Introduction :: BHUTAN
-
In 1865, Britain and Bhutan signed the Treaty of Sinchulu, under which Bhutan would receive an annual subsidy in exchange for ceding some border land to British India. Under British influence, a monarchy was set up in 1907; three years later, a treaty was signed whereby the British agreed not to interfere in Bhutanese internal affairs, and Bhutan allowed Britain to direct its foreign affairs. This role was assumed by independent India after 1947. Two years later, a formal Indo-Bhutanese accord returned to Bhutan the areas annexed by the British, formalized the annual subsidies the country received, and defined India's responsibilities in defense and foreign relations.
In March 2005, King Jigme Singye WANGCHUCK unveiled the government's draft constitution - which introduced major democratic reforms - and pledged to hold a national referendum for its approval. In December 2006, the King abdicated the throne in favor of his son, Jigme Khesar Namgyel WANGCHUCK. In early 2007, India and Bhutan renegotiated their treaty, eliminating the clause that stated that Bhutan would be "guided by" India in conducting its foreign policy, although Thimphu continues to coordinate closely with New Delhi. Elections for seating the country's first parliament were completed in March 2008; the king ratified the country's first constitution in July 2008. Bhutan experienced a peaceful turnover of power following parliamentary elections in 2013, which routed the incumbent party. The disposition of some 23,000 Nepali Bhutanese refugees who fled or were forced out of Bhutan in the 1990s - housed in two UN refugee camps in Nepal - remains unresolved.
Geography :: BHUTAN
-
Southern Asia, between China and India
27 30 N, 90 30 E
Asia
total: 38,394 sq km
land: 38,394 sq km
water: 0 sq km
country comparison to the world: 137
about one-half the size of Indiana
total: 1,136 km
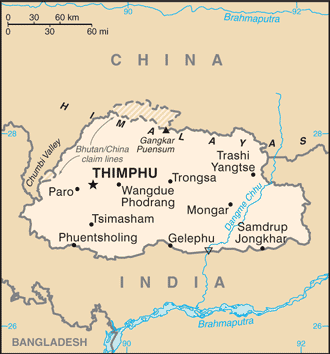
border countries (2): China 477 km, India 659 km
0 km (landlocked)
none (landlocked)
varies; tropical in southern plains; cool winters and hot summers in central valleys; severe winters and cool summers in Himalayas
mostly mountainous with some fertile valleys and savanna
lowest point: Drangeme Chhu 97 m
highest point: Gangkar Puensum 7,570 m
timber, hydropower, gypsum, calcium carbonate
agricultural land: 13.6%
arable land 2.6%; permanent crops 0.3%; permanent pasture 10.7%
forest: 85.5%
other: 0.9% (2011 est.)
319.1 sq km (2010)
78 cu km (2011)
total: 0.34 cu km/yr (5%/1%/94%)
per capita: 458 cu m/yr (2008)
violent storms from the Himalayas are the source of the country's name, which translates as Land of the Thunder Dragon; frequent landslides during the rainy season
soil erosion; limited access to potable water
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea
landlocked; strategic location between China and India; controls several key Himalayan mountain passes
People and Society :: BHUTAN
-
noun: Bhutanese (singular and plural)
adjective: Bhutanese
Ngalop (also known as Bhote) 50%, ethnic Nepalese 35% (includes Lhotsampas - one of several Nepalese ethnic groups), indigenous or migrant tribes 15%
Sharchhopka 28%, Dzongkha (official) 24%, Lhotshamkha 22%, other 26% (includes foreign languages) (2005 est.)
Lamaistic Buddhist 75.3%, Indian- and Nepalese-influenced Hinduism 22.1%, other 2.6% (2005 est.)
741,919
note: the Factbook population estimate is consistent with the first modern census of Bhutan, conducted in 2005; previous Factbook population estimates for Bhutan, which were on the order of three times the total population reported here, were based on Bhutanese Government publications that did not include the census (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
0-14 years: 26.76% (male 101,418/female 97,132)
15-24 years: 19.68% (male 74,373/female 71,600)
25-54 years: 41.6% (male 164,520/female 144,089)
55-64 years: 5.85% (male 23,271/female 20,144)
65 years and over: 6.12% (male 23,754/female 21,618) (2015 est.)
population pyramid:

total dependency ratio: 46.9%
youth dependency ratio: 39.5%
elderly dependency ratio: 7.4%
potential support ratio: 13.4% (2015 est.)
total: 26.7 years
male: 27.2 years
female: 26.1 years (2015 est.)
