
-
Introduction :: Afghanistan
-
Background:
Ahmad Shah DURRANI unified the Pashtun tribes and founded Afghanistan in 1747. The country served as a buffer between the British and Russian Empires until it won independence from notional British control in 1919. A brief experiment in democracy ended in a 1973 coup and a 1978 communist countercoup. The Soviet Union invaded in 1979 to support the tottering Afghan communist regime, touching off a long and destructive war. The USSR withdrew in 1989 under relentless pressure by internationally supported anti-communist mujahidin rebels. A series of subsequent civil wars saw Kabul finally fall in 1996 to the Taliban, a hardline Pakistani-sponsored movement that emerged in 1994 to end the country's civil war and anarchy. Following the 11 September 2001 terrorist attacks, a US, Allied, and anti-Taliban Northern Alliance military action toppled the Taliban for sheltering Usama BIN LADIN.
A UN-sponsored Bonn Conference in 2001 established a process for political reconstruction that included the adoption of a new constitution, a presidential election in 2004, and National Assembly elections in 2005. In December 2004, Hamid KARZAI became the first democratically elected president of Afghanistan, and the National Assembly was inaugurated the following December. KARZAI was reelected in August 2009 for a second term. The 2014 presidential election was the country's first to include a runoff, which featured the top two vote-getters from the first round, Abdullah ABDULLAH and Ashraf GHANI. Throughout the summer of 2014, their campaigns disputed the results and traded accusations of fraud, leading to a US-led diplomatic intervention that included a full vote audit as well as political negotiations between the two camps. In September 2014, GHANI and ABDULLAH agreed to form the Government of National Unity, with GHANI inaugurated as president and ABDULLAH elevated to the newly-created position of chief executive officer. The day after the inauguration, the GHANI administration signed the US-Afghan Bilateral Security Agreement and NATO Status of Forces Agreement, which provide the legal basis for the post-2014 international military presence in Afghanistan.
Despite gains toward building a stable central government, the Taliban remains a serious challenge for the Afghan Government in almost every province. The Taliban still considers itself the rightful government of Afghanistan, and it remains a capable and confident insurgent force despite its last two spiritual leaders being killed; it continues to declare that it will pursue a peace deal with Kabul only after foreign military forces depart.
AFGHANISTAN SUMMARY: PDF
PDF
-
Geography :: Afghanistan
-
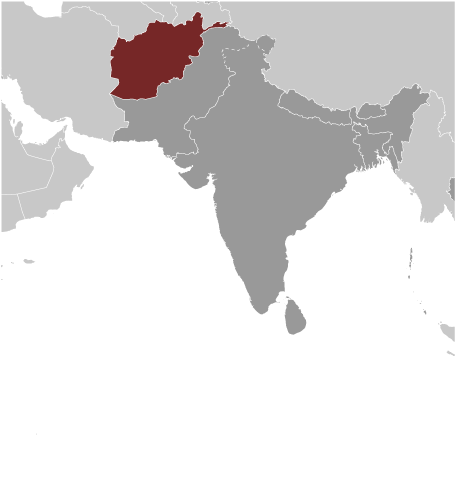
Location:Southern Asia, north and west of Pakistan, east of IranGeographic coordinates:33 00 N, 65 00 EMap references:AsiaArea:total: 652,230 sq kmland: 652,230 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 42Area - comparative:almost six times the size of Virginia; slightly smaller than TexasArea comparison map:
 The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth Asia :: Afghanistan Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth Asia :: Afghanistan Print Image Description
Image Descriptionalmost six times the size of Virginia; slightly smaller than Texas
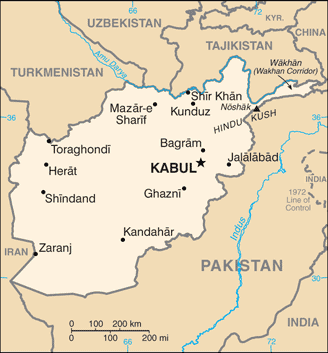
Land boundaries:total: 5,987 kmborder countries (6): China 91 km, Iran 921 km, Pakistan 2670 km, Tajikistan 1357 km, Turkmenistan 804 km, Uzbekistan 144 kmCoastline:0 km (landlocked)Maritime claims:none (landlocked)Climate:arid to semiarid; cold winters and hot summersTerrain:mostly rugged mountains; plains in north and southwestElevation:mean elevation: 1,884 melevation extremes: 258 m lowest point: Amu Darya7492 highest point: NoshakNatural resources:natural gas, petroleum, coal, copper, chromite, talc, barites, sulfur, lead, zinc, iron ore, salt, precious and semiprecious stones, arable landLand use:agricultural land: 58.1% (2014 est.)arable land: 20.5% (2014 est.) / permanent crops: 0.37% (2014 est.) / permanent pasture: 79% (2014 est.)forest: 2.07% (2014 est.)other: 39.9% (2014 est.)Irrigated land:32,080 sq km (2012)Population distribution:populations tend to cluster in the foothills and periphery of the rugged Hindu Kush range; smaller groups are found in many of the country's interior valleys; in general, the east is more densely settled, while the south is sparsely populatedNatural hazards:damaging earthquakes occur in Hindu Kush mountains; flooding; droughtsEnvironment - current issues:limited natural freshwater resources; inadequate supplies of potable water; soil degradation; overgrazing; deforestation (much of the remaining forests are being cut down for fuel and building materials); desertification; air and water pollution in overcrowded urban areasEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protectionsigned, but not ratified: Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life ConservationGeography - note:landlocked; the Hindu Kush mountains that run northeast to southwest divide the northern provinces from the rest of the country; the highest peaks are in the northern Vakhan (Wakhan Corridor) -
