-
Introduction :: Maldives
-
Background:
A sultanate since the 12th century, the Maldives became a British protectorate in 1887. The islands became a republic in 1968, three years after independence. President Maumoon Abdul GAYOOM dominated Maldives' political scene for 30 years, elected to six successive terms by single-party referendums. Following political demonstrations in the capital Male in August 2003, GAYOOM and his government pledged to embark upon a process of liberalization and democratic reforms, including a more representative political system and expanded political freedoms. Political parties were legalized in 2005.
In June 2008, a constituent assembly - termed the "Special Majlis" - finalized a new constitution ratified by GAYOOM in August 2008. The first-ever presidential elections under a multi-candidate, multi-party system were held in October 2008. GAYOOM was defeated in a runoff poll by Mohamed NASHEED, a political activist who had been jailed several years earlier by the GAYOOM regime. In early February 2012, after several weeks of street protests in response to his ordering the arrest of a top judge, NASHEED purportedly resigned the presidency and handed over power to Vice President Mohammed WAHEED Hassan Maniku. A government-appointed Commission of National Inquiry concluded there was no evidence of a coup, but recommended strengthening the country's democratic institutions to avert similar events in the future. NASHEED contends that police and military personnel forced him to resign. NASHEED, WAHEED, and Abdulla YAMEEN Abdul Gayoom ran in the 2013 elections with YAMEEN ultimately winning the presidency after three rounds of voting. As president, YAMEEN has sought to weaken democratic institutions, curtail civil liberties, jail his political opponents, restrict the press, and exert control over the judiciary to strengthen his hold on power and limit dissent. In February 2018, he declared successive states of emergency in response to a supreme court order to release political prisoners and allow members of parliament who switch parties to retain their seats. Maldivian officials have played a prominent role in international climate change discussions (due to the islands' vulnerability to rising sea-level), though in practice, the YAMEEN government has destroyed mangroves, coral beds, and other natural habitats to make way for development projects.
-
Geography :: Maldives
-
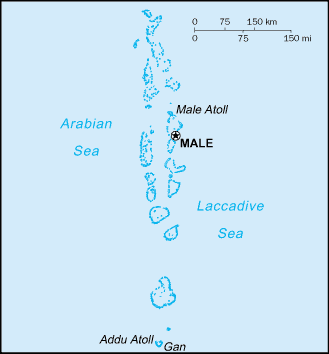
Location:Southern Asia, group of atolls in the Indian Ocean, south-southwest of IndiaGeographic coordinates:3 15 N, 73 00 EMap references:AsiaArea:total: 298 sq kmland: 298 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 210Area - comparative:about 1.7 times the size of Washington, DCLand boundaries:0 kmCoastline:644 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmmeasured from claimed archipelagic straight baselinesClimate:tropical; hot, humid; dry, northeast monsoon (November to March); rainy, southwest monsoon (June to August)Terrain:flat, with white sandy beachesElevation:mean elevation: 1.8 melevation extremes: 0 m lowest point: Indian Ocean5 highest point: 8th tee, golf course, Villingi IslandNatural resources:fishLand use:agricultural land: 23.3% (2011 est.)arable land: 10% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 10% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 3.3% (2011 est.)forest: 3% (2011 est.)other: 73.7% (2011 est.)Irrigated land:0 sq km (2012)Population distribution:about a third of the population lives in the centrally located capital city of Male and almost a tenth in southern Addu City; the remainder of the populace is spread over the 200 or so populated islands of the archipelagoNatural hazards:tsunamis; low elevation of islands makes them sensitive to sea level riseEnvironment - current issues:depletion of freshwater aquifers threatens water supplies; inadequate sewage treatment; coral reef bleachingEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollutionsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:smallest Asian country; archipelago of 1,190 coral islands grouped into 26 atolls (200 inhabited islands, plus 80 islands with tourist resorts); strategic location astride and along major sea lanes in Indian Ocean
-
People and Society :: Maldives
-
Population:392,473 (July 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 176Nationality:noun: Maldivian(s)adjective: MaldivianEthnic groups:South Indians, Sinhalese, ArabsLanguages:Dhivehi (official, dialect of Sinhala, script derived from Arabic), English (spoken by most government officials)Religions:Sunni Muslim (official)Age structure:0-14 years: 21.62% (male 43,293 /female 41,563)15-24 years: 19.15% (male 42,849 /female 32,326)25-54 years: 48.47% (male 106,083 /female 84,160)55-64 years: 6.22% (male 11,888 /female 12,540)65 years and over: 4.53% (male 8,101 /female 9,670) (2018 est.)population pyramid:
 The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth Asia :: Maldives Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalSouth Asia :: Maldives Print Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Maldives. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Maldives. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 38 (2015 est.)youth dependency ratio: 32.3 (2015 est.)elderly dependency ratio: 5.7 (2015 est.)potential support ratio: 17.7 (2015 est.)Median age:total: 28.6 yearsmale: 28.4 yearsfemale: 28.8 years (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 134Population growth rate:-0.06% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 202Birth rate:16.1 births/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 112Death rate:4 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 209Net migration rate:-12.7 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 213Population distribution:about a third of the population lives in the centrally located capital city of Male and almost a tenth in southern Addu City; the remainder of the populace is spread over the 200 or so populated islands of the archipelagoUrbanization:urban population: 39.8% of total population (2018)rate of urbanization: 2.93% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:177,000 MALE (capital) (2018)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female (2017 est.)0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female (2017 est.)15-24 years: 1.37 male(s)/female (2017 est.)25-54 years: 1.34 male(s)/female (2017 est.)55-64 years: 1 male(s)/female (2017 est.)65 years and over: 0.89 male(s)/female (2017 est.)total population: 1.23 male(s)/female (2017 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:23.9 years (2009 est.)note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
Maternal mortality rate:68 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Infant mortality rate:total: 21.3 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)male: 23.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)female: 18.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 76Life expectancy at birth:total population: 76 years (2018 est.)male: 73.7 years (2018 est.)female: 78.5 years (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 94Total fertility rate:1.72 children born/woman (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 168Contraceptive prevalence rate:34.7% (2009)Health expenditures:13.7% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 4Physicians density:3.61 physicians/1,000 population (2015)Hospital bed density:4.3 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved: urban: 99.5% of populationrural: 97.9% of populationtotal: 98.6% of populationunimproved: urban: 0.5% of populationrural: 2.1% of populationtotal: 1.4% of population (2015 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved: urban: 97.5% of population (2015 est.)rural: 98.3% of population (2015 est.)total: 97.9% of population (2015 est.)unimproved: urban: 2.5% of population (2015 est.)rural: 1.7% of population (2015 est.)total: 2.1% of population (2015 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:NAHIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:NAHIV/AIDS - deaths:NAObesity - adult prevalence rate:8.6% (2016)country comparison to the world: 148Children under the age of 5 years underweight:17.8% (2009)country comparison to the world: 33Education expenditures:4.3% of GDP (2016)country comparison to the world: 103Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and write (2015 est.)total population: 99.3% (2015 est.)male: 99.8% (2015 est.)female: 98.8% (2015 est.)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 12.4% (2014 est.)male: 12.5% (2014 est.)female: 12.3% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 106 -
Government :: Maldives
-
Country name:conventional long form: Republic of Maldivesconventional short form: Maldiveslocal long form: Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaalocal short form: Dhivehi Raajjeetymology: archipelago apparently named after the main island (and capital) of Male; the word "Maldives" means "the islands (dives) of Male"; alternatively, the name may derive from the Sanskrit word "maladvipa" meaning "garland of islands"; Dhivehi Raajje in Dhivehi means "Kingdom of the Dhivehi people"Government type:presidential republicCapital:name: Malegeographic coordinates: 4 10 N, 73 30 Etime difference: UTC+5 (10 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:21 administrative atolls (atholhuthah, singular - atholhu); Addu (Addu City), Ariatholhu Dhekunuburi (South Ari Atoll), Ariatholhu Uthuruburi (North Ari Atoll), Faadhippolhu, Felidhuatholhu (Felidhu Atoll), Fuvammulah, Hahdhunmathi, Huvadhuatholhu Dhekunuburi (South Huvadhu Atoll), Huvadhuatholhu Uthuruburi (North Huvadhu Atoll), Kolhumadulu, Maale (Male), Maaleatholhu (Male Atoll), Maalhosmadulu Dhekunuburi (South Maalhosmadulu), Maalhosmadulu Uthuruburi (North Maalhosmadulu), Miladhunmadulu Dhekunuburi (South Miladhunmadulu), Miladhunmadulu Uthuruburi (North Miladhunmadulu), Mulakatholhu (Mulaku Atoll), Nilandheatholhu Dhekunuburi (South Nilandhe