
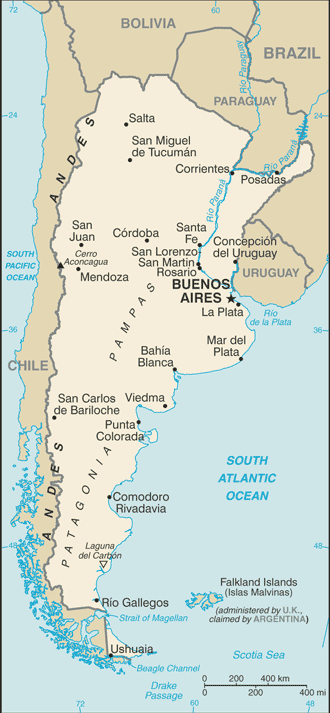
-
Introduction :: Argentina
-
Background:
In 1816, the United Provinces of the Rio Plata declared their independence from Spain. After Bolivia, Paraguay, and Uruguay went their separate ways, the area that remained became Argentina. The country's population and culture were heavily shaped by immigrants from throughout Europe, with Italy and Spain providing the largest percentage of newcomers from 1860 to 1930. Up until about the mid-20th century, much of Argentina's history was dominated by periods of internal political unrest and conflict between civilian and military factions.
After World War II, an era of Peronist populism and direct and indirect military interference in subsequent governments was followed by a military junta that took power in 1976. Democracy returned in 1983 after a failed bid to seize the Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas) by force, and has persisted despite numerous challenges, the most formidable of which was a severe economic crisis in 2001-02 that led to violent public protests and the successive resignations of several presidents. The years 2003-15 saw Peronist rule by Nestor and Cristina FERNANDEZ de KIRCHNER, whose policies isolated Argentina and caused economic stagnation. With the election of Mauricio MACRI in November 2015, Argentina began a period of reform and international reintegration.
ARGENTINA SUMMARY: PDF
PDF
-
Geography :: Argentina
-
Location:Southern South America, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Chile and UruguayGeographic coordinates:34 00 S, 64 00 WMap references:South AmericaArea:total: 2,780,400 sq kmland: 2,736,690 sq kmwater: 43,710 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 9Area - comparative:slightly less than three-tenths the size of the USArea comparison map:
 The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth America :: Argentina Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth America :: Argentina Print Image Description
Image Descriptionslightly less than three-tenths the size of the US
Land boundaries:total: 11,968 kmborder countries (5): Bolivia 942 km, Brazil 1263 km, Chile 6691 km, Paraguay 2531 km, Uruguay 541 kmCoastline:4,989 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental marginClimate:mostly temperate; arid in southeast; subantarctic in southwestTerrain:rich plains of the Pampas in northern half, flat to rolling plateau of Patagonia in south, rugged Andes along western borderElevation:mean elevation: 595 melevation extremes: -105 m lowest point: Laguna del Carbon (located between Puerto San Julian and Comandante Luis Piedra Buena in the province of Santa Cruz)6962 highest point: Cerro Aconcagua (located in the northwestern corner of the province of Mendoza; highest point in South America)Natural resources:fertile plains of the pampas, lead, zinc, tin, copper, iron ore, manganese, petroleum, uranium, arable landLand use:agricultural land: 53.9% (2014 est.)arable land: 13.9% (2014 est.) / permanent crops: 0.4% (2014 est.) / permanent pasture: 39.6% (2014 est.)forest: 10.7% (2014 est.)other: 35.4% (2014 est.)Irrigated land:23,600 sq km (2012)Population distribution:one-third of the population lives in Buenos Aires; pockets of agglomeration occur throughout the northern and central parts of the country; Patagonia to the south remains sparsely populatedNatural hazards:San Miguel de Tucuman and Mendoza areas in the Andes subject to earthquakes; pamperos are violent windstorms that can strike the pampas and northeast; heavy flooding in some areas
volcanism: volcanic activity in the Andes Mountains along the Chilean border; Copahue (2,997 m) last erupted in 2000; other historically active volcanoes include Llullaillaco, Maipo, Planchon-Peteroa, San Jose, Tromen, Tupungatito, and Viedma