People and Society :: Afghanistan
-
Population:34,940,837 (July 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 39Nationality:noun: Afghan(s)adjective: AfghanEthnic groups:Pashtun, Tajik, Hazara, Uzbek, other (includes smaller numbers of Baloch, Turkmen, Nuristani, Pamiri, Arab, Gujar, Brahui, Qizilbash, Aimaq, Pashai, and Kyrghyz) (2015)
note: current statistical data on the sensitive subject of ethnicity in Afghanistan are not available, and ethnicity data from small samples of respondents to opinion polls are not a reliable alternative; Afghanistan's 2004 constitution recognizes 14 ethnic groups: Pashtun, Tajik, Hazara, Uzbek, Baloch, Turkmen, Nuristani, Pamiri, Arab, Gujar, Brahui, Qizilbash, Aimaq, and Pashai
Languages:Afghan Persian or Dari (official) 80% (Dari functions as the lingua franca), Pashto (official) 47%, Uzbek 11%, English 5%, Turkmen 2%, Urdu 2%, Pashayi 1%, Nuristani 1%, Arabic 1%, Balochi, Shughni, Pamiri, Hindi, Russian, German, French (2017 est.)note: data represent most widely spoken languages; shares sum to more than 100% because there is much bilingualism in the country and because respondents were allowed to select more than one language
note: the Turkic languages Uzbek and Turkmen, as well as Balochi, Pashayi, Nuristani, and Pamiri are the third official languages in areas where the majority speaks them
Religions:Muslim 99.7% (Sunni 84.7 - 89.7%, Shia 10 - 15%), other 0.3% (2009 est.)Age structure:0-14 years: 40.92% (male 7,263,716 /female 7,033,427)15-24 years: 21.85% (male 3,883,693 /female 3,749,760)25-54 years: 30.68% (male 5,456,305 /female 5,263,332)55-64 years: 3.95% (male 679,766 /female 699,308)65 years and over: 2.61% (male 420,445 /female 491,085) (2018 est.)population pyramid: The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth Asia :: Afghanistan Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth Asia :: Afghanistan Print Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Afghanistan. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Afghanistan. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 88.8 (2015 est.)youth dependency ratio: 84.1 (2015 est.)elderly dependency ratio: 4.7 (2015 est.)potential support ratio: 21.2 (2015 est.)Median age:total: 19 yearsmale: 19 yearsfemale: 19.1 years (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Population growth rate:2.37% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 29Birth rate:37.5 births/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 12Death rate:13.2 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 9Net migration rate:-0.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 134Population distribution:populations tend to cluster in the foothills and periphery of the rugged Hindu Kush range; smaller groups are found in many of the country's interior valleys; in general, the east is more densely settled, while the south is sparsely populatedUrbanization:urban population: 25.5% of total population (2018)rate of urbanization: 3.37% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:4.012 million KABUL (capital) (2018)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female (2017 est.)0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female (2017 est.)15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female (2017 est.)25-54 years: 1.04 male(s)/female (2017 est.)55-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female (2017 est.)65 years and over: 0.86 male(s)/female (2017 est.)total population: 1.03 male(s)/female (2017 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:19.9 years (2015 est.)note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
Maternal mortality rate:396 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 28Infant mortality rate:total: 108.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)male: 115.7 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)female: 100.