Atoll), Nilandheatholhu Uthuruburi (North Nilandhe Atoll), Thiladhunmathee Dhekunuburi (South Thiladhunmathi), Thiladhunmathee Uthuruburi (North Thiladhunmathi)Independence:26 July 1965 (from the UK)National holiday:Independence Day, 26 July (1965)Constitution:history: many previous; latest ratified 7 August 2008 (2018)amendments: proposed by Parliament; passage requires at least three-quarters majority vote by its membership and the signature of the president of the republic; passage of amendments to constitutional articles on rights and freedoms and the terms of office of Parliament and of the president also requires a majority vote in a referendum; amended 2015 (2018)Legal system:Islamic religious legal system with English common law influences, primarily in commercial mattersInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictionCitizenship:citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Maldivesdual citizenship recognized: yesresidency requirement for naturalization: unknownSuffrage:18 years of age; universalJudicial branch:highest courts: Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice and 4 judges); note - only 4 justices as of February 2018; the chief justice and one justice were arrested and imprisoned in early February 2018 following President YAMEEN’s declaration of a state of emergencyjudge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the president in consultation with the Judicial Service Commission - a 10-member body of selected high government officials and the public - and upon confirmation by voting members of the People's Majlis; judges serve until mandatory retirement at age 70subordinate courts: High Court; Criminal, Civil, Family, Juvenile, and Drug Courts; Magistrate Courts (on each of the inhabited islands)Executive branch:chief of state: President Ibrahim "Ibu" Mohamed SOLIH (since 17 November 2018); Vice President Faisal NASEEM (since 17 November 2018); the president is both chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President Ibrahim Mohamed SOLIH (since 19 November 2018); Vice President Faisal NASEEM (since 17 November 2018)cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers appointed by the president, approved by Parliamentelections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 23 September 2018 (next to be held in 2023)election results: Ibrahim Mohamed SOLIH elected president (in 1 round); Ibrahim Mohamed SOLIH (MDP) 58.3%, Abdulla YAMEEN Abdul Gayoom (PPM) 41.7%Legislative branch:description: unicameral Parliament or People's Majlis (85 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 5-year terms)elections: last held on 22 March 2014 (next to be held in 2019)election results: percent of vote - MDP 40.8%, PPM 27.7%, JP 13.6%, MDA 4%, AP 2.7% other 0.3%, independent 10.9%; seats by party - PPM 33, MDP 26, JP 15, MDA 5, AP 1, independent 5; composition - men 80, women 5, percent of women 5.9%Political parties and leaders:Adhaalath (Justice) Party or AP [Sheikh Imran ABDULLA]
Maldives Development Alliance or MDA [Ahmed Shiyam MOHAMED]
Maldivian Democratic Party or MDP [Hassan LATHEEF, chairperson]
Progressive Party of Maldives or PPM [Abdulla YAMEEN]
Progressive Party of Maldives or PPM - Gayoom faction [Maumoon Abdul GAYOOM]
Republican (Jumhooree) Party or JP [Qasim IBRAHIM]International organization participation:ADB, AOSIS, C, CP, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, SAARC, SACEP, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Ali NASEER Mohamed (since 21 July 2017)chancery: 801 Second Avenue, Suite 400E, New York, NY 10017telephone: [1] (212) 599-6194 and 599-6195FAX: [1] (212) 661-6405Diplomatic representation from the US:the US does not have an embassy in Maldives; US Ambassador to Sri Lanka, Atul KESHAP (since 21 August 2015), is accredited to MaldivesFlag description:red with a large green rectangle in the center bearing a vertical white crescent moon; the closed side of the crescent is on the hoist side of the flag; red recalls those who have sacrificed their lives in defense of their country, the green rectangle represents peace and prosperity, and the white crescent signifies IslamNational symbol(s):coconut palm, yellowfin tuna; national colors: red, green, whiteNational anthem:name: "Gaumee Salaam" (National Salute)lyrics/music: Mohamed Jameel DIDI/Wannakuwattawaduge DON AMARADEVAnote: lyrics adopted 1948, music adopted 1972; between 1948 and 1972, the lyrics were sung to the tune of "Auld Lang Syne"
-
Economy :: Maldives
-
Economy - overview:
Maldives has quickly become a middle-income country, driven by the rapid growth of its tourism and fisheries sectors, but the country still contends with a large and growing fiscal deficit. Infrastructure projects, largely funded by China, could add significantly to debt levels. Political turmoil and the declaration of a state of emergency in February 2018 led to the issuance of travel warnings by several countries whose citizens visit Maldives in significant numbers, but the overall impact on tourism revenue was unclear.