Environment - current issues:environmental problems (urban and rural) typical of an industrializing economy such as deforestation, soil degradation (erosion, salinization), desertification, air pollution, and water pollutionnote: Argentina is a world leader in setting voluntary greenhouse gas targets
Environment - international agreements:party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: Marine Life ConservationGeography - note:second-largest country in South America (after Brazil); strategic location relative to sea lanes between the South Atlantic and the South Pacific Oceans (Strait of Magellan, Beagle Channel, Drake Passage); diverse geophysical landscapes range from tropical climates in the north to tundra in the far south; Cerro Aconcagua is the Western Hemisphere's tallest mountain, while Laguna del Carbon is the lowest point in the Western Hemisphere; shares Iguazu Falls, the world's largest waterfalls system, with Brazil -
People and Society :: Argentina
-
Population:44,694,198 (July 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 31Nationality:noun: Argentine(s)adjective: ArgentineEthnic groups:European (mostly Spanish and Italian descent) and mestizo (mixed European and Amerindian ancestry) 97.2%, Amerindian 2.4%, African 0.4% (2010 est.)Languages:Spanish (official), Italian, English, German, French, indigenous (Mapudungun, Quechua)Religions:nominally Roman Catholic 92% (less than 20% practicing), Protestant 2%, Jewish 2%, other 4%Demographic profile:
Argentina's population continues to grow but at a slower rate because of its steadily declining birth rate. Argentina's fertility decline began earlier than in the rest of Latin America, occurring most rapidly between the early 20th century and the 1950s, and then becoming more gradual. Life expectancy has been improving, most notably among the young and the poor. While the population under age 15 is shrinking, the youth cohort - ages 15-24 - is the largest in Argentina's history and will continue to bolster the working-age population. If this large working-age population is well-educated and gainfully employed, Argentina is likely to experience an economic boost and possibly higher per capita savings and investment. Although literacy and primary school enrollment are nearly universal, grade repetition is problematic and secondary school completion is low. Both of these issues vary widely by region and socioeconomic group.
Argentina has been primarily a country of immigration for most of its history, welcoming European immigrants (often providing needed low-skilled labor) after its independence in the 19th century and attracting especially large numbers from Spain and Italy. More than 7 million European immigrants are estimated to have arrived in Argentina between 1880 and 1930, when it adopted a more restrictive immigration policy. European immigration also began to wane in the 1930s because of the global depression. The inflow rebounded temporarily following WWII and resumed its decline in the 1950s when Argentina's military dictators tightened immigration rules and European economies rebounded. Regional migration increased, however, supplying low-skilled workers escaping economic and political instability in their home countries. As of 2015, immigrants made up almost 5% of Argentina's population, the largest share in South America. Migration from neighboring countries accounted for approximately 80% of Argentina's immigrant population in 2015.
The first waves of highly skilled Argentine emigrant workers headed mainly to the United States and Spain in the 1960s and 1970s, driven by economic decline and repressive military dictatorships. The 2008 European economic crisis drove the return migration of some Argentinean and other Latin American nationals, as well as the immigration of Europeans to South America, where Argentina was a key recipient. In 2015, Argentina received the highest number of legal migrants in Latin America and the Caribbean. The majority of its migrant inflow came from Paraguay and Bolivia.
