|
|
|
Colonized by the Portuguese in the 16th century, Macau was the first European settlement in the Far East. Pursuant to an agreement signed by China and Portugal on 13 April 1987, Macau became the Macau Special Administrative Region (SAR) of the People's Republic of China on 20 December 1999. In this agreement, China promised that, under its "one country, two systems" formula, China's socialist economic system would not be practiced in Macau, and that Macau would enjoy a high degree of autonomy in all matters except foreign and defense affairs for the next 50 years.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Eastern Asia, bordering the South China Sea and China
|
|
|
|
|
22 10 N, 113 33 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 28.2 sq km
country comparison to the world: 235
land:
28.2 sq km
water:
0 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
less than one-sixth the size of Washington, DC
|
|
|
|
|
total: 0.34 km
regional border:
China 0.34 km
|
|
|
|
|
41 km
|
|
|
|
|
not specified
|
|
|
|
|
subtropical; marine with cool winters, warm summers
|
|
|
|
|
generally flat
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: South China Sea 0 m
highest point:
Coloane Alto 172 m
|
|
|
|
|
NEGL
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 0%
permanent crops:
0%
other:
100% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
typhoons
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Marine Dumping (associate member), Ship Pollution (associate member)
|
|
|
|
|
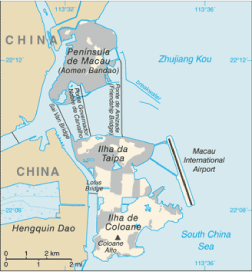
essentially urban; an area of land reclaimed from the sea measuring 5.2 sq km and known as Cotai now connects the islands of Coloane and Taipa; the island area is connected to the mainland peninsula by three bridges
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
559,846 (July 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 16.1% (male 47,853/female 42,019)
15-64 years:
76.2% (male 199,593/female 227,010)
65 years and over:
7.7% (male 20,245/female 23,126) (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 35.2 years
male:
35.9 years
female:
34.6 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.995% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
|
|
|
|
|
8.88 births/1,000 population (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 213
|
|
|
|
|
3.5 deaths/1,000 population (July 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 213
|
|
|
|
|
14.56 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 100% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
0.7% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.14 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.88 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.88 male(s)/female
total population:
0.92 male(s)/female (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3.22 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 219
male:
3.37 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
3.05 deaths/1,000 live births (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 84.36 years
country comparison to the world: 1
male:
81.39 years
female:
87.47 years (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.91 children born/woman (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 223
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Chinese
adjective:
Chinese
|
|
|
|
|
Chinese 94.3%, other 5.7% (includes Macanese - mixed Portuguese and Asian ancestry) (2006 census)
|
|
|
|
|
Buddhist 50%, Roman Catholic 15%, none or other 35% (1997 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
Cantonese 85.7%, Hokkien 4%, Mandarin 3.2%, other Chinese dialects 2.7%, English 1.5%, Tagalog 1.3%, other 1.6% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
91.3%
male:
95.3%
female:
87.8% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 15 years
male:
16 years
female:
14 years (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
2.4% of GDP (2005)
country comparison to the world: 160
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Macau Special Administrative Region
conventional short form:
Macau
local long form:
Aomen Tebie Xingzhengqu (Chinese); Regiao Administrativa Especial de Macau (Portuguese)
local short form:
Aomen (Chinese); Macau (Portuguese)
|
|
|
|
|
special administrative region of China
|
|
|
|
|
limited democracy
|
|
|
|
|
none (special administrative region of the People's Republic of China)
|
|
|
|
|
none (special administrative region of China)
|
|
|
|
|
National Day (Anniversary of the Founding of the People's Republic of China), 1 October (1949); note - 20 December 1999 is celebrated as Macau Special Administrative Region Establishment Day
|
|
|
|
|
Basic Law, approved on 31 March 1993 by China's National People's Congress, is Macau's "mini-constitution"
|
|
|
|
|
based on Portuguese civil law system
