|
|
Bolivia, named after independence fighter Simon BOLIVAR, broke away from Spanish rule in 1825; much of its subsequent history has consisted of a series of nearly 200 coups and countercoups. Democratic civilian rule was established in 1982, but leaders have faced difficult problems of deep-seated poverty, social unrest, and illegal drug production. In December 2005, Bolivians elected Movement Toward Socialism leader Evo MORALES president - by the widest margin of any leader since the restoration of civilian rule in 1982 - after he ran on a promise to change the country's traditional political class and empower the nation's poor, indigenous majority. However, since taking office, his controversial strategies have exacerbated racial and economic tensions between the Amerindian populations of the Andean west and the non-indigenous communities of the eastern lowlands. In December 2009, President MORALES easily won reelection, and his party took control of the legislative branch of the government, which will allow him to continue his process of change.
|
|
|
|
|
|
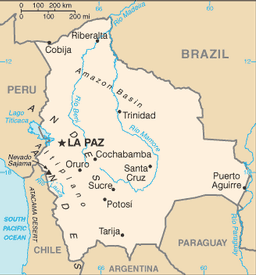
Central South America, southwest of Brazil
|
|
|
|
|
17 00 S, 65 00 W
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1,098,581 sq km
country comparison to the world: 28
land:
1,083,301 sq km
water:
15,280 sq km
|
|
|
|
|
slightly less than three times the size of Montana
|
|
|
|
|
total: 6,940 km
border countries:
Argentina 832 km, Brazil 3,423 km, Chile 860 km, Paraguay 750 km, Peru 1,075 km
|
|
|
|
|
0 km (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
none (landlocked)
|
|
|
|
|
varies with altitude; humid and tropical to cold and semiarid
|
|
|
|
|
rugged Andes Mountains with a highland plateau (Altiplano), hills, lowland plains of the Amazon Basin
|
|
|
|
|
lowest point: Rio Paraguay 90 m
highest point:
Nevado Sajama 6,542 m
|
|
|
|
|
tin, natural gas, petroleum, zinc, tungsten, antimony, silver, iron, lead, gold, timber, hydropower
|
|
|
|
|
arable land: 2.78%
permanent crops:
0.19%
other:
97.03% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
1,320 sq km (2003)
|
|
|
|
|
622.5 cu km (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 1.44 cu km/yr (13%/7%/81%)
per capita:
157 cu m/yr (2000)
|
|
|
|
|
flooding in the northeast (March-April)
volcanism:
Bolivia experiences volcanic activity in Andes Mountains on the border with Chile; historically active volcanoes in this region are Irruputuncu (elev. 5,163 m, 16,939 ft), which last erupted in 1995 and Olca-Paruma
|
|
|
|
|
the clearing of land for agricultural purposes and the international demand for tropical timber are contributing to deforestation; soil erosion from overgrazing and poor cultivation methods (including slash-and-burn agriculture); desertification; loss of biodiversity; industrial pollution of water supplies used for drinking and irrigation
|
|
|
|
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Environmental Modification, Marine Life Conservation
|
|
|
|
|
landlocked; shares control of Lago Titicaca, world's highest navigable lake (elevation 3,805 m), with Peru
|
|
|
|
|
|
9,947,418 (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|
|
0-14 years: 35.5% (male 1,767,310/female 1,701,744)
15-64 years:
60% (male 2,877,605/female 2,992,043)
65 years and over:
4.5% (male 193,196/female 243,348) (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 22.2 years
male:
21.5 years
female:
22.9 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.72% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
|
|
|
|
|
25.16 births/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
|
|
|
|
|
6.95 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
|
|
|
|
|
-1.01 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
|
|
|
|
|
urban population: 66% of total population (2008)
rate of urbanization:
2.5% annual rate of change (2005-10 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years:
0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.79 male(s)/female
total population:
0.98 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 43.41 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 63
male:
47.26 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
39.37 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
total population: 67.23 years
country comparison to the world: 155
male:
64.52 years
female:
70.07 years (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.07 children born/woman (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
|
|
|
|
|
0.2% (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
|
|
|
|
|
8,100 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
|
|
|
|
|
fewer than 500 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
|
|
|
|
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
dengue fever, malaria, and yellow fever
water contact disease:
leptospirosis (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
noun: Bolivian(s)
adjective:
Bolivian
|
|
|
|
|
Quechua 30%, mestizo (mixed white and Amerindian ancestry) 30%, Aymara 25%, white 15%
|
|
|
|
|
Roman Catholic 95%, Protestant (Evangelical Methodist) 5%
|
|
|
|
|
Spanish 60.7% (official), Quechua 21.2% (official), Aymara 14.6% (official), foreign languages 2.4%, other 1.2% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
86.7%
male:
93.1%
female:
80.7% (2001 census)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 14 years
male:
14 years
female:
14 years (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
6.3% of GDP (2006)
country comparison to the world: 31
|
|
|
|