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 1Life expectancy at birth:total population: 52.1 years (2018 est.)male: 50.6 years (2018 est.)female: 53.6 years (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 223Total fertility rate:5.02 children born/woman (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 11Contraceptive prevalence rate:22.5% (2015/16)Health expenditures:8.2% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 52Physicians density:0.3 physicians/1,000 population (2016)Hospital bed density:0.5 beds/1,000 population (2014)Drinking water source:improved: urban: 78.2% of populationrural: 47% of populationtotal: 55.3% of populationunimproved: urban: 21.8% of populationrural: 53% of populationtotal: 44.7% of population (2015 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved: urban: 45.1% of population (2015 est.)rural: 27% of population (2015 est.)total: 31.9% of population (2015 est.)unimproved: urban: 54.9% of population (2015 est.)rural: 73% of population (2015 est.)total: 68.1% of population (2015 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:<.1% (2016 est.)HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:7,500 (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 109HIV/AIDS - deaths:<500 (2016 est.)Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: intermediate (2016)food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever (2016)vectorborne diseases: malaria (2016)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:5.5% (2016)country comparison to the world: 176Children under the age of 5 years underweight:25% (2013)country comparison to the world: 16Education expenditures:3.2% of GDP (2015)country comparison to the world: 138Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and write (2015 est.)total population: 38.2% (2015 est.)male: 52% (2015 est.)female: 24.2% (2015 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 11 years (2014)male: 13 years (2014)female: 8 years (2014) -
Government :: Afghanistan
-
Country name:conventional long form: Islamic Republic of Afghanistanconventional short form: Afghanistanlocal long form: Jamhuri-ye Islami-ye Afghanistanlocal short form: Afghanistanformer: Republic of Afghanistanetymology: the name "Afghan" originally referred to the Pashtun people (today it is understood to include all the country's ethnic groups), while the suffix "-stan" means "place of" or "country"; so Afghanistan literally means the "Land of the Afghans"Government type:presidential Islamic republicCapital:name: Kabulgeographic coordinates: 34 31 N, 69 11 Etime difference: UTC+4.5 (9.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)etymology: named for the Kabul River, but the river's name is of unknown originAdministrative divisions:34 provinces (welayat, singular - welayat); Badakhshan, Badghis, Baghlan, Balkh, Bamyan, Daykundi, Farah, Faryab, Ghazni, Ghor, Helmand, Herat, Jowzjan, Kabul, Kandahar, Kapisa, Khost, Kunar, Kunduz, Laghman, Logar, Nangarhar, Nimroz, Nuristan, Paktika, Paktiya, Panjshir, Parwan, Samangan, Sar-e Pul, Takhar, Uruzgan, Wardak, ZabulIndependence:19 August 1919 (from UK control over Afghan foreign affairs)National holiday:Independence Day, 19 August (1919)Constitution:history: several previous; latest drafted 14 December 2003 - 4 January 2004, signed 16 January 2004, ratified 26 January 2004 (2017)amendments: proposed by a commission formed by presidential decree followed by the convention of a Grand Council (Loya Jirga) decreed by the president; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Loya Jirga membership and endorsement by the president (2017)Legal system:mixed legal system of civil, customary, and Islamic lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictionCitizenship:citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must have been born in - and continuously lived in - Afghanistandual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 5 yearsSuffrage:18 years of age; universalJudicial branch:highest courts: Supreme Court or Stera Mahkama (consists of the supreme court chief and 8 justices organized into criminal, public security, civil, and commercial divisions or dewans)judge selection and term of office: court chief and justices appointed by the president with the approval of the Wolesi Jirga; court chief and justices serve single 10-year termssubordinate courts: Appeals Courts; Primary Courts; Special Courts for issues including narcotics, security, property, family, and juvenilesExecutive branch:chief of state: President of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan Ashraf GHANI Ahmadzai (since 29 September 2014); CEO Abdullah ABDULLAH, Dr. (since 29 September 2014); First Vice President Abdul Rashid DOSTAM (since 29 September 2014); Second Vice President Sarwar DANESH (since 29 September 2014); First Deputy CEO Khyal Mohammad KHAN; Second Deputy CEO Mohammad MOHAQQEQ; note - the president is both chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan Ashraf GHANI Ahmadzai (since 29 September 2014); CEO Abdullah ABDULLAH, Dr. (since 29 September 2014); First Vice President Abdul Rashid DOSTAM (since 29 September 2014); Second Vice President Sarwar DANESH (since 29 September 2014); First Deputy CEO Khyal Mohammad KHAN; Second Deputy CEO Mohammad MOHAQQEQcabinet: Cabinet consists of 25 ministers appointed by the president, approved by the National Assemblyelections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held in 2 rounds on 5 April and 14 June 2014 (next originally scheduled for April 2019 has been postponed by several months)election results: Ashraf GHANI elected president in the second round; percent of vote in first round - Abdullah ABDULLAH (National Coalition of Afghanistan) 45%, Ashraf GHANI (independent) 31.6%, Zalmai RASSOUL 11.4%, other 12%; percent of vote in second round - Ashraf GHANI 56.4%, Abdullah ABDULLAH 43.6%Legislative branch:description: bicameral National Assembly consists of:
Meshrano Jirga or House of Elders (102 seats; 34 members indirectly elected by district councils to serve 3-year terms, 34 indirectly elected by provincial councils to serve 4-year terms, and 34 nominated by the president of which 17 must be women, 2 must represent the disabled, and 2 must be Kuchi nomads; members nominated by the president serve 5-year terms)
Wolesi Jirga or House of People (249 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote to serve 5-year terms)elections:
Meshrano Jirga - last held 10 January 2015 (next to be held in 2018)
Wolesi Jirga - last held on 20 October 2018) (next tobe held in 2023)election results:
Meshrano Jirga - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; composition - men 84, women 18, percent of women 17.6%
Wolesi Jirga - percent of vote by party NA; seats by party - NA; composition - men 148, women 69, percent of women 27.7%; note - total National Assembly percent of women 24.8%note: the constitution allows the government to convene a constitutional Loya Jirga (Grand Council) on issues of independence, national sovereignty, and territorial integrity; it consists of members of the National Assembly and chairpersons of the provincial and district councils; a Loya Jirga can amend provisions of the constitution and prosecute the president; no constitutional Loya Jirga has ever been held, and district councils have never been elected; the president appointed 34 members of the Meshrano Jirga that the district councils should have indirectly electedPolitical parties and leaders:note - the Ministry of Justice licensed 57 political parties as of September 2016International organization participation:ADB, CICA, CP, ECO, EITI (candidate country), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, OSCE (partner), SAARC, SACEP, SCO (dialogue member), UN, UNAMA, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Hamdullah MOHIB (since 17 September 2015)chancery: 2341 Wyoming Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 483-6410FAX: [1] (202) 483-6488consulate(s) general: Los Angeles, New York, Washington, DCDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador John BASS (since December 2017)embassy: Bibi Mahru, Kabulmailing address: U.S. Embassy Kabul, APO, AE 09806telephone: [00 93] 0700 108 001FAX: [00 93] 0700 108 564Flag description:three equal vertical bands of black (hoist side), red, and green, with the national emblem in white centered on the red band and slightly overlapping the other 2 bands; the center of the emblem features a mosque with pulpit and flags on either side, below the mosque are numerals for the solar year 1298 (1919 in the Gregorian calendar, the year of Afghan independence from the UK); this central image is circled by a border consisting of sheaves of wheat on the left and right, in the upper-center is an Arabic inscription of the Shahada (Muslim creed) below which are rays of the rising sun over the Takbir (Arabic expression meaning "God is great"), and at bottom center is a scroll bearing the name Afghanistan; black signifies the past, red is for the blood shed for independence, and green can represent either hope for the future, agricultural prosperity, or Islamnote: Afghanistan had more changes to its national flag in the 20th century - 19 by one count - than any other country; the colors black, red, and green appeared on most of them
National symbol(s):lion; national colors: red, green, blackNational anthem:name: "Milli Surood" (National Anthem)lyrics/music: Abdul Bari JAHANI/Babrak WASAnote: adopted 2006; the 2004 constitution of the post-Taliban government mandated that a new national anthem should be written containing the phrase "Allahu Akbar" (God is Greatest) and mentioning the names of Afghanistan's ethnic groups
-
Economy :: Afghanistan
-
Economy - overview:
Despite improvements in life expectancy, incomes, and literacy since 2001, Afghanistan is extremely poor, landlocked, and highly dependent on foreign aid. Much of the population continues to suffer from shortages of housing, clean water, electricity, medical care, and jobs. Corruption, insecurity, weak governance, lack of infrastructure, and the Afghan Government's difficulty in extending rule of law to all parts of the country pose challenges to future economic growth. Afghanistan's living standards are among the lowest in the world. Since 2014, the economy has slowed, in large part because of the withdrawal of nearly 100,000 foreign troops that had artificially inflated the country’s economic growth.