Age structure:0-14 years: 24.44% (male 5,629,345 /female 5,293,680)15-24 years: 15.2% (male 3,476,344 /female 3,317,151)25-54 years: 39.46% (male 8,808,591 /female 8,826,379)55-64 years: 9.12% (male 1,977,421 /female 2,096,665)65 years and over: 11.79% (male 2,216,487 /female 3,052,135) (2018 est.)population pyramid: The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth America :: Argentina Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth America :: Argentina Print Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Argentina. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Argentina. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 56.5 (2015 est.)youth dependency ratio: 39.4 (2015 est.)elderly dependency ratio: 17.1 (2015 est.)potential support ratio: 5.8 (2015 est.)Median age:total: 31.9 yearsmale: 30.7 yearsfemale: 33.1 years (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 107Population growth rate:0.89% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 121Birth rate:16.5 births/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 109Death rate:7.5 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 108Net migration rate:-0.1 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 102Population distribution:one-third of the population lives in Buenos Aires; pockets of agglomeration occur throughout the northern and central parts of the country; Patagonia to the south remains sparsely populatedUrbanization:urban population: 91.9% of total population (2018)rate of urbanization: 1.07% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:14.967 million BUENOS AIRES (capital), 1.548 million Cordoba, 1.488 million Rosario, 1.133 million Mendoza, 956,000 San Miguel de Tucuman, 864,000 La Plata (2018)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female (2017 est.)0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female (2017 est.)15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female (2017 est.)25-54 years: 1 male(s)/female (2017 est.)55-64 years: 0.94 male(s)/female (2017 est.)65 years and over: 0.71 male(s)/female (2017 est.)total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2017 est.)Maternal mortality rate:52 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 94Infant mortality rate:total: 9.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)male: 10.4 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)female: 8.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 138Life expectancy at birth:total population: 77.5 years (2018 est.)male: 74.4 years (2018 est.)female: 80.8 years (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 70Total fertility rate:2.25 children born/woman (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Contraceptive prevalence rate:81.3% (2013)Health expenditures:4.8% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 146Physicians density:3.91 physicians/1,000 population (2013)Hospital bed density:5 beds/1,000 population (2014)Drinking water source:improved: urban: 99% of populationrural: 100% of populationtotal: 99.1% of populationunimproved: urban: 1% of populationrural: 0% of populationtotal: 0.9% of population (2015 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved: urban: 96.2% of population (2015 est.)rural: 98.3% of population (2015 est.)total: 96.4% of population (2015 est.)unimproved: urban: 3.8% of population (2015 est.)rural: 1.7% of population (2015 est.)total: 3.6% of population (2015 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.4% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 68HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:120,000 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 38HIV/AIDS - deaths:2,000 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 50Major infectious diseases:note: active local transmission of Zika virus by Aedes species mosquitoes has been identified in this country (as of August 2016); it poses an important risk (a large number of cases possible) among US citizens if bitten by an infective mosquito; other less common ways to get Zika are through sex, via blood transfusion, or during pregnancy, in which the pregnant woman passes Zika virus to her fetus
Obesity - adult prevalence rate:28.3% (2016)country comparison to the world: 30Education expenditures:5.9% of GDP (2015)country comparison to the world: 37Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and write (2015 est.)total population: 98.1% (2015 est.)male: 98% (2015 est.)female: 98.1% (2015 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 17 years (2014)male: 16 years (2014)female: 18 years (2014)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 18.3% (2014 est.)male: 15.6% (2014 est.)female: 22.8% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 71 -
Government :: Argentina
-
Country name:conventional long form: Argentine Republicconventional short form: Argentinalocal long form: Republica Argentinalocal short form: Argentinaetymology: originally the area was referred to as Tierra Argentina, i.e., "Land beside the Silvery River" or "silvery land," which referred to the massive estuary in the east of the country, the Rio de la Plata (River of Silver); over time the name shortened to simply Argentina or "silvery"Government type:presidential republicCapital:name: Buenos Airesgeographic coordinates: 34 36 S, 58 22 Wtime difference: UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)etymology: the name translates as "fair winds" in Spanish and derives from the original designation of the settlement that would become the present-day city, "Santa Maria del Buen Aire" (Saint Mary of the Fair Winds)Administrative divisions:23 provinces (provincias, singular - provincia) and 1 autonomous city*; Buenos Aires, Catamarca, Chaco, Chubut, Ciudad Autonoma de Buenos Aires*, Cordoba, Corrientes, Entre Rios, Formosa, Jujuy, La Pampa, La Rioja, Mendoza, Misiones, Neuquen, Rio Negro, Salta, San Juan, San Luis, Santa Cruz, Santa Fe, Santiago del Estero, Tierra del Fuego - Antartida e Islas del Atlantico Sur (Tierra del Fuego - Antarctica and the South Atlantic Islands), Tucuman
note: the US does not recognize any claims to Antarctica