|
|
|
|
|
direct election 18 years of age for some non-executive positions, universal for permanent residents living in Macau for the past seven years; indirect election limited to organizations registered as "corporate voters" (257 are currently registered) and a 300-member Election Committee drawn from broad regional groupings, municipal organizations, and central government bodies
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President of China HU Jintao (since 15 March 2003)
head of government:
Chief Executive Edmund HO Hau-wah (since 20 December 1999)
cabinet:
Executive Council consists of 1 government secretary, 3 legislators, 4 businessmen, 1 pro-Beijing unionist, and 1 pro-Beijing educator
elections:
chief executive chosen by a 300-member Election Committee for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held 26 July 2009 (next to be held on in July 2014)
election results:
Edmund HO Hau-wah reelected with 296 votes in 2004 election; Fernando CHUI Sai-on elected in 2009 with 282 votes, takes office on 20 December 2009
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral Legislative Assembly (29 seats; 12 members elected by popular vote, 10 by indirect vote, and 7 appointed by the chief executive; serve four-year terms)
elections:
last held 25 September 2005 (next to be held on 20 September 2009)
election results:
percent of vote - New Democratic Macau Association 18.8%, Macau United Citizens' Association 16.6%, Union for Development 13.3%, Union for Promoting Progress 9.6%, Macau Development Alliance 9.3%, others 32.4%; seats by political group - New Democratic Macau Association 2, Macau United Citizens' Association 2, Union for Development 2, Union for Promoting Progress 2, Macau Development Alliance 1, New Hope 1, Convergence for Development 1, General Union for the Good of Macau 1; 10 seats filled by professional and business groups; seven members appointed by chief executive
|
|
|
|
|
Court of Final Appeal in Macau Special Administrative Region
|
|
|
|
|
New Hope [Jose Maria Pereira COUTINHO]; Development Union [KWAN Tsui-hang]; Macau Development Alliance [Angela LEONG On-kei]; Macau United Citizens' Association [CHAN Meng-kam]; New Democratic Macau Association [Antonio NG Kuok-cheong]; Union for Promoting Progress [LEONG Heng-teng]
note:
there is no political party ordinance, so there are no registered political parties; politically active groups register as societies or companies
|
|
|
|
|
Civic Power [Agnes LAM Lok-fong]; Macau Society of Tourism and Entertainment or STDM [Stanley HO]; Macau Worker's Union [HO Heng-kuok]; Roman Catholic Church; Union for Democracy Development [Antonio NG Kuok-cheong]
|
|
|
|
|
IHO, IMF, IMO (associate), ISO (correspondent), UNESCO (associate), UNWTO (associate), UPU, WCO, WFTU, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
none (special administrative region of China)
|
|
|
|
|
the US has no offices in Macau; US Consulate General in Hong Kong is accredited to Macau
|
|
|
|
|
light green with a lotus flower above a stylized bridge and water in white, beneath an arc of five gold, five-pointed stars: one large in the center of the arc and two smaller on either side; the lotus is the floral emblem of Macau, the three petals represent the peninsula and two islands that make up Macau; the five stars echo those on the flag of China
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Macau's economy has enjoyed strong growth in recent years on the back of its expanding tourism and gaming sectors. After opening up its locally-controlled casino industry to foreign competition in 2001, the territory attracted tens of billions of dollars in foreign investment, transforming Macao into the world's largest gaming center. By 2006, Macau's gaming revenue surpassed that of the Las Vegas strip, and gaming-related taxes accounted for 75% of total government revenue. In 2008, government revenue from gaming was set to double 2006 collections. The expanding casino sector, and China's decision beginning in 2002 to relax travel restrictions, reenergized Macau's tourism industry. This city of just over 500,000 hosted more than 30 million visitors in 2008. Almost 60% came from mainland China despite increasing restrictions on travel to the SAR. Macau's traditional manufacturing industry has been in a slow decline since the termination of the Multi-Fiber Agreement in 2005. In 2008, exports of textiles and garments generated only $1.1 billion, compared to $13.7 billion in gross gaming receipts. The Closer Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) between Macau and mainland China that came into effect on 1 January 2004 offers many Macau-made products tariff-free access to the mainland. Macau's currency, the Pataca, is closely tied to the Hong Kong dollar, which is also freely accepted in the territory.