|
|
conventional long form: Plurinational State of Bolivia
conventional short form:
Bolivia
local long form:
Estado Plurinacional de Bolivia
local short form:
Bolivia
|
|
|
|
|
republic; note - the new constitution defines Bolivia as a "Social Unitarian State"
|
|
|
|
|
name: La Paz (administrative capital)
geographic coordinates:
16 30 S, 68 09 W
time difference:
UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)
note:
Sucre (constitutional capital)
|
|
|
|
|
9 departments (departamentos, singular - departamento); Beni, Chuquisaca, Cochabamba, La Paz, Oruro, Pando, Potosi, Santa Cruz, Tarija
|
|
|
|
|
6 August 1825 (from Spain)
|
|
|
|
|
Independence Day, 6 August (1825)
|
|
|
|
|
7 February 2009
|
|
|
|
|
based on Spanish law and Napoleonic Code; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; the 2009 Constitution incorporates indigenous community justice into Bolivia's judicial system
|
|
|
|
|
18 years of age, universal and compulsory (married); 21 years of age, universal and compulsory (single)
|
|
|
|
|
chief of state: President Juan Evo MORALES Ayma (since 22 January 2006); Vice President Alvaro GARCIA Linera (since 22 January 2006); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Juan Evo MORALES Ayma (since 22 January 2006); Vice President Alvaro GARCIA Linera (since 22 January 2006)
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by the president
(For more information visit the World Leaders website  ) )
elections:
president and vice president elected on the same ticket by popular vote for a five-year term and are eligible for a single re-election; election last held on 6 December 2009 (next to be held in 2014)
election results:
Juan Evo MORALES Ayma reelected president; percent of vote - Juan Evo MORALES Ayma 64%; Manfred REYES VILLA 26%; Samuel DORIA MEDINA Arana 6%; Rene JOAQUINO 2%; other 2%
|
|
|
|
|
bicameral Plurinational Legislative Assembly or Asamblea Legislativa Plurinacional consists of Chamber of Senators or Camara de Senadores (36 seats; members are elected by proportional representation from party lists to serve five-year terms) and Chamber of Deputies or Camara de Diputados (130 seats total; 70 uninominal deputies directly elected from a single district, 7 "special" indigenous deputies directly elected from non-contiguous indigenous districts, and 53 plurinominal deputies elected by proportional representation from party lists; all deputies serve five-year terms)
elections:
Chamber of Senators and Chamber of Deputies - last held on 6 December 2009 (next to be held in 2014)
election results:
Chamber of Senators - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - MAS 26, PPB-CN 10; Chamber of Deputies - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - MAS 89, PPB-CN 36, UN 3, AS 2
|
|
|
|
|
Supreme Court or Corte Suprema (judges elected by popular vote from list of candidates pre-selected by Assembly for six-year terms); District Courts (one in each department); Plurinational Constitutional Court (five primary or titulares and five alternate or suplente magistrates elected by popular vote from list of candidates pre-selected by Assembly for six-year terms; to rule on constitutional issues); Plurinational Electoral Organ (seven members elected by the Assembly and the president; one member must be of indigenous origin to six-year terms); Agro-Environmental Court (judges elected by popular vote from list of candidates pre-selected by Assembly for six-year terms; to run on agro-environmental issues); provincial and local courts (to try minor cases)
|
|
|
|
|
Bolivia-National Convergence or PPB-CN [Manfred REYES VILLA]; Fearless Movement or MSM [Juan DE GRANADO Cosio]; Movement Toward Socialism or MAS [Juan Evo MORALES Ayma]; National Unity or UN [Samuel DORIA MEDINA Arana]; People or Gente [Roman LOAYZA]; Social Alliance or AS [Rene JOAQUINO]
|
|
|
|
|
Bolivian Workers Central or COR; Federation of Neighborhood Councils of El Alto or FEJUVE; Landless Movement or MST; National Coordinator for Change or CONALCAM; Sole Confederation of Campesino Workers of Bolivia or CSUTCB
other:
Cocalero groups; indigenous organizations (including Confederation of Indigenous Peoples of Eastern Bolivia or CIDOB and National Council of Ayullus and Markas of Quollasuyu or CONAMAQ); labor unions (including the Central Bolivian Workers' Union or COB and Cooperative Miners Federation or FENCOMIN)
|
|
|
|
|
CAN, FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, Mercosur (associate), MIGA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, RG, UN, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNMIL, UNMIS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Erika Angela DUENAS Loayza
chancery:
3014 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 483-4410
FAX:
[1] (202) 328-3712
consulate(s) general:
Los Angeles, Miami, New York, San Francisco
note:
as of September 2008, the US has expelled the Bolivian ambassador to the US
|
|
|
|
|
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires John CREAMER
embassy:
Avenida Arce 2780, Casilla 425, La Paz
mailing address:
P. O. Box 425, La Paz; APO AA 34032
telephone:
[591] (2) 216-8000
FAX:
[591] (2) 216-8111
note:
in September 2008, the Bolivian Government expelled the US Ambassador to Bolivia, and the countries have yet to reinstate ambassadors
|
|
|
|
|
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), yellow, and green with the coat of arms centered on the yellow band; red stands for bravery and the blood of national heroes, yellow for the nation's mineral resources, and green for the fertility of the land