Independence:9 July 1816 (from Spain)National holiday:Revolution Day (May Revolution Day), 25 May (1810)Constitution:history: several previous; latest effective 11 May 1853 (2018)amendments: a declaration of proposed amendments requires two-thirds majority vote by both houses of the National Congress followed by approval by an ad hoc, multi-member constitutional convention; amended many times, last significantly in 1994 (2018)Legal system:civil law system based on West European legal systems; note - in mid-2015, Argentina adopted a new civil code, replacing the old one in force since 1871International law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictionCitizenship:citizenship by birth: yescitizenship by descent only: yesdual citizenship recognized: yesresidency requirement for naturalization: 2 yearsSuffrage:18-70 years of age; universal and compulsory; 16-17 years of age - optional for national electionsJudicial branch:highest courts: Supreme Court or Corte Suprema (consists of the court president, vice-president, and 5 judges)judge selection and term of office: judges nominated by the president and approved by the Senate; judges can serve until mandatory retirement at age 75subordinate courts: federal level appellate, district, and territorial courts; provincial level supreme, appellate, and first instance courtsExecutive branch:chief of state: President Mauricio MACRI (since 10 December 2015); Vice President Gabriela MICHETTI (since 10 December 2015); note - the president is both chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President Mauricio MACRI (since 10 December 2015); Vice President Gabriela MICHETTI (since 10 December 2015)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the presidentelections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot by qualified majority popular vote for a 4-year term (eligible for a second consecutive term); election last held in 2 rounds on 25 October and 22 November 2015 (next to be held on 27 October 2019)election results: Mauricio MACRI elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Daniel SCIOLI (PJ) 37.1%, Mauricio MACRI (PRO) 34.2%, Sergio MASSA (FR/PJ) 21.4%, other 7.3%; percent of vote in second round - Mauricio MACRI (PRO) 51.4%, Daniel SCIOLI (PJ) 48.6%Legislative branch:description: bicameral National Congress or Congreso Nacional consists of:
Senate (72 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 6-year terms with one-third of the membership elected every 2 years)
Chamber of Deputies (257 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms with one-half of the membership renewed every 2 years)elections:
Senate - last held on 22 October 2017 (next to be held in October 2019)
Chamber of Deputies - last held on 22 October 2017 (next to be held in October 2019)election results: Senate - percent of vote by bloc or party - NA; seats by bloc or party - Cambiemos 12, UC 6, PJ 4, FRC 2; composition - men 42, women 30, percent of women 41.7%
Chamber of Deputies - percent of vote by bloc or party - NA; seats by bloc or party - Cambiemos 61, UC 28, PJ 18, FR 7, FCS 3, FRC 2, other 8; composition - men 159, women 98, percent of women 38.1%; note - total National Congress percent of women 38.9%Political parties and leaders:Cambiemos [Mauricio MACRI] (coalition of CC-ARI, PRO, and UCR)
Citizen's Unity or UC [Cristina FERNANDEZ DE KIRCHNER]
Civic Coalition ARI or CC-ARI [ Elisa CARRIO]
Civic Front for Santiago or FCS [Gerardo ZAMORA]
Front for the Renewal of Concord or FRC
Front for Victory or FpV [Cristina FERNANDEZ DE KIRCHNER] (left-wing faction of PJ)
Generation for a National Encounter or GEN [Margarita STOLBIZER]
Justicialist Party or PJ [Jose Luis GIOJA]
Radical Civic Union or UCR [Alfredo CORNEJO]
Renewal Front (Frente Renovador) or FR [Sergio MASSA]
Republican Proposal or PRO [Mauricio MACRI]
Socialist Party or PS [Antonio BONFATTI]
United for a New Alternative or UNA (includes FR)
numerous provincial partiesInternational organization participation:AfDB (nonregional member), Australia Group, BCIE, BIS, CAN (associate), CD, CELAC, FAO, FATF, G-15, G-20, G-24, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA, Mercosur, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, NAM (observer), NSG, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, Paris Club (associate), PCA, SICA (observer), UN, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina (observer), UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZCDiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Fernando ORIS DE ROA (since 24 January 2018)chancery: 1600 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20009telephone: [1] (202) 238-6400FAX: [1] (202) 332-3171consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, Washington, DCDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Edward Charles PRADO (since 16 May 2018)embassy: Avenida Colombia 4300, C1425GMN Buenos Airesmailing address: international mail: use embassy street address; APO address: US Embassy Buenos Aires, Unit 4334, APO AA 34034telephone: [54] (11) 5777-4533FAX: [54] (11) 5777-4240Flag description:three equal horizontal bands of sky blue (top), white, and sky blue; centered in the white band is a radiant yellow sun with a human face (delineated in brown) known as the Sun of May; the colors represent the clear skies and snow of the Andes; the sun symbol commemorates the appearance of the sun through cloudy skies on 25 May 1810 during the first mass demonstration in favor of independence; the sun features are those of Inti, the Inca god of the sunNational symbol(s):Sun of May (a sun-with-face symbol); national colors: sky blue, whiteNational anthem:name: "Himno Nacional Argentino" (Argentine National Anthem)lyrics/music: Vicente LOPEZ y PLANES/Jose Blas PARERAnote: adopted 1813; Vicente LOPEZ was inspired to write the anthem after watching a play about the 1810 May Revolution against Spain
-
Economy :: Argentina
-
Economy - overview:
Argentina benefits from rich natural resources, a highly literate population, an export-oriented agricultural sector, and a diversified industrial base. Although one of the world's wealthiest countries 100 years ago, Argentina suffered during most of the 20th century from recurring economic crises, persistent fiscal and current account deficits, high inflation, mounting external debt, and capital flight.