The international community remains committed to Afghanistan's development, pledging over $83 billion at ten donors' conferences between 2003 and 2016. In October 2016, the donors at the Brussels conference pledged an additional $3.8 billion in development aid annually from 2017 to 2020. Even with this help, Government of Afghanistan still faces number of challenges, including low revenue collection, anemic job creation, high levels of corruption, weak government capacity, and poor public infrastructure.
In 2017 Afghanistan's growth rate was only marginally above that of the 2014-2016 average. The drawdown of international security forces that started in 2012 has negatively affected economic growth, as a substantial portion of commerce, especially in the services sector, has catered to the ongoing international troop presence in the country. Afghan President Ashraf GHANI Ahmadzai is dedicated to instituting economic reforms to include improving revenue collection and fighting corruption. The government has implemented reforms to the budget process and in some other areas. However, many other reforms will take time to implement and Afghanistan will remain dependent on international donor support over the next several years.
GDP (purchasing power parity):$69.45 billion (2017 est.)$67.65 billion (2016 est.)$66.21 billion (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 101GDP (official exchange rate):$20.24 billion (2017 est.) (2017 est.)GDP - real growth rate:2.7% (2017 est.)2.2% (2016 est.)1% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 124GDP - per capita (PPP):$2,000 (2017 est.)$2,000 (2016 est.)$2,000 (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 209Gross national saving:22.7% of GDP (2017 est.)25.8% of GDP (2016 est.)21.4% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 78GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 81.6% (2016 est.)government consumption: 12% (2016 est.)investment in fixed capital: 17.2% (2016 est.)investment in inventories: 30% (2016 est.)exports of goods and services: 6.7% (2016 est.)imports of goods and services: -47.6% (2016 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 23% (2016 est.)industry: 21.1% (2016 est.)services: 55.9% (2016 est.)note: data exclude opium production
Agriculture - products:opium, wheat, fruits, nuts, wool, mutton, sheepskins, lambskins, poppiesIndustries:small-scale production of bricks, textiles, soap, furniture, shoes, fertilizer, apparel, food products, non-alcoholic beverages, mineral water, cement; handwoven carpets; natural gas, coal, copperIndustrial production growth rate:-1.9% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 181Labor force:8.478 million (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 61Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 44.3%industry: 18.1%services: 37.6% (2017 est.)Unemployment rate:23.9% (2017 est.)22.6% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 194Population below poverty line:54.5% (2017 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 3.8% (2008)highest 10%: 24% (2008)Distribution of family income - Gini index:29.4 (2008)country comparison to the world: 136Budget:revenues: 2.276 billion (2017 est.)expenditures: 5.328 billion (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues:11.2% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 210Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-15.1% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 217Public debt:7% of GDP (2017 est.)7.8% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 202Fiscal year:21 December - 20 DecemberInflation rate (consumer prices):5% (2017 est.)4.4% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 171Commercial bank prime lending rate:15% (31 December 2016 est.)15% (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 37Stock of narrow money:$6.644 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$6.192 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 94Stock of broad money:$6.945 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$6.544 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 95Stock of domestic credit:-$240.6 million (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 192Market value of publicly traded shares:NA
Current account balance:$1.014 billion (2017 est.)$1.409 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 48Exports:$784 million (2017 est.)$614.2 million (2016 est.)note: not including illicit exports or reexports
