|
|
Albania declared its independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1912, but was conquered by Italy in 1939. Communist partisans took over the country in 1944. Albania allied itself first with the USSR (until 1960), and then with China (to 1978). In the early 1990s, Albania ended 46 years of xenophobic Communist rule and established a multiparty democracy. The transition has proven challenging as successive governments have tried to deal with high unemployment, widespread corruption, a dilapidated physical infrastructure, powerful organized crime networks, and combative political opponents. Albania has made progress in its democratic development since first holding multiparty elections in 1991, but deficiencies remain. International observers judged elections to be largely free and fair since the restoration of political stability following the collapse of pyramid schemes in 1997; however, there have been claims of electoral fraud in every one of Albania's post-communist elections. In the 2005 general elections, the Democratic Party and its allies won a decisive victory on pledges to reduce crime and corruption, promote economic growth, and decrease the size of government. The election, and particularly the orderly transition of power, was considered an important step forward. Albania joined NATO in April 2009 and is a potential candidate for EU accession. Although Albania's economy continues to grow, the country is still one of the poorest in Europe, hampered by a large informal economy and an inadequate energy and transportation infrastructure.
|
|
|
|
|
|
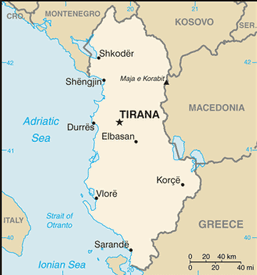
Southeastern Europe, bordering the Adriatic Sea and Ionian Sea, between Greece in the south and Montenegro and Kosovo to the north
|
|
|
|
|
41 00 N, 20 00 E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 28,748 sq km
country comparison to the world: 144
land:
27,398 sq km
water:
1,350 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly smaller than Maryland
|
|
|
|
|
total: 717 km
border countries:
Greece 282 km, Macedonia 151 km, Montenegro 172 km, Kosovo 112 km
|
|
|
|
|
362 km
|
|
|
|
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
continental shelf:
200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
|
|
|
|
|
mild temperate; cool, cloudy, wet winters; hot, clear, dry summers; interior is cooler and wetter
|
|
|
|
|
mostly mountains and hills; small plains along coast
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Adriatic Sea 0 m
highest point:
Maja e Korabit (Golem Korab) 2,764 m
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum, natural gas, coal, bauxite, chromite, copper, iron ore, nickel, salt, timber, hydropower
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 20.1%
permanent crops:
4.21%
other:
75.69% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
3,530 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
41.7 cu km (2001)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1.71 cu km/yr (27%/11%/62%)
per capita:
546 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
destructive earthquakes; tsunamis occur along southwestern coast; floods; drought
|
|
|
|
|
deforestation; soil erosion; water pollution from industrial and domestic effluents
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
|
|
|
|
|
strategic location along Strait of Otranto (links Adriatic Sea to Ionian Sea and Mediterranean Sea)
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,986,952 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 23.1% (male 440,528/female 400,816)
15-64 years:
67.1% (male 1,251,001/female 1,190,841)
65 years and over:
9.8% (male 165,557/female 190,710) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 30 years
male:
28.9 years
female:
31.1 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0.249% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178
|
|
|
|
|
11.88 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
|
|
|
|
|
6.04 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
|
|
|
|
|
-3.35 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 189
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 47% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
1.9% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.123 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.1 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.87 male(s)/female
total population:
1.04 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 15.11 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 123
male:
16.79 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
13.23 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 77.22 years
country comparison to the world: 59
male:
74.65 years
female:
80.11 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.47 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 189
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
NA
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Albanian(s)
adjective:
Albanian
|
|
|
|
|
Albanian 95%, Greek 3%, other 2% (Vlach, Roma (Gypsy), Serb, Macedonian, Bulgarian) (1989 est.)
