Main Content
Europe
::
Jan Mayen
Print
Page last updated on December 18, 2019
The World Factbook
Country/Location Flag Modal
Europe ::
Jan Mayen
Print
Flag Description
the flag of Norway is used
The World Factbook
Country/Location Locator Map Modal
Europe ::
Jan Mayen
Print
The World Factbook
Country/Location Photo Gallery Modal
Europe ::
Jan Mayen

1 /
1
Caption
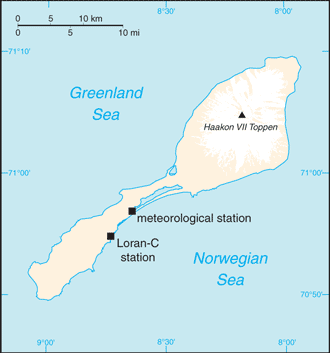
Tiny Jan Mayen Island sits about 650 km (1,040 mi) northeast of Iceland between the Norwegian and Greenland Seas. Covering 377 sq km (146 sq mi), the island is about twice the size of Washington, D.C. The white peak on the northeast section of the island is Haakon VII Toppen/Beerenberg, the northernmost active volcano in the world. Image courtesy of NASA.
Dimensions
File Size
Download
Usage
Factbook photos - obtained from a variety of sources - are in the public domain
and are copyright free.
Agency Copyright Notice
Agency Copyright Notice
- Jump to topic
-
Introduction :: Jan Mayen
-
Background: This entry usually highlights major historic events and current issues and may include a statement about one or two key future trends.
 This desolate, arctic, mountainous island was named after a Dutch whaling captain who indisputably discovered it in 1614 (earlier claims are inconclusive). Visited only occasionally by seal hunters and trappers over the following centuries, the island came under Norwegian sovereignty in 1929. The long dormant Beerenberg volcano, the northernmost active volcano on earth, resumed activity in 1970 and the most recent eruption occurred in 1985.
This desolate, arctic, mountainous island was named after a Dutch whaling captain who indisputably discovered it in 1614 (earlier claims are inconclusive). Visited only occasionally by seal hunters and trappers over the following centuries, the island came under Norwegian sovereignty in 1929. The long dormant Beerenberg volcano, the northernmost active volcano on earth, resumed activity in 1970 and the most recent eruption occurred in 1985. -
Geography :: Jan Mayen
-
Location: This entry identifies the country's regional location, neighboring countries, and adjacent bodies of water.
 Northern Europe, island between the Greenland Sea and the Norwegian Sea, northeast of IcelandGeographic coordinates: This entry includes rounded latitude and longitude figures for the centroid or center point of a country expressed in degrees and minutes; it is based on the locations provided in the Geographic Names Server (GNS), maintained by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency on behalf of the US Board on Geographic Names.
Northern Europe, island between the Greenland Sea and the Norwegian Sea, northeast of IcelandGeographic coordinates: This entry includes rounded latitude and longitude figures for the centroid or center point of a country expressed in degrees and minutes; it is based on the locations provided in the Geographic Names Server (GNS), maintained by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency on behalf of the US Board on Geographic Names. 71 00 N, 8 00 WMap references: This entry includes the name of the Factbook reference map on which a country may be found. Note that boundary representations on these maps are not necessarily authoritative. The entry on Geographic coordinates may be helpful in finding some smaller countries.
71 00 N, 8 00 WMap references: This entry includes the name of the Factbook reference map on which a country may be found. Note that boundary representations on these maps are not necessarily authoritative. The entry on Geographic coordinates may be helpful in finding some smaller countries. Arctic RegionArea: This entry includes three subfields. Total area is the sum of all land and water areas delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Land area is the aggregate of all surfaces delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines, excluding inland water bodies (lakes, reservoirs, rivers). Water area is the sum of the surfaces of all inland water bodies, such as lakes, reservoirs, or rivers, as delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines.
Arctic RegionArea: This entry includes three subfields. Total area is the sum of all land and water areas delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Land area is the aggregate of all surfaces delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines, excluding inland water bodies (lakes, reservoirs, rivers). Water area is the sum of the surfaces of all inland water bodies, such as lakes, reservoirs, or rivers, as delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Area - comparative: This entry provides an area comparison based on total area equivalents. Most entities are compared with the entire US or one of the 50 states based on area measurements (1990 revised) provided by the US Bureau of the Census. The smaller entities are compared with Washington, DC (178 sq km, 69 sq mi) or The Mall in Washington, DC (0.59 sq km, 0.23 sq mi, 146 acres).