1.11% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
17.78 births/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
6.69 deaths/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
urban population: 38.6% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: 3.69% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
THIMPHU (capital) 152,000 (2014)
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.14 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.16 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 1.1 male(s)/female
total population: 1.09 male(s)/female (2015 est.)
total: 35.91 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 36.27 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 35.53 deaths/1,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
total population: 69.51 years
male: 68.56 years
female: 70.51 years (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
1.97 children born/woman (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
65.6% (2010)
3.6% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 167
0.26 physicians/1,000 population (2012)
1.8 beds/1,000 population (2012)
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 77.9% of population
rural: 33.1% of population
total: 50.4% of population
unimproved:
urban: 22.1% of population
rural: 66.9% of population
total: 49.6% of population (2015 est.)
0.13% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
600 (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
NA
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria (2013)
5.9% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 154
12.8% (2010)
country comparison to the world: 59
5.5% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 86
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 64.9%
male: 73.1%
female: 55% (2015 est.)
total: 13 years
male: 13 years
female: 13 years (2012)
total number: 25,801
percentage: 18% (2010 est.)
total: 7.2%
male: 7.3%
female: 7.2% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
Government :: BHUTAN
-
conventional long form: Kingdom of Bhutan
conventional short form: Bhutan
local long form: Druk Gyalkhap
local short form: Druk Yul
constitutional monarchy
name: Thimphu
geographic coordinates: 27 28 N, 89 38 E
time difference: UTC+6 (11 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
20 districts (dzongkhag, singular and plural); Bumthang, Chhukha, Chirang, Daga, Gasa, Geylegphug, Ha, Lhuntshi, Mongar, Paro, Pemagatsel, Punakha, Samchi, Samdrup Jongkhar, Shemgang, Tashigang, Tashi Yangtse, Thimphu, Tongsa, Wangdi Phodrang
1907 (became a unified kingdom under its first hereditary king)
National Day (Ugyen WANGCHUCK became first hereditary king), 17 December (1907)
previous (various royal decrees); first constitution drafted November 2001 - March 2005, ratified 18 July 2008 (2011)
civil law based on Buddhist religious law
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
18 years of age; universal
chief of state: King Jigme Khesar Namgyel WANGCHUCK (since 14 December 2006); note - King Jigme Singye WANGCHUCK abdicated the throne on 14 December 2006 and his son immediately succeeded him; the nearly 2-year delay between the former King's abdication and his son's coronation on 6 November 2008 was to ensure an astrologically auspicious coronation date and to give the new king, who had limited experience, deeper administrative expertise under the guidance of his father
head of government: Prime Minister Tshering TOBGAY (since July 2013)
cabinet: Council of Ministers or Lhengye Zhungtshog members nominated by the monarch in consultation with the prime minister and approved by the National Assembly; members serve 5-year tern
elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary, but can be removed by a two-third vote of Parliament; leader of the majority party in Parliament is nominated as the prime minister, appointed by the monarch
description: bicameral Parliament or Chi Tshog consists of the non-partisan National Council or Gyelyong Tshogde (25 seats; 20 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 5 members appointed by the king; members serve 4-year terms) and the National Assembly or Tshogdu (47 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote to serve 5-year terms)
elections: National Council election last held on 23 April 2013 (next to be held in 2017); National Assembly election (first round) held on 31 May 2013; second round on 13 July 2013
election results: National Council - independents 20; note - all candidates required to run as independents; National Assembly - first round poll held on 31 May 2013 - percent of vote by party - DPT 44.52%; PDP 32.53%; DNT 17.04%; DCT 5.9%; second round poll held on 13 July 2013 - percent of vote by party - PDP 54.88%, DPT 45.12%; seats by party - PDP 32, DPT 15
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of 5 justices including the chief justice); note - the Supreme Court has sole jurisdiction in constitutional matters