note:
in 1989, other estimates of the Greek population ranged from 1% (official Albanian statistics) to 12% (from a Greek organization)
|
|
|
|
|
Muslim 70%, Albanian Orthodox 20%, Roman Catholic 10%
note:
percentages are estimates; there are no available current statistics on religious affiliation; all mosques and churches were closed in 1967 and religious observances prohibited; in November 1990, Albania began allowing private religious practice
|
|
|
|
|
Albanian (official - derived from Tosk dialect), Greek, Vlach, Romani, Slavic dialects
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 9 and over can read and write
total population:
98.7%
male:
99.2%
female:
98.3% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 11 years
male:
11 years
female:
11 years (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
2.9% of GDP (2002)
country comparison to the world: 148
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Republic of Albania
conventional short form:
Albania
local long form:
Republika e Shqiperise
local short form:
Shqiperia
former:
People's Socialist Republic of Albania
|
|
|
|
|
republic
|
|
|
|
|
name: Tirana (Tirane)
geographic coordinates:
41 19 N, 19 49 E
time difference:
UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
daylight saving time:
+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
|
|
|
|
|
12 counties (qarqe, singular - qark); Berat, Diber, Durres, Elbasan, Fier, Gjirokaster, Korce, Kukes, Lezhe, Shkoder, Tirane, Vlore
|
|
|
|
|
28 November 1912 (from the Ottoman Empire)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 28 November (1912)
|
|
|
|
|
approved by parliament on 21 October 1998; adopted by popular referendum on 22 November 1998; promulgated 28 November 1998
|
|
|
|
|
has a civil law system; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; has accepted jurisdiction of the International Criminal Court for its citizens
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age; universal
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President of the Republic Bamir TOPI (since 24 July 2007)
head of government:
Prime Minister Sali BERISHA (since 10 September 2005)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers proposed by the prime minister, nominated by the president, and approved by parliament
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president elected by the Assembly for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); four election rounds held between 8 and 20 July 2007 (next election to be held in 2012); prime minister appointed by the president
election results:
Bamir TOPI elected president; Assembly vote, fourth round (three-fifths majority, 84 votes, required): Bamir TOPI 85 votes, Neritan CEKA 5 votes
|
|
|
|
|
unicameral National Assembly or Kuvendi (140 deputies; 100 deputies elected directly in single member electoral zones with an approximate number of voters; 40 deputies elected from multi-name lists of parties or party coalitions according to their respective order)
elections:
last held on 28 June 2009 (next to be held in 2013)
election results:
percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PD 68, PS 65, LSI 4, other 3
|
|
|
|
|
Constitutional Court, Supreme Court (chairman is elected by the People's Assembly for a four-year term) and multiple appeals and district courts
|
|
|
|
|
Democratic Party or PD [Sali BERISHA]; Party for Justice and Integration or PDI [Tahir MUCHEDINI]; Republican Party or PR [Fatmir MEDIU]; Socialist Movement for Integration or LSI [Ilir META]; Socialist Party or PS [Edi RAMA]; Unity for Humen Rights Party or PBDNJ [Vangjel DULE]
|
|
|
|
|
Citizens Advocacy Office [Kreshnik SPAHIU]; Confederation of Trade Unions of Albania or KSSH [Kastriot MUCO]; Front for Albanian National Unification or FBKSH [Gafur ADILI]; Mjaft Movement [Elton KACIDHJA]; Omonia [Ligorag KARAMELO]; Union of Independent Trade Unions of Albania or BSPSH [Gezim KALAJA]
|
|
|
|
|
BSEC, CE, CEI, EAPC, EBRD, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NATO, OIC, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, SECI, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Gilbert GALANXHI
chancery:
2100 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 223-4942
FAX:
[1] (202) 628-7342
consulate(s) general:
New York
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Alexander ARVIZU
embassy:
Rruga e Elbasanit, Labinoti #103, Tirana
mailing address:
US Department of State, 9510 Tirana Place, Dulles, VA 20189-9510
telephone:
[355] (4) 2247285
FAX:
[355] (4) 2232222
|
|
|
|
|
red with a black two-headed eagle in the center; the design is claimed to be that of 15th-century hero George Castriota SKANDERBERG, who led a successful uprising against the Turks that resulted in a short-lived independence for some Albanian regions (1443-1478); an unsubstantiated explanation for the eagle symbol is the tradition that Albanians see themselves as descendants of the eagle; they refer to themselves as "Shkypetars," which translates as "sons of the eagle"
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Hymni i Flamurit" (Hymn to the Flag)
lyrics/music:
Aleksander Stavre DRENOVA/Ciprian PORUMBESCU
