crude oil, refined petroleum products, natural gas, chemicals
|
|
|
|
|
Italy 38%, Germany 12%, France 7.4%, Spain 6.9%, US 6.4%, Switzerland 4.6% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$26.55 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
$17.7 billion (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery, semi-finished goods, food, transport equipment, consumer products
|
|
|
|
|
Italy 22.2%, China 9.3%, Germany 8.6%, Turkey 6.1%, Tunisia 5.8%, South Korea 4.7%, US 4.1%, France 4.1% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$92.51 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
$79.6 billion (31 December 2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$6.223 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
$4.837 billion (31 December 2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$11.23 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
$8.775 billion (31 December 2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$5.15 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
$3.7 billion (31 December 2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Libyan dinars (LYD) per US dollar - 1.2112 (2008 est.), 1.2604 (2007), 1.3108 (2006), 1.3084 (2005), 1.305 (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.033 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 79
|
|
|
|
|
4.828 million (2008)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: telecommunications system is state-owned and service is poor, but investment is being made to upgrade; state retains monopoly in fixed-line services; mobile cellular telephone system became operational in 1996; multiple providers for a mobile telephone system that is growing rapidly; combined fixed line and mobile telephone density is approaching 100 telephones per 100 persons
domestic:
microwave radio relay, coaxial cable, cellular, tropospheric scatter, and a domestic satellite system with 14 earth stations
international:
country code - 218; satellite earth stations - 4 Intelsat, NA Arabsat, and NA Intersputnik; submarine cables to France and Italy; microwave radio relay to Tunisia and Egypt; tropospheric scatter to Greece; participant in Medarabtel (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 16, FM 3, shortwave 3 (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
12 (plus 1 repeater) (1999)
|
|
|
|
|
.ly
|
|
|
|
|
11,751 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|
|
323,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 123
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
137 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 41
|
|
|
|
|
total: 59
over 3,047 m:
23
2,438 to 3,047 m:
6
1,524 to 2,437 m:
23
914 to 1,523 m:
6
under 914 m:
1 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 78
over 3,047 m:
4
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2
1,524 to 2,437 m:
14
914 to 1,523 m:
41
under 914 m:
17 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
2 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
condensate 776 km; gas 2,860 km; oil 6,987 km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 100,024 km
country comparison to the world: 41
paved:
57,214 km
unpaved:
42,810 km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 17
country comparison to the world: 101
by type:
cargo 9, liquefied gas 3, petroleum tanker 4, roll on/roll off 1
foreign-owned:
4 (Kuwait 1, Norway 1, Syria 2)
registered in other countries:
3 (Malta 3) (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
As Sidrah, Az Zuwaytinah, Marsa al Burayqah, Ra's Lanuf, Tripoli, Zawiyah
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Armed Peoples on Duty (APOD, Army), Libyan Arab Navy, Libyan Arab Air Force (Al-Quwwat al-Jawwiya al-Jamahiriya al-Arabia al-Libyya, LAAF), Libyan Coast Guard (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
17 years of age (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,682,183
females age 16-49:
1,611,001 (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,466,578
females age 16-49:
1,409,684 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 60,710
female:
58,219 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.9% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Libya |
|
|
|
Libya has claimed more than 32,000 sq km in southeastern Algeria and about 25,000 sq km in the Tommo region of Niger in a currently dormant dispute; various Chadian rebels from the Aozou region reside in southern Libya
|
|
|
|
|
refugees (country of origin): 8,000 (Palestinian Territories) (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
current situation: Libya is a transit and destination country for men and women from sub-Saharan Africa and Asia trafficked for the purposes of forced labor and commercial sexual exploitation
tier rating:
Tier 2 Watch List - Libya is on the Tier 2 Watch List for its failure to provide evidence of increasing efforts to address trafficking in persons in 2007 when compared to 2006, particularly in the area of investigating and prosecuting trafficking offenses; Libya did not publicly release any data on investigations or punishment of any trafficking offenses (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
|