note:
similar to the flag of Ghana, which has a large black five-pointed star centered in the yellow band; in 2009, a presidential decree made it mandatory for a so-called wiphala - a square, multi-colored flag representing the country's indigenous peoples - to be used alongside the traditional flag
|
|
|
|
|
name: "Cancion Patriotica" (Patriotic Song)
lyrics/music:
Jose Ignacio de SANJINES/Leopoldo Benedetto VINCENTI
note:
adopted 1852
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bolivia is one of the poorest and least developed countries in Latin America. Following a disastrous economic crisis during the early 1980s, reforms spurred private investment, stimulated economic growth, and cut poverty rates in the 1990s. The period 2003-05 was characterized by political instability, racial tensions, and violent protests against plans - subsequently abandoned - to export Bolivia's newly discovered natural gas reserves to large northern hemisphere markets. In 2005, the government passed a controversial hydrocarbons law that imposed significantly higher royalties and required foreign firms then operating under risk-sharing contracts to surrender all production to the state energy company in exchange for a predetermined service fee. After higher prices for mining and hydrocarbons exports produced a fiscal surplus in 2008, the global recession in 2009 slowed growth. A decline in commodity prices that began in late 2008, a lack of foreign investment in the mining and hydrocarbon sectors, a poor infrastructure, and the suspension of trade benefits with the United States will pose challenges for the Bolivian economy.
|
|
|
|
|
$47.98 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
$46.22 billion (2009 est.)
$44.7 billion (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
$19.18 billion (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3.8% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
3.4% (2009 est.)
6.1% (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$4,800 (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
$4,700 (2009 est.)
$4,700 (2008 est.)
note:
data are in 2010 US dollars
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 11%
industry:
38%
services:
51% (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
4.614 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|
|
agriculture: 40%
industry:
17%
services:
43% (2006 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
8.3% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
7.7% (2009 est.)
note:
data are for urban areas; widespread underemployment
|
|
|
|
|
30.3% of population living on less than $2/day (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
lowest 10%: 0.5%
highest 10%:
44.1% (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
58.2 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 9
44.7 (1999)
|
|
|
|
|
17.5% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
|
|
|
|
|
40.3% of GDP (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
40.3% of GDP (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
2.1% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
3.3% (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
3% (31 October 2010)
country comparison to the world: 26
13% (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
10% (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
12.36% (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$4.374 billion (31 December 2010 est)
country comparison to the world: 97
$3.524 billion (31 December 2009 est)
|
|
|
|
|
$12.16 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 95
$11.04 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$8.314 billion (31 December 2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
$7.233 billion (31 December 2007 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$2.792 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 90
$2.672 billion (31 December 2008)
$2.263 billion (31 December 2007)
|
|
|
|
|
soybeans, coffee, coca, cotton, corn, sugarcane, rice, potatoes; timber
|
|
|
|
|
mining, smelting, petroleum, food and beverages, tobacco, handicrafts, clothing
|
|
|
|
|
4% (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
|
|
|
|
|
5.495 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
|
|
|
|
|
4.665 billion kWh (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
0 kWh (2008 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
47,050 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
|
|
|
|
|
59,000 bbl/day (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
|
|
|
|
|
10,950 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
6,172 bbl/day (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
|
|
|
|
|
465 million bbl (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
|
|
|
|
|
14.2 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
|
|
|
|
|
2.41 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
|
|
|
|
|
11.79 billion cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
|
|
|
|
|
0 cu m (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
|
|
|
|
|
750.4 billion cu m (1 January 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
|
|
|
|
|
$878 million (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
$800.7 million (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$6.058 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
$4.848 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
natural gas, soybeans and soy products, crude petroleum, zinc ore, tin
|
|
|
|
|