note:
adopted 1912
|
|
|
|
|
|
Albania, a formerly closed, centrally-planned state, is making the difficult transition to a more modern open-market economy. Macroeconomic growth averaged around 6% between 2004-08, but declined to about 3% in 2009-10. Inflation is low and stable. The government has taken measures to curb violent crime, and recently adopted a fiscal reform package aimed at reducing the large gray economy and attracting foreign investment. The economy is bolstered by annual remittances from abroad representing about 15% of GDP, mostly from Albanians residing in Greece and Italy; this helps offset the towering trade deficit. The agricultural sector, which accounts for over half of employment but only about one-fifth of GDP, is limited primarily to small family operations and subsistence farming because of lack of modern equipment, unclear property rights, and the prevalence of small, inefficient plots of land. Energy shortages because of a reliance on hydropower, and antiquated and inadequate infrastructure contribute to Albania's poor business environment and lack of success in attracting new foreign investment needed to expand the country's export base. The completion of a new thermal power plant near Vlore has helped diversify generation capacity, and plans to upgrade transmission lines between Albania and Montenegro and Kosovo would help relieve the energy shortages. Also, with help from EU funds, the government is taking steps to improve the poor national road and rail network, a long-standing barrier to sustained economic growth.
|
|
|
|
|
$23.95 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
$23.23 billion (2009 est.)
$22.49 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
Albania has an informal, and unreported, sector that may be as large as 50% of official GDP
|
|
|
|
|
$11.58 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.1% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
3.3% (2009 est.)
7.8% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$8,000 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
$7,800 (2009 est.)
$7,500 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 21.2%
industry:
19.5%
services:
59.3% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.1 million (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 140
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 58%
industry:
15%
services:
27% (September 2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
12.7% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
12.8% (2009 est.)
note:
these are official rates, but actual rates may exceed 30% due to preponderance of near-subsistence farming
|
|
|
|
|
25% (2004 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 3.2%
highest 10%:
25.9% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
26.7 (2005)
country comparison to the world: 126
|
|
|
|
|
29.8% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
|
|
|
|
|
59.3% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
58.1% of GDP (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.4% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
2.2% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5.25% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 71
6.25% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
12.66% (31 December 2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
13.02% (31 December 2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.708 billion (31 December 2010 est)
country comparison to the world: 113
$2.995 billion (31 December 2009 est)
|
|
|
|
|
$9.096 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 105
$9.279 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$7.701 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
$8.231 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA
|
|
|
|
|
wheat, corn, potatoes, vegetables, fruits, sugar beets, grapes; meat, dairy products
|
|
|
|
|
food processing, textiles and clothing; lumber, oil, cement, chemicals, mining, basic metals, hydropower
|
|
|
|
|
3% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
|
|
|
|
|
2.888 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
|
|
|
|
|
3.603 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.475 billion kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
5,400 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
|
|
|
|
|
36,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
|
|
|
|
|
749 bbl/day (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
|
|
|
|
|
24,080 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
|
|
|
|
|
199.1 million bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
|
|
|
|
|
30 million cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
|
|
|
|
|
30 million cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
849.5 million cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
|
|
|
|
|
-$1.245 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
-$1.845 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.339 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144
$1.048 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