In 2015, Maldives’ Parliament passed a constitutional amendment legalizing foreign ownership of land; foreign land-buyers must reclaim at least 70% of the desired land from the ocean and invest at least $1 billion in a construction project approved by Parliament.
Diversifying the economy beyond tourism and fishing, reforming public finance, increasing employment opportunities, and combating corruption, cronyism, and a growing drug problem are near-term challenges facing the government. Over the longer term, Maldivian authorities worry about the impact of erosion and possible global warming on their low-lying country; 80% of the area is 1 meter or less above sea level.
GDP (purchasing power parity):$6.901 billion (2017 est.)$6.583 billion (2016 est.)$6.3 billion (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 168GDP (official exchange rate):$4.505 billion (2017 est.) (2017 est.)GDP - real growth rate:4.8% (2017 est.)4.5% (2016 est.)2.2% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 57GDP - per capita (PPP):$19,200 (2017 est.)$18,600 (2016 est.)$18,100 (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 93Gross national saving:0.5% of GDP (2017 est.)-4.5% of GDP (2016 est.)12.6% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 180GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: NA (2016 est.)government consumption: NA (2016 est.)investment in fixed capital: NA (2016 est.)investment in inventories: NA (2016 est.)exports of goods and services: 93.6% (2016 est.)imports of goods and services: 89% (2016 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 3% (2015 est.)industry: 16% (2015 est.)services: 81% (2015 est.)Agriculture - products:coconuts, corn, sweet potatoes; fishIndustries:tourism, fish processing, shipping, boat building, coconut processing, woven mats, rope, handicrafts, coral and sand miningIndustrial production growth rate:14% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Labor force:222,200 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 168Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 7.7%industry: 22.8%services: 69.5% (2017 est.)Unemployment rate:2.9% (2017 est.)3.2% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 35Population below poverty line:15% (2009 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 33.3% (FY09/10)highest 10%: 33.3% (FY09/10)Distribution of family income - Gini index:38.4 (2009 est.)37.4 (2004 est.)country comparison to the world: 77Budget:revenues: 1.19 billion (2016 est.)expenditures: 1.643 billion (2016 est.)Taxes and other revenues:26.4% (of GDP) (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 111Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-10.1% (of GDP) (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 212Public debt:63.9% of GDP (2017 est.)61.7% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):2.3% (2017 est.)0.8% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 116Central bank discount rate:7% (30 September 2017)7% (30 September 2016)country comparison to the world: 50Commercial bank prime lending rate:10.5% (31 December 2012 est.)10.2% (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 82Stock of narrow money:$908.6 million (31 October 2017 est.)$865.9 million (31 October 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 160Stock of broad money:$1.982 billion (31 October 2017)$2.043 billion (31 October 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 143Stock of domestic credit:$1.559 billion (31 December 2012 est.)$1.601 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 160Market value of publicly traded shares:$555 million (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 112Current account balance:-$876 million (2017 est.)-$1.033 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 137Exports:$256.2 million (2016 est.)$239.8 million (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 188Exports - partners:Thailand 42.8%, Sri Lanka 8.7%, Bangladesh 6.4%, France 6.2%, US 6.1%, Germany 5%, Ireland 4.6% (2017)Exports - commodities:fishImports:$2.125 billion (2016 est.)$1.896 billion (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 164Imports - commodities:petroleum products, clothing, intermediate and capital goodsImports - partners:UAE 17.1%, India 13.5%, Singapore 13.3%, China 10.8%, Sri Lanka 6.7%, Malaysia 6%, Thailand 4.5% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$477.9 million (31 December 2016 est.)$575.8 million (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 153Debt - external:$848.8 million (31 December 2016 est.)$696.2 million (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 168Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$324 million (31 December 2015)$256 million (31 December 2013)country comparison to the world: 133Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$448 million (31 December 2016 est.)$307.7 million (31 December 2015)country comparison to the world: 98Exchange rates:rufiyaa (MVR) per US dollar -15.42 (2017 est.)15.35 (2016 est.) -
Energy :: Maldives
-