country comparison to the world: 171Exports - partners:India 56.5%, Pakistan 29.6% (2017)Exports - commodities:opium, fruits and nuts, handwoven carpets, wool, cotton, hides and pelts, precious and semi-precious gems, and medical herbsImports:$7.616 billion (2017 est.)$6.16 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 114Imports - commodities:machinery and other capital goods, food, textiles, petroleum productsImports - partners:China 21%, Iran 20.5%, Pakistan 11.8%, Kazakhstan 11%, Uzbekistan 6.8%, Malaysia 5.3% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$7.187 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$6.901 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 85Debt - external:$2.84 billion (FY/)country comparison to the world: 144Exchange rates:afghanis (AFA) per US dollar -7.87 (2017 est.)68.03 (2016 est.)67.87 (2015)61.14 (2014 est.)57.25 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Afghanistan
-
Electricity access:population without electricity: 18,999,254 (2012)electrification - total population: 43% (2012)electrification - urban areas: 83% (2012)electrification - rural areas: 32% (2012)Electricity - production:1.211 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 146Electricity - consumption:5.526 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 119Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 96Electricity - imports:4.4 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 42Electricity - installed generating capacity:634,100 kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 138Electricity - from fossil fuels:45% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 159Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 32Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:52% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 34Electricity - from other renewable sources:4% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 111Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 101Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 82Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 84Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 99Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 110Refined petroleum products - consumption:35,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 117Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 124Refined petroleum products - imports:34,210 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 97Natural gas - production:164.2 million cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 79Natural gas - consumption:164.2 million cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 108Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 81Natural gas - proved reserves:49.55 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:9.067 million Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 111
-
Communications :: Afghanistan
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 118,769 (2017 est.)subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 138Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 23,929,713 (2017 est.)subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 70 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 52Telephone system:general assessment: progress has been made on Afghanistan's first limited fixed-line telephone service and nationwide optical fibre backbone; aided by the presence of multiple providers, mobile-cellular telephone service continues to improve swiftly; the Afghan Ministry of Communications and Information claims that more than 90% of the population live in areas with access to mobile-cellular services (2017)domestic: less than 1 per 100 for fixed-line teledensity; 70 per 100 for mobile-cellular; an increasing number of Afghans utilize mobile-cellular phone networks (2017)international: country code - 93; multiple VSAT's provide international and domestic voice and data connectivity (2016)Broadcast media:state-owned broadcaster, Radio Television Afghanistan (RTA), operates a series of radio and television stations in Kabul and the provinces; an estimated 150 private radio stations, 50 TV stations, and about a dozen international broadcasters are available (2018)Internet country code:.afInternet users:total: 3,531,770 (July 2016 est.)percent of population: 10.6% (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Broadband - fixed subscriptions:total: 16,810 (2017 est.)subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 156
-
Transportation :: Afghanistan