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the monarch upon the advice of the National Judicial Commission, a 4-member body to include the Legislative Committee of the National Assembly, the attorney general, the Chief Justice of Bhutan and the senior Associate Justice of the Supreme Court; other judges (drangpons) appointed by the monarch from among the High Court judges selected by the National Judicial Commission; chief justice serves a 5-year term or until reaching age 65 years, whichever is earlier; the 4 other judges serve 10-year terms or until age 65, whichever is earlier
subordinate courts: High Court (first appellate court); District or Dzongkhag Courts; sub-district or Dungkhag Courts
Bhutan Kuen-Nyam Party or BNK [Sonam TOBGAY]
Bhutan Peace and Prosperity Party (Druk Phuensum Tshogpa) or DPT [Jigme THINLEY]
Druck Chirwang Tshogpa or DCT
Druk Nymrub Tshogpa or DNT
People's Democratic Party or PDP [Tshering TOBGAY]
Druk National Congress (exiled)
United Front for Democracy (exiled)
other: Buddhist clergy; ethnic Nepali-Bhutanese organizations (exiled); Indian merchant community
ADB, BIMSTEC, CP, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, SAARC, SACEP, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
none; note - the Permanent Mission to the UN for Bhutan has consular jurisdiction in the US; the permanent representative to the UN is Kunzang C. NAMGYEL (since February 2014); address: 343 East 43rd Street, New York, NY 10017; telephone [1] (212) 682-2268; FAX [1] (212) 661-0551
consulate(s) general: New York
the US and Bhutan have no formal diplomatic relations, although frequent informal contact is maintained via the US embasssy in New Delhi (India) and Bhutan's Permanent Mission to the UN
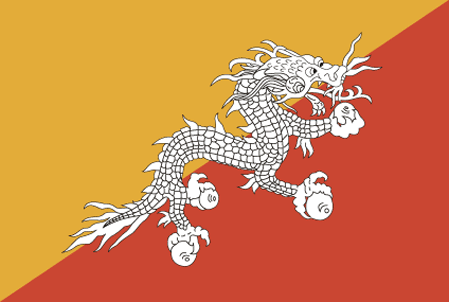
divided diagonally from the lower hoist-side corner; the upper triangle is yellow and the lower triangle is orange; centered along the dividing line is a large black and white dragon facing away from the hoist side; the dragon, called the Druk (Thunder Dragon), is the emblem of the nation; its white color stands for purity and the jewels in its claws symbolize wealth; the background colors represent spiritual and secular powers within Bhutan: the orange is associated with Buddhism, while the yellow denotes the ruling dynasty
thunder dragon known as Druk Gyalpo; national colors: orange, yellow
name: "Druk tsendhen" (The Thunder Dragon Kingdom)
lyrics/music: Gyaldun Dasho Thinley DORJI/Aku TONGMI
note: adopted 1953
Economy :: BHUTAN
-
Bhutan's economy, small and less developed, is based largely on hydropower, agriculture, and forestry, which provide the main livelihood for more than half of the population. Because rugged mountains dominate the terrain and make the building of roads and other infrastructure difficult and expensive, industrial production is primarily of the cottage industry type. The economy is closely aligned with India's through strong trade and monetary links and is dependent on India for financial assistance and migrant laborers for development projects, especially for road construction. Multilateral development organizations administer most educational, social, and environment programs, and take into account the government's desire to protect the country's environment and cultural traditions. For example, the government, in its cautious expansion of the tourist sector, encourages visits by upscale, environmentally conscientious tourists. Complicated controls and uncertain policies in areas such as industrial licensing, trade, labor, and finance continue to hamper foreign investment. Bhutan’s largest export - hydropower to India - could spur sustainable growth in the coming years if Bhutan resolves chronic delays in construction. Bhutan currently taps only 5% of its 30,000-megawatt hydropower potential and is behind schedule in building 12 new hydropower dams with a combined capacity of 10,000 megawatts by 2020 in accordance with a deal signed in 2008 with India. The high volume of imported materials to build hydropower plants has expanded Bhutan's trade and current account deficits. However, Bhutan and India in April 2014 agreed to begin four additional hydropower projects, which would generate 2,120 megawatts in total. A declining GDP growth rate in each of the past three years in the absence of new hydropower facilities has constrained Bhutan’s ability to institute economic reforms. Bhutan inked a pact in December 2014 to expand duty-free trade with Bangladesh, the only trade partner with which Bhutan enjoys a surplus.
$5.855 billion (2014 est.)
$5.505 billion (2013 est.)
$5.245 billion (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 170
$2.092 billion (2014 est.)
6.4% (2014 est.)
5% (2013 est.)
6.5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
$7,600 (2014 est.)
$7,200 (2013 est.)
$6,800 (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 148
22.1% of GDP (2014 est.)