Cristina FERNANDEZ DE KIRCHNER succeeded her husband as president in late 2007, and in 2008 the rapid economic growth of previous years slowed sharply as government policies held back exports and the world economy fell into recession. In 2010 the economy rebounded strongly, but slowed in late 2011 even as the government continued to rely on expansionary fiscal and monetary policies, which kept inflation in the double digits.
In order to deal with these problems, the government expanded state intervention in the economy: it nationalized the oil company YPF from Spain's Repsol, expanded measures to restrict imports, and further tightened currency controls in an effort to bolster foreign reserves and stem capital flight. Between 2011 and 2013, Central Bank foreign reserves dropped $21.3 billion from a high of $52.7 billion. In July 2014, Argentina and China agreed on an $11 billion currency swap; the Argentine Central Bank has received the equivalent of $3.2 billion in Chinese yuan, which it counts as international reserves.
With the election of President Mauricio MACRI in November 2015, Argentina began a historic political and economic transformation, as his administration took steps to liberalize the Argentine economy, lifting capital controls, floating the peso, removing export controls on some commodities, cutting some energy subsidies, and reforming the country’s official statistics. Argentina negotiated debt payments with holdout bond creditors, continued working with the IMF to shore up its finances, and returned to international capital markets in April 2016.
In 2017, Argentina’s economy emerged from recession with GDP growth of nearly 3.0%. The government passed important pension, tax, and fiscal reforms. And after years of international isolation, Argentina took on several international leadership roles, including hosting the World Economic Forum on Latin America and the World Trade Organization Ministerial Conference, and is set to assume the presidency of the G-20 in 2018.
GDP (purchasing power parity):$922.1 billion (2017 est.)$896.5 billion (2016 est.)$913.2 billion (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 28GDP (official exchange rate):$637.6 billion (2017 est.) (2017 est.)GDP - real growth rate:2.9% (2017 est.)-1.8% (2016 est.)2.7% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 117GDP - per capita (PPP):$20,900 (2017 est.)$20,600 (2016 est.)$21,200 (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 88Gross national saving:17.6% of GDP (2017 est.)16.8% of GDP (2016 est.)15.8% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 114GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 65.9% (2017 est.)government consumption: 18.2% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 14.8% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: 3.7% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 11.2% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -13.8% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 10.8% (2017 est.)industry: 28.1% (2017 est.)services: 61.1% (2017 est.)Agriculture - products:sunflower seeds, lemons, soybeans, grapes, corn, tobacco, peanuts, tea, wheat; livestockIndustries:food processing, motor vehicles, consumer durables, textiles, chemicals and petrochemicals, printing, metallurgy, steelIndustrial production growth rate:2.7% (2017 est.)note: based on private sector estimates
country comparison to the world: 111Labor force:18 million (2017 est.)note: urban areas only
country comparison to the world: 33Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 5.3%industry: 28.6%services: 66.1% (2017 est.)Unemployment rate:8.4% (2017 est.)8.5% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Population below poverty line:25.7% (2017 est.)note: data are based on private estimates
Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 31% (2017 est.)highest 10%: 31% (2017 est.)Distribution of family income - Gini index:41.7 (2017 est.)45.8 (2009)country comparison to the world: 54Budget:revenues: 120.6 billion (2017 est.)expenditures: 158.6 billion (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues:18.9% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 157Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-6% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 182Public debt:57.6% of GDP (2017 est.)55% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 77Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):25.7% (2017 est.)26.5% (2016 est.)note: data are derived from private estimates
country comparison to the world: 219Central bank discount rate:NA