Brazil 41.38%, US 13.87%, Japan 5.62%, Colombia 5.32%, South Korea 4.7%, Peru 4.16% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$5.006 billion (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
$4.095 billion (2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
petroleum products, plastics, paper, aircraft and aircraft parts, prepared foods, automobiles, insecticides, soybeans
|
|
|
|
|
Brazil 27.12%, Argentina 15.69%, US 12.77%, Chile 9.11%, Peru 6.85% (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
$8.739 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
$8.581 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$6.13 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
$5.653 billion (31 December 2009 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2009)
$5.998 billion (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
$NA (31 December 2010)
$63.8 million (31 December 2008)
|
|
|
|
|
bolivianos (BOB) per US dollar - 7.0699 (2010), 7.07 (2009), 7.253 (2008), 7.8616 (2007), 8.0159 (2006)
|
|
|
|
|
|
810,200 (2009)
country comparison to the world: 87
|
|
|
|
|
7.148 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 81
|
|
|
|
|
general assessment: privatization begun in 1995; primary trunk system, which is being expanded, employs digital microwave radio relay; some areas are served by fiber-optic cable; overall reliability has steadily improved
domestic:
most telephones are concentrated in La Paz and other cities; mobile-cellular telephone use expanding rapidly and, in 2009, teledensity reached 75 per 100 persons; fixed-line teledensity is low at less than 10 per 100 persons
international:
country code - 591; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
large number of radio and television broadcasting stations with private media outlets dominating; state-owned and private radio and television stations generally operating freely, although both pro-government and anti-government groups have attacked media outlets in response to their reporting (2007)
|
|
|
|
|
.bo
|
|
|
|
|
125,462 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 74
|
|
|
|
|
1.103 million (2009)
country comparison to the world: 95
|
|
|
|
|
|
881 (2010)
country comparison to the world: 8
|
|
|
|
|
total: 16
over 3,047 m:
3
2,438 to 3,047 m:
4
1,524 to 2,437 m:
4
914 to 1,523 m:
5 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 865
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
4
1,524 to 2,437 m:
58
914 to 1,523 m:
187
under 914 m:
615 (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
gas 5,192 km; liquid petroleum gas 51 km; oil 2,488 km; refined products 1,590 km (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 3,504 km
country comparison to the world: 50
narrow gauge:
3,504 km 1.000-m gauge (2008)
|
|
|
|
|
total: 62,479 km
country comparison to the world: 73
paved:
3,749 km
unpaved:
58,730 km (2004)
|
|
|
|
|
10,000 km (commercially navigable almost exclusively in the northern and eastern parts of the country) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 13
|
|
|
|
|
total: 22
country comparison to the world: 98
by type:
bulk carrier 3, cargo 11, carrier 1, passenger/cargo 1, petroleum tanker 2, roll on/roll off 3, specialized tanker 1
foreign-owned:
7 (Bahamas 1, Ecuador 1, Iran 1, Syria 4) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
Puerto Aguirre (inland port on the Paraguay/Parana waterway at the Bolivia/Brazil border); Bolivia has free port privileges in maritime ports in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, and Paraguay
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bolivian Armed Forces: Bolivian Army (Ejercito Boliviano, EB), Bolivian Navy (Fuerza Naval Boliviana, FNB; includes marines), Bolivian Air Force (Fuerza Aerea Boliviana, FAB) (2010)
|
|
|
|
|
18-49 years of age for 12-month compulsory military service; when annual number of volunteers falls short of goal, compulsory recruitment is effected, including conscription of boys as young as 14; 15-19 years of age for voluntary premilitary service, provides exemption from further military service (2009)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 2,415,712
females age 16-49:
2,482,359 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
males age 16-49: 1,714,438
females age 16-49:
1,959,763 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
male: 108,336
female:
104,934 (2010 est.)
|
|
|
|
|
1.3% of GDP (2009)
country comparison to the world: 115
|
|
|
|
| Transnational Issues ::Bolivia |
|
|
Chile and Peru rebuff Bolivia's reactivated claim to restore the Atacama corridor, ceded to Chile in 1884, but Chile offers instead unrestricted but not sovereign maritime access through Chile for Bolivian natural gas and other commodities; an accord placed the long-disputed Isla Suarez/Ilha de Guajara-Mirim, a fluvial island on the Rio Mamore, under Bolivian administration in 1958, but sovereignty remains in dispute
|
|
|
|
|
world's third-largest cultivator of coca (after Colombia and Peru) with an estimated 29,500 hectares under cultivation in 2007, increased slightly when compared to 2006; third largest producer of cocaine, estimated at 120 metric tons potential pure cocaine in 2007; transit country for Peruvian and Colombian cocaine destined for Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Paraguay, and Europe; cultivation generally increasing since 2000, despite eradication and alternative crop programs; weak border controls; some money-laundering activity related to narcotics trade; major cocaine consumption
(2008)
|
|
|
|
|