|
|
|
|
|
$18.14 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
$12.5 billion (2006)
note:
data are in 2008 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$22.04 billion (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
15% (2008)
country comparison to the world: 2
16.6% (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
$30,000 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 45
$28,400 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 0.1%
industry:
2.8%
services:
97.1% (2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
337,400 (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
|
|
|
|
|
manufacturing 7.4%, construction 12.6%, transport and communications 5%, wholesale and retail trade 12.5%, restaurants and hotels 12.7%, gambling 14%, public sector 6%, financial services 2.1%, other services and agriculture 27.7% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3% (2008)
country comparison to the world: 33
3.1% (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%:
NA%
|
|
|
|
|
revenues: $6.2 billion
expenditures:
$2.9 billion (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
6.2% (December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 105
7.2% (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
5.43% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.591 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 77
$1.16 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$22.15 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 41
$21.91 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$11.5 billion (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 68
$NA (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.3 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
$NA (31 December 2007)
$413.1 million (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
only 2% of land area is cultivated, mainly by vegetable growers; fishing, mostly for crustaceans, is important; some of the catch is exported to Hong Kong
|
|
|
|
|
tourism, gambling, clothing, textiles, electronics, footwear, toys
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
1.106 billion kWh (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
|
|
|
|
|
3.311 billion kWh (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.215 billion kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
|
|
|
|
|
16,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
|
|
|
|
|
5,027 bbl/day (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
|
|
|
|
|
0 bbl (1 January 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 162
|
|
|
|
|
81.6 million cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008)
country comparison to the world: 158
|
|
|
|
|
81.9 million cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
|
|
|
|
|
300,000 cu m (1 January 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
|
|
|
|
|
$2 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
$2.557 billion (2006 est.); note - includes reexports
|
|
|
|
|
clothing, textiles, footwear, toys, electronics, machinery and parts
|
|
|
|
|
US 39.9%, Hong Kong 19.7%, China 12.3%, Germany 4% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$5.4 billion (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
$4.559 billion (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
raw materials and semi-manufactured goods, consumer goods (foodstuffs, beverages, tobacco), capital goods, mineral fuels and oils
|
|
|
|
|
China 39.3%, Hong Kong 10.1%, Japan 8.5%, US 5.5%, France 5.3%, Switzerland 4.7% (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$0 (2006)
country comparison to the world: 205
|
|
|
|
|
$7.9 billion (2007)
country comparison to the world: 82
$6.5 billion (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.9 billion (2007)
country comparison to the world: 65
$1.1 billion (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
patacas (MOP) per US dollar - 8.011 (2007), 8.0015 (2006), 8.011 (2005), 8.022 (2004), 8.021 (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
173,533 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 127
|
|
|
|
|
993,545 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 145
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: fairly modern communication facilities maintained for domestic and international services
domestic:
termination of monopoly over mobile-cellular telephone services in 2001 spurred sharp increase in subscriptions with mobile-cellular teledensity approaching 180 per 100 persons in 2008; fixed-line subscribership appears to have peaked and is now in decline
international:
country code - 853; landing point for the SEA-ME-WE-3 submarine cable network that provides links to Asia, the Middle East, and Europe; HF radiotelephone communication facility; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
AM 1, FM 2, shortwave 0 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.mo
|
|
|
|
|
244 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 183
|
|
|
|
|
259,000 (2008)
country comparison to the world: 130
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 221
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1
over 3,047 m:
1 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
2 (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 404 km
country comparison to the world: 196
paved:
404 km (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
Macau
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
no regular military forces; defense is the responsibility of China (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 121,825 (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 122,962
females age 16-49:
148,809 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 4,578
female:
4,052 (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
defense is the responsibility of China
|
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Macau |
|
|
|
none
|
|
|
|
|
transshipment point for drugs going into mainland China; consumer of opiates and amphetamines
|
|
|
|
|
|