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 4 (2015)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 20 (2015)annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 1,929,907 (2015)annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 33,102,038 mt-km (2015)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:YA (2016)Airports:43 (2016)country comparison to the world: 99Airports - with paved runways:total: 25 (2017)over 3,047 m: 4 (2017)2,438 to 3,047 m: 4 (2017)1,524 to 2,437 m: 14 (2017)914 to 1,523 m: 2 (2017)under 914 m: 1 (2017)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 18 (2016)2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 (2016)1,524 to 2,437 m: 8 (2016)914 to 1,523 m: 4 (2016)under 914 m: 5 (2016)Heliports:9 (2013)Pipelines:466 km gas (2013)Roadways:total: 42,150 km (2006)paved: 12,350 km (2006)unpaved: 29,800 km (2006)country comparison to the world: 86Waterways:1,200 km (chiefly Amu Darya, which handles vessels up to 500 DWT) (2011)country comparison to the world: 58Ports and terminals:river port(s): Kheyrabad, Shir Khan
-
Military and Security :: Afghanistan
-
Military expenditures:0.89% of GDP (2016)0.99% of GDP (2015)1.33% of GDP (2014)1.06% of GDP (2013)1.14% of GDP (2012)country comparison to the world: 125Military branches:Afghan National Defense and Security Forces (ANDSF) comprised of military, police, and other security elements: Afghan National Army (includes Afghan Air Force), Afghan National Police, Afghan Local Police, and the National Directorate of Security (2017)Military service age and obligation:18 is the legal minimum age for voluntary military service; no conscription (2017)
-
Terrorism :: Afghanistan
-
Terrorist groups - home based:al-Qa'ida (AQ):
aim(s): eject Western influence from the Islamic world, unite the worldwide Muslim community, overthrow governments perceived as un-Islamic, and ultimately, establish a pan-Islamic caliphate under a strict Salafi Muslim interpretation of sharia
area(s) of operation: maintains established networks and a longtime operational presence in Afghanistan, especially in the south, northwest, and northeast near the Afghanistan-Pakistan border (April 2018)Islamic Jihad Union (IJU):
aim(s): drive NATO forces out of Afghanistan and destabilize the country; overthrow the Government of Uzbekistan
area(s) of operation: conducts attacks in collaboration with other extremist groups, including the Taliban, against NATO and Afghan forces across the country, especially in the northern and eastern Paktika, Paktia, and Nangarhar provinces (April 2018)Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan (IMU):
aim(s): enhance its networks and secure territory in Afghanistan to establish a secure presence from which it can pursue its historic goal of establishing an Islamic state in the Fergana Valley, a fertile valley spread across eastern Uzbekistan, southern Kyrgyzstan, and northern Tajikistan
area(s) of operation: operates mostly in the north along the Afghanistan-Pakistan border, with its heaviest presence in Badakhshan Province, where IMU has operated paramilitary training camps and bases
note: the IMU is fractured and mostly supports ISIS-K although some members have continued working with the Taliban (April 2018)Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham-Khorasan (ISIS-K):
aim(s): establish an Islamic caliphate in Afghanistan, Pakistan, and parts of Central Asia; counter Westerners and Shia Muslims
area(s) of operation: stronghold in Nangarhar Province near the Afghanistan-Pakistan border and operating in Kunar, Laghman, Jowzjan provinces with pockets of support throughout Afghanistan
note: recruits from among the local population, Central Asian extremists in Afghanistan, and other militant groups, such as Tehrik-e Taliban Pakistan, the Afghan Taliban, and the Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan (April 2018)Tehrik-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP):
aim(s): drive foreign troops from Afghanistan; remove Pakistani forces from Pakistan's Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA) and, ultimately, overthrow the Pakistan Government to implement TTP's strict interpretation of sharia
area(s) of operation: headquartered in several eastern Afghanistan provinces near the Afghanistan-Pakistan border; operates primarily along the northeastern Afghanistan-Pakistan border, especially in Kunar and Paktika provinces, where TTP has established sanctuaries (April 2018)Terrorist groups - foreign based:al-Qa'ida in the Indian Subcontinent (AQIS):
aim(s): establish an Islamic caliphate in the Indian subcontinent
area(s) of operation: heaviest presence is in Afghanistan, especially in the eastern and southern regions, where most of the Afghan-based leaders are located
note: targets primarily Afghan military and security personnel and US interests (April 2018)Haqqani Taliban Network (HQN):
aim(s): expel US and Coalition forces and replace the Afghan Government with an Islamic state operating according to a strict Salafi Muslim interpretation of sharia under the Afghan Taliban