Area - comparative: This entry provides an area comparison based on total area equivalents. Most entities are compared with the entire US or one of the 50 states based on area measurements (1990 revised) provided by the US Bureau of the Census. The smaller entities are compared with Washington, DC (178 sq km, 69 sq mi) or The Mall in Washington, DC (0.59 sq km, 0.23 sq mi, 146 acres). slightly more than twice the size of Washington, DCLand boundaries: This entry contains the total length of all land boundaries and the individual lengths for each of the contiguous border countries. When available, official lengths published by national statistical agencies are used. Because surveying methods may differ, country border lengths reported by contiguous countries may differ.
slightly more than twice the size of Washington, DCLand boundaries: This entry contains the total length of all land boundaries and the individual lengths for each of the contiguous border countries. When available, official lengths published by national statistical agencies are used. Because surveying methods may differ, country border lengths reported by contiguous countries may differ. 0 kmCoastline: This entry gives the total length of the boundary between the land area (including islands) and the sea.
0 kmCoastline: This entry gives the total length of the boundary between the land area (including islands) and the sea. 124.1 kmMaritime claims: This entry includes the following claims, the definitions of which are excerpted from the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which alone contains the full and definitive descriptions: territorial sea - the sovereignty of a coastal state extends beyond its land territory and internal waters to an adjacent belt of sea, described as the territorial sea in the UNCLOS (Part II); this sovereignty extends to the air space over the territorial sea as well as its underlying s . . . more
124.1 kmMaritime claims: This entry includes the following claims, the definitions of which are excerpted from the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which alone contains the full and definitive descriptions: territorial sea - the sovereignty of a coastal state extends beyond its land territory and internal waters to an adjacent belt of sea, described as the territorial sea in the UNCLOS (Part II); this sovereignty extends to the air space over the territorial sea as well as its underlying s . . . more territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmcontinental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitationClimate: This entry includes a brief description of typical weather regimes throughout the year; in the Word entry only, it includes four subfields that describe climate extremes:ten driest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and inches for selected countries with climate extremes. ten wettest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and i . . . more
territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmcontinental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitationClimate: This entry includes a brief description of typical weather regimes throughout the year; in the Word entry only, it includes four subfields that describe climate extremes:ten driest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and inches for selected countries with climate extremes. ten wettest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and i . . . more arctic maritime with frequent storms and persistent fogTerrain: This entry contains a brief description of the topography.
arctic maritime with frequent storms and persistent fogTerrain: This entry contains a brief description of the topography. volcanic island, partly covered by glaciersElevation: This entry includes the mean elevation and elevation extremes, lowest point and highest point.
volcanic island, partly covered by glaciersElevation: This entry includes the mean elevation and elevation extremes, lowest point and highest point. lowest point: Norwegian Sea 0 mhighest point: Haakon VII Toppen on Beerenberg 2,277note: Beerenberg volcano has numerous peaks; the highest point on the volcano rim is named Haakon VII Toppen, after Norway's first king following the reestablishment of Norwegian independence in 1905Natural resources: This entry lists a country's mineral, petroleum, hydropower, and other resources of commercial importance, such as rare earth elements (REEs). In general, products appear only if they make a significant contribution to the economy, or are likely to do so in the future.
lowest point: Norwegian Sea 0 mhighest point: Haakon VII Toppen on Beerenberg 2,277note: Beerenberg volcano has numerous peaks; the highest point on the volcano rim is named Haakon VII Toppen, after Norway's first king following the reestablishment of Norwegian independence in 1905Natural resources: This entry lists a country's mineral, petroleum, hydropower, and other resources of commercial importance, such as rare earth elements (REEs). In general, products appear only if they make a significant contribution to the economy, or are likely to do so in the future. noneLand use: This entry contains the percentage shares of total land area for three different types of land use: agricultural land, forest, and other; agricultural land is further divided into arable land - land cultivated for crops like wheat, maize, and rice that are replanted after each harvest, permanent crops - land cultivated for crops like citrus, coffee, and rubber that are not replanted after each harvest, and includes land under flowering shrubs, fruit trees, nut trees, and vines, and permane . . . more
noneLand use: This entry contains the percentage shares of total land area for three different types of land use: agricultural land, forest, and other; agricultural land is further divided into arable land - land cultivated for crops like wheat, maize, and rice that are replanted after each harvest, permanent crops - land cultivated for crops like citrus, coffee, and rubber that are not replanted after each harvest, and includes land under flowering shrubs, fruit trees, nut trees, and vines, and permane . . . more agricultural land: 0% (2011 est.)arable land: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 0% (2011 est.)forest: 0% (2011 est.)other: 100% (2011 est.)Irrigated land: This entry gives the number of square kilometers of land area that is artificially supplied with water.
agricultural land: 0% (2011 est.)arable land: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 0% (2011 est.)forest: 0% (2011 est.)other: 100% (2011 est.)Irrigated land: This entry gives the number of square kilometers of land area that is artificially supplied with water. 0 sq km (2012)Natural hazards: This entry lists potential natural disasters. For countries where volcanic activity is common, a volcanism subfield highlights historically active volcanoes.