Commercial bank prime lending rate:26.58% (31 December 2017 est.)31.23% (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 9Stock of narrow money:$62.61 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$59 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 48Stock of broad money:$62.61 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$59 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 48Stock of domestic credit:$219.4 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$194 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 44Market value of publicly traded shares:$56.13 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$60.14 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$53.1 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 50Current account balance:-$31.32 billion (2017 est.)-$14.69 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 200Exports:$58.45 billion (2017 est.)$57.78 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Exports - partners:Brazil 16.1%, US 7.9%, China 7.5%, Chile 4.4% (2017)Exports - commodities:soybeans and derivatives, petroleum and gas, vehicles, corn, wheatImports:$63.97 billion (2017 est.)$53.5 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 48Imports - commodities:machinery, motor vehicles, petroleum and natural gas, organic chemicals, plasticsImports - partners:Brazil 26.9%, China 18.5%, US 11.3%, Germany 4.9% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$55.33 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$38.43 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 38Debt - external:$214.9 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$190.2 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 34Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$76.58 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$72.11 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 52Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$40.94 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$39.74 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 46Exchange rates:Argentine pesos (ARS) per US dollar -16.92 (2017 est.)14.76 (2016 est.)14.76 (2015 est.)9.23 (2014 est.)8.08 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Argentina
-
Electricity access:population without electricity: 1.5 million (2013)electrification - total population: 96.4% (2013)electrification - urban areas: 99.2% (2013)electrification - rural areas: 96% (2013)Electricity - production:131.9 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Electricity - consumption:121 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Electricity - exports:55 million kWh (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 85Electricity - imports:9.851 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 26Electricity - installed generating capacity:38.35 million kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 27Electricity - from fossil fuels:69% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 112Electricity - from nuclear fuels:4% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 23Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:24% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 79Electricity - from other renewable sources:3% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Crude oil - production:479,400 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 29Crude oil - exports:36,630 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 43Crude oil - imports:16,740 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Crude oil - proved reserves:2.162 billion bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 32Refined petroleum products - production:669,800 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 26Refined petroleum products - consumption:806,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 27Refined petroleum products - exports:58,360 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 51Refined petroleum products - imports:121,400 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Natural gas - production:40.92 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 20Natural gas - consumption:49.04 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 17Natural gas - exports:76.45 million cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Natural gas - imports:9.826 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 27Natural gas - proved reserves:336.6 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 35Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:203.7 million Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 32
-
Communications :: Argentina
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 9,530,349 (2017 est.)subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 22 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 19Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 61,897,379 (2017 est.)subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 140 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 26Telephone system:general assessment: Argentina opened its telecommunications market to competition and foreign investment encouraging the growth of modern telecommunications technology in 1998; major networks are entirely digital and the availability of telephone service continues to improve to rural areas; even with numerous providers there is a lack of competition; still Argentina is the 3rd largest in the region after Brazil and Mexico (2017)domestic: microwave radio relay, fiber-optic cable, and a domestic satellite system with 40 earth stations serve the trunk network; 22 per 100 fixed-line, 144 per 100 mobile-cellular (2017)international: country code - 54; landing point for the Atlantis-2, UNISUR, South America-1, and South American Crossing/Latin American Nautilus submarine cable systems that provide links to Europe, Africa, South and Central America, and US; satellite earth stations - 112; 2 international gateways near Buenos Aires; building started on the ARBR submarine cable between Argentina and Brazil (2017)Broadcast media:government owns a TV station and radio network; more than 2 dozen TV stations and hundreds of privately owned radio stations; high rate of cable TV subscription usage (2009)Internet country code:.arInternet users:total: 30,786,889 (July 2016 est.)percent of population: 70.2% (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 24Broadband - fixed subscriptions:total: 7,870,222 (2017 est.)subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 18 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 20