area(s) of operation: stages attacks from Kurram and North Waziristan Agency in Pakistan's Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA) across from Afghanistan's southeastern border; operational throughout the country, especially in Kabul and Paktiya and Khost provinces
note: plays a leading role in planning and executing high-profile attacks against Afghan personnel, NATO's Resolute Support Mission, US and Coalition Forces, and other US and Western interests (April 2018)Harakat ul-Jihad-i-Islami (HUJI):
aim(s): implement sharia in Afghanistan; enhance its networks and drive foreign troops from Afghanistan
area(s) of operation: operations throughout Afghanistan, targeting primarily Afghan Government personnel and Coalition forces (April 2018)Harakat ul-Mujahidin (HUM):
aim(s): enhance its networks and paramilitary training in Afghanistan and, ultimately, incorporate Kashmir into Pakistan; establish an Islamic state in Kashmir
area(s) of operation: maintains paramilitary training camps in eastern Afghanistan (April 2018)Jaish-e-Mohammed (JEM):
aim(s): participate in the insurgency against Afghan and international forces to support a Taliban return to power in Afghanistan and annex the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir to Pakistan
area(s) of operation: historically operated in Afghanistan's eastern provinces (April 2018)Jaysh al Adl:
aim(s): enhance its operational networks and capabilities for staging cross-border attacks into Pakistan and Iran
area(s) of operation: operational in the greater Balochistan area, where fighters stage attacks targeting Shia Muslims in Iran and Pakistan
note: formerly known as Jundallah (April 2018)Lashkar i Jhangvi (LJ):
aim(s): enhance its networks and paramilitary training in Afghanistan; exterminate Shia Muslims, rid the Afghanistan-Pakistan region of Western influence
area(s) of operation: headquartered in the east; operates paramilitary training camps near the Afghanistan-Pakistan border across from the central area of Pakistan's Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA) region; operatives conduct operations inside Afghanistan (April 2018)Lashkar-e Tayyiba (LT):
aim(s): annex the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir to Pakistan and foment Islamic insurgency in India; attack Western, Indian, and Afghan interests in Afghanistan; support the Taliban's return to power; enhance its recruitment networks and paramilitary training in Afghanistan, and, ultimately, install Islamic rule throughout South Asia
area(s) of operation: targets Coalition forces and Western interests throughout the country; maintains several facilities, such as paramilitary training camps, medical clinics serving locals, and schools for youths; targets Pashtun youth for recruitmentAdministered Tribal Areas (FATA) region; operatives conduct operations inside Afghanistan (April 2018) -
Transnational Issues :: Afghanistan
-
Disputes - international:Afghan, Coalition, and Pakistan military meet periodically to clarify the alignment of the boundary on the ground and on maps and since 2014 have met to discuss collaboration on the Taliban insurgency and counterterrorism effortsAfghan and Iranian commissioners have discussed boundary monument densification and resurveyIran protests Afghanistan's restricting flow of dammed Helmand River tributaries during droughtPakistan has sent troops across and built fences along some remote tribal areas of its treaty-defined Durand Line border with Afghanistan which serve as bases for foreign terrorists and other illegal activitiesRussia remains concerned about the smuggling of poppy derivatives from Afghanistan through Central Asian countriesRefugees and internally displaced persons:refugees (country of origin): 75,893 (Pakistan) (2017)IDPs: 1.286 million (mostly Pashtuns and Kuchis displaced in the south and west due to natural disasters and political instability) (2017)Illicit drugs:world's largest producer of opium; poppy cultivation increased 63 percent, to 328,304 hectares in 2017; while eradication increased slightly, it still remains well below levels achieved in 2015; the 2017 crop yielded an estimated 9,000 mt of raw opium, a 88% increase over 2016; the Taliban and other antigovernment groups participate in and profit from the opiate trade, which is a key source of revenue for the Taliban inside Afghanistan; widespread corruption and instability impede counterdrug efforts; most of the heroin consumed in Europe and Eurasia is derived from Afghan opium; Afghanistan is also struggling to respond to a burgeoning domestic opiate addiction problem; a 2015 national drug use survey found that roughly 11% of the population tested positive for one or more illicit drugs; vulnerable to drug money laundering through informal financial networks; illicit cultivation of cannabis and regional source of hashish (2018)