Electricity access:electrification - total population: 100% (2016)Electricity - production:402 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 171Electricity - consumption:373.9 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 178Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 165Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 171Electricity - installed generating capacity:278,000 kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 161Electricity - from fossil fuels:96% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 40Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 137Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 185Electricity - from other renewable sources:4% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 114Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 168Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 160Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 160Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 164Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 172Refined petroleum products - consumption:11,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 160Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 177Refined petroleum products - imports:10,840 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 144Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 165Natural gas - consumption:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 171Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 146Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 153Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 166Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:1.648 million Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 161
-
Communications :: Maldives
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 20,377 (2017 est.)subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 5 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 176Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 900,120 (2017 est.)subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 229 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 161Telephone system:general assessment: telephone services have improved; inter-atoll communication through microwave links; all inhabited islands and resorts are connected with telephone and fax service (2016)domestic: each island now has at least 1 public telephone, and there are mobile-cellular networks with a rapidly expanding subscribership that has reached over 200 per 100 persons (2016)international: country code - 960; linked to international submarine cable Fiber-Optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG); satellite earth station - 3 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) (2016)Broadcast media:state-owned radio and TV monopoly until recently; 1 state-operated and 7 privately owned TV stations and 4 state-operated and 7 privately owned radio stations (2018)Internet country code:.mvInternet users:total: 232,210 (July 2016 est.)percent of population: 59.1% (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 167Broadband - fixed subscriptions:total: 36,001 (2017 est.)subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 9 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 135
-
Transportation :: Maldives
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 3 (2015)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 15 (2015)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:8Q (2016)Airports:9 (2013)country comparison to the world: 158Airports - with paved runways:total: 7 (2017)over 3,047 m: 1 (2017)2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 (2017)1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2017)914 to 1,523 m: 4 (2017)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 2 (2013)914 to 1,523 m: 2 (2013)Roadways:total: 93 km (2018)paved: 93 km - 60 km in Male; 16 km on Addu Atolis; 17 km on Laamu (2018)
note: island roads are mainly compacted coral
country comparison to the world: 216Merchant marine:total: 66 (2017)by type: bulk carrier 1, container ship 1, general cargo 27, oil tanker 14, other 23 (2017)country comparison to the world: 104Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Male -
Military and Security :: Maldives
-
Military branches:Maldives National Defense Force (MNDF): Marine Corps, Special Protection Group, Coast Guard (2018)Military service age and obligation:18-28 years of age for voluntary service; no conscription; 10th grade or equivalent education required; must not be a member of a political party (2012)Military - note:Maldives National Defense Force (MNDF), with its small size and with little serviceable equipment, is inadequate to prevent external aggression and is primarily tasked to reinforce Maldives Police Service (MPS) and ensure security in the exclusive economic zone (2008)
-
Transnational Issues :: Maldives
-
Disputes - international:noneTrafficking in persons:current situation: Maldives is a destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking and a source country for women and children subjected to labor and sex trafficking; primarily Bangladeshi and Indian migrants working both legally and illegally in the construction and service sectors face conditions of forced labor, including fraudulent recruitment, confiscation of identity and travel documents, nonpayment and withholding of wages, and debt bondage; a small number of women from Asia, Eastern Europe, and former Soviet states are trafficked to Maldives for sexual exploitation; Maldivian women may be subjected to sex trafficking domestically or in Sri Lanka; some Maldivian children are transported to the capital for domestic service, where they may also be victims of sexual abuse and forced labortier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – Maldives does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; the government adopted a national action plan for 2015-19 and is continuing to develop victim identification, protection, and referral procedures, but overall its anti-trafficking efforts did not increase; only five trafficking investigations were conducted, no new prosecutions were initiated for the second consecutive year, and no convictions were made, down from one in 2013; some officials warned businesses in advance of planned raids for suspected trafficking offenses; victim protection deteriorated when the state-run shelter for female victims barred access to victims shortly after opening in January 2014, in part because of bureaucratic disputes, which dissuaded victims from pursuing charges against perpetrators; the government did not prosecute or hold accountable any employers or government officials for withholding passports (2015)