28.5% of GDP (2013 est.)
26.7% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
household consumption: 39%
government consumption: 20.6%
investment in fixed capital: 71.4%
investment in inventories: 0%
exports of goods and services: 36.4%
imports of goods and services: -67.5%
(2014 est.)
agriculture: 14.4%
industry: 41.6%
services: 44% (2014 est.)
rice, corn, root crops, citrus; dairy products, eggs
cement, wood products, processed fruits, alcoholic beverages, calcium carbide, tourism
8% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
345,800
note: major shortage of skilled labor (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
agriculture: 56%
industry: 22%
services: 22% (2013 est.)
3.2% (2014 est.)
2.1% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
12% (2012 est.)
lowest 10%: 2.3%
highest 10%: 37.6% (2003)
38.7 (2012)
38.1 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 70
revenues: $407.1 million
expenditures: $614 million
note: the government of India finances nearly one-quarter of Bhutan's budget expenditures (2014 est.)
19.5% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 168
-9.9% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
91.5% of GDP (2014 est.)
97% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
1 July - 30 June
7.7% (2014 est.)
8.8% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200
NA%
14% (31 December 2014 est.)
14% (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
$636 million (31 December 2014 est.)
$550.6 million (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
$1.099 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
$1.062 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
$796.1 million (31 December 2014 est.)
$726.2 million (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
$320 million (31 December 2013)
$283.4 million (31 December 2012)
country comparison to the world: 115
-$459 million (2014 est.)
-$553.3 million (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
$650.3 million (2014 est.)
$352 million (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
electricity (to India), ferrosilicon, cement, calcium carbide, copper wire, manganese, vegetable oil
India 83.8%, Hong Kong 10.8% (2013 est.)
$980.6 million (2014 est.)
$905.3 million (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 180
fuel and lubricants, passenger cars, machinery and parts, fabrics, rice
India 72.3%, South Korea 6% (2013 est.)
$1.707 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$1.578 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
$173.7 million (31 December 2014 est.)
$131.7 million (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
ngultrum (BTN) per US dollar -
60.42 (2014 est.)
58.6 (2013 est.)
53.44 (2012 est.)
46.67 (2011 est.)
45.73 (2010 est.)
Energy :: BHUTAN
-
7.55 billion kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
1.841 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144
5.625 billion kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
37 million kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
1.499 million kW (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
0.7% of total installed capacity (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 207
0% of total installed capacity (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
99.3% of total installed capacity (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
0% of total installed capacity (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 163
0 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
0 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
0 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
0 bbl (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
0 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
1,870 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
0 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
1,870 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181
0 cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
0 cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
0 cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
0 cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
0 cu m (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
320,800 Mt (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 189
Communications :: BHUTAN
-
total subscriptions: 23,800
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 3 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 176
total: 628,300
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 86 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
general assessment: urban towns and district headquarters have telecommunications services
domestic: low teledensity; domestic service is poor especially in rural areas; mobile-cellular service, started in 2003, is now widely available
international: country code - 975; international telephone and telegraph service via landline and microwave relay through India; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (2012)
state-owned TV station established in 1999; cable TV service offers dozens of Indian and other international channels; first radio station, privately launched in 1973, is now state-owned; 5 private radio stations are currently broadcasting (2012)
AM 0, FM 9, shortwave 1 (2007)
1 (2007)
.bt
total: 203,100
percent of population: 27.7% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
Transportation :: BHUTAN
-
2 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 198
total: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2013)
total: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2012)
total: 10,578 km
paved: 2,975 km (includes 2,180 km of natonal highways)
unpaved: 7,603 km (2013)
country comparison to the world: 135
Military :: BHUTAN
-
Royal Bhutan Army (includes Royal Bodyguard and Royal Bhutan Police) (2009)
18 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; militia training is compulsory for males aged 20-25, over a 3-year period (2012)
males age 16-49: 202,407
females age 16-49: 180,349 (2010 est.)
males age 16-49: 157,664
females age 16-49: 144,861 (2010 est.)
male: 7,363
female: 7,095 (2010 est.)
Transnational Issues :: BHUTAN
-
lacking any treaty describing the boundary, Bhutan and China continue negotiations to establish a common boundary alignment to resolve territorial disputes arising from substantial cartographic discrepancies, the largest of which lie in Bhutan's northwest and along the Chumbi salient
 Central Intelligence Agency
Central Intelligence Agency