textiles and footwear; asphalt, metals and metallic ores, crude oil; vegetables, fruits, tobacco
|
|
|
|
|
Italy 58.75%, Greece 9.69%, Austria 6.73%, China 5.68% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.337 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
$4.264 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
machinery and equipment, foodstuffs, textiles, chemicals
|
|
|
|
|
Italy 29.94%, Greece 14.05%, Turkey 7.1%, Germany 6.9%, China 5.39% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.992 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
$2.37 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$1.55 billion (2004)
country comparison to the world: 143
|
|
|
|
|
leke (ALL) per US dollar - 106.5 (2010), 94.979 (2009), 79.546 (2008), 92.668 (2007), 98.384 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
363,000 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
4.162 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 102
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: despite new investment in fixed lines teledensity remains low with roughly 10 fixed lines per 100 people; mobile-cellular telephone use is widespread and generally effective; combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity is now exceeds 100 per 100 persons
domestic:
offsetting the shortage of fixed line capacity, mobile-cellular phone service has been available since 1996; by 2003, two companies were providing mobile services at a greater teledensity than some of Albania's neighbors; Internet broadband services initiated in 2005; Internet cafes are popular in Tirana and have started to spread outside the capital
international:
country code - 355; submarine cable provides connectivity to Italy, Croatia, and Greece; the Trans-Balkan Line, a combination submarine cable and land fiber-optic system, provides additional connectivity to Bulgaria, Macedonia, and Turkey; international traffic carried by fiber-optic cable and, when necessary, by microwave radio relay from the Tirana exchange to Italy and Greece (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
2 public television networks, one of which transmits by satellite to Albanian-language communities in neighboring countries; more than 60 private television stations operating; many viewers can pick up Italian and Greek TV broadcasts via terrestrial reception; cable TV service is available; 2 public radio networks and roughly 50 private radio stations; several international broadcasters are available (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
.al
|
|
|
|
|
15,098 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 117
|
|
|
|
|
1.3 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 90
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 177
|
|
|
|
|
total: 4
2,438 to 3,047 m:
3
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1
914 to 1,523 m:
1 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
1 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 339 km; oil 207 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 896 km
country comparison to the world: 96
standard gauge:
896 km 1.435-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 18,000 km
country comparison to the world: 117
paved:
7,020 km
unpaved:
10,980 km (2002)
|
|
|
|
|
43 km (on the Bojana River) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 105
|
|
|
|
|
total: 25
country comparison to the world: 92
by type:
bulk carrier 1, cargo 23, roll on/roll off 1
foreign-owned:
1 (Turkey 1)
registered in other countries:
4 (Antigua and Barbuda 1, Panama 3) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Durres, Sarande, Shengjin, Vlore
|
|
|
|
|
|
Joint Force Command (includes Land, Naval, and Aviation Brigade Commands), Joint Support Command (includes Logistic Command), Training and Doctrine Command (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
19 years of age (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 947,446
females age 16-49:
910,145 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 802,097
females age 16-49:
768,953 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 35,249
female:
31,855 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.49% of GDP (2005 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Albania |
|
|
the Albanian Government calls for the protection of the rights of ethnic Albanians in neighboring countries, and the peaceful resolution of interethnic disputes; some ethnic Albanian groups in neighboring countries advocate for a "greater Albania," but the idea has little appeal among Albanian nationals; the mass emigration of unemployed Albanians remains a problem for developed countries, chiefly Greece and Italy
|
|
|
|
|
increasingly active transshipment point for Southwest Asian opiates, hashish, and cannabis transiting the Balkan route and - to a lesser extent - cocaine from South America destined for Western Europe; limited opium and expanding cannabis production; ethnic Albanian narcotrafficking organizations active and expanding in Europe; vulnerable to money laundering associated with regional trafficking in narcotics, arms, contraband, and illegal aliens
|
|
|
|
|