-
Transportation :: Argentina
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 6 (2015)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 107 (2015)annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 14,245,183 (2015)annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 243,772,567 mt-km (2015)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:LV (2016)Airports:1,138 (2013)country comparison to the world: 6Airports - with paved runways:total: 161 (2017)over 3,047 m: 4 (2017)2,438 to 3,047 m: 29 (2017)1,524 to 2,437 m: 65 (2017)914 to 1,523 m: 53 (2017)under 914 m: 10 (2017)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 977 (2013)over 3,047 m: 1 (2013)2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 (2013)1,524 to 2,437 m: 43 (2013)914 to 1,523 m: 484 (2013)under 914 m: 448 (2013)Heliports:2 (2013)Pipelines:29930 km gas, 41 km liquid petroleum gas, 6248 km oil, 3631 km refined products (2013)Railways:total: 36,917 km (2014)standard gauge: 2,745.1 km 1.435-m gauge (41.1 km electrified) (2014)narrow gauge: 7,523.3 km 1.000-m gauge (2014)broad gauge: 26,391 km 1.676-m gauge (149 km electrified) (2014)258 0.750-m gaugecountry comparison to the world: 6Roadways:total: 231,374 km (2004)paved: 69,412 km (includes 734 km of expressways) (2004)unpaved: 161,962 km (2004)country comparison to the world: 22Waterways:11,000 km (2012)country comparison to the world: 11Merchant marine:total: 161 (2017)by type: container ship 1, general cargo 9, oil tanker 27, other 124 (2017)country comparison to the world: 69Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Bahia Blanca, Buenos Aires, La Plata, Punta Colorada, Ushuaiacontainer port(s) (TEUs): Buenos Aires (1,851,701)LNG terminal(s) (import): Bahia Blancariver port(s): Arroyo Seco, Rosario, San Lorenzo-San Martin (Parana)
-
Military and Security :: Argentina
-
Military expenditures:0.95% of GDP (2016)0.86% of GDP (2015)0.88% of GDP (2014)0.84% of GDP (2013)0.78% of GDP (2012)country comparison to the world: 118Military branches:Argentine Army (Ejercito Argentino), Navy of the Argentine Republic (Armada Republica; includes naval aviation and naval infantry), Argentine Air Force (Fuerza Aerea Argentina, FAA) (2013)Military service age and obligation:18-24 years of age for voluntary military service (18-21 requires parental consent); no conscription; if the number of volunteers fails to meet the quota of recruits for a particular year, Congress can authorize the conscription of citizens turning 18 that year for a period not exceeding one year (2012)Military - note:the Argentine military is a well-organized force constrained by the country's prolonged economic hardship; the military is implementing a modernization plan aimed at making the ground forces lighter and more responsive (2008)
-
Terrorism :: Argentina
-
Terrorist groups - foreign based:Hizballah:
aim(s): largely limited to generating political and financial support from the Lebanese diaspora
area(s) of operation: conducted operations in the 1990s; maintains a limited presence (April 2018) -
Transnational Issues :: Argentina
-
Disputes - international:Argentina continues to assert its claims to the UK-administered Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas), South Georgia, and the South Sandwich Islands in its constitution, forcibly occupying the Falklands in 1982, but in 1995 agreed to no longer seek settlement by forceUK continues to reject Argentine requests for sovereignty talksterritorial claim in Antarctica partially overlaps UK and Chilean claimsuncontested dispute between Brazil and Uruguay over Braziliera/Brasiliera Island in the Quarai/Cuareim River leaves the tripoint with Argentina in questionin 2010, the ICJ ruled in favor of Uruguay's operation of two paper mills on the Uruguay River, which forms the border with Argentinathe two countries formed a joint pollution monitoring regimethe joint boundary commission, established by Chile and Argentina in 2001 has yet to map and demarcate the delimited boundary in the inhospitable Andean Southern Ice Field (Campo de Hielo Sur)contraband smuggling, human trafficking, and illegal narcotic trafficking are problems in the porous areas of the border with BoliviaRefugees and internally displaced persons:refugees (country of origin): 94,632 (Venezuela) (economic and political crisis; includes Venezuelans who have claimed asylum or have received alternative legal stay) (2018)Illicit drugs:a transshipment country for cocaine headed for Europe, heroin headed for the US, and ephedrine and pseudoephedrine headed for Mexico; some money-laundering activity, especially in the Tri-Border Area; law enforcement corruption; a source for precursor chemicals; increasing domestic consumption of drugs in urban centers, especially cocaine base and synthetic drugs