0 sq km (2012)Natural hazards: This entry lists potential natural disasters. For countries where volcanic activity is common, a volcanism subfield highlights historically active volcanoes.
dominated by the volcano Beerenberg
volcanism: Beerenberg (2,227 m) is Norway's only active volcano; volcanic activity resumed in 1970; the most recent eruption occurred in 1985
Environment - current issues: This entry lists the most pressing and important environmental problems. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: Acidification - the lowering of soil and water pH due to acid precipitation and deposition usually through precipitation; this process disrupts ecosystem nutrient flows and may kill freshwater fish and plants dependent on more neutral or alkaline conditions (see acid rain). Acid rain - characterized as containing harmful levels of sulfur dioxi . . . more pollutants transported from southerly latitudes by winds, ocean currents, and rivers accumulate in the food chains of native animals; climate changeGeography - note: This entry includes miscellaneous geographic information of significance not included elsewhere.
pollutants transported from southerly latitudes by winds, ocean currents, and rivers accumulate in the food chains of native animals; climate changeGeography - note: This entry includes miscellaneous geographic information of significance not included elsewhere. barren volcanic spoon-shaped island with some moss and grass flora; island consists of two parts: a larger northeast Nord-Jan (the spoon "bowl") and the smaller Sor-Jan (the "handle"), linked by a 2.5 km-wide isthmus (the "stem") with two large lakes, Sorlaguna (South Lagoon) and Nordlaguna (North Lagoon)
barren volcanic spoon-shaped island with some moss and grass flora; island consists of two parts: a larger northeast Nord-Jan (the spoon "bowl") and the smaller Sor-Jan (the "handle"), linked by a 2.5 km-wide isthmus (the "stem") with two large lakes, Sorlaguna (South Lagoon) and Nordlaguna (North Lagoon) -
People and Society :: Jan Mayen
-
Population: This entry gives an estimate from the US Bureau of the Census based on statistics from population censuses, vital statistics registration systems, or sample surveys pertaining to the recent past and on assumptions about future trends. The total population presents one overall measure of the potential impact of the country on the world and within its region. Note: Starting with the 1993 Factbook, demographic estimates for some countries (mostly African) have explicitly taken into account t . . . more
 no indigenous inhabitants
no indigenous inhabitantsnote: military personnel operate the the weather and coastal services radio station
-
Government :: Jan Mayen
-
Country name: This entry includes all forms of the country's name approved by the US Board on Geographic Names (Italy is used as an example): conventional long form (Italian Republic), conventional short form (Italy), local long form (Repubblica Italiana), local short form (Italia), former (Kingdom of Italy), as well as the abbreviation. Also see the Terminology note.
 conventional long form: noneconventional short form: Jan Mayenetymology: named after Dutch Captain Jan Jacobszoon MAY, one of the first explorers to reach the island in 1614Dependency status: This entry describes the formal relationship between a particular nonindependent entity and an independent state.
conventional long form: noneconventional short form: Jan Mayenetymology: named after Dutch Captain Jan Jacobszoon MAY, one of the first explorers to reach the island in 1614Dependency status: This entry describes the formal relationship between a particular nonindependent entity and an independent state. territory of Norway; since August 1994, administered from Oslo through the county governor (fylkesmann) of Nordland; however, authority has been delegated to a station commander of the Norwegian Defense Communication Service; in 2010, Norway designated the majority of Jan Mayen as a nature reserveLegal system: This entry provides the description of a country's legal system. A statement on judicial review of legislative acts is also included for a number of countries. The legal systems of nearly all countries are generally modeled upon elements of five main types: civil law (including French law, the Napoleonic Code, Roman law, Roman-Dutch law, and Spanish law); common law (including United State law); customary law; mixed or pluralistic law; and religious law (including Islamic law). An addition . . . more
territory of Norway; since August 1994, administered from Oslo through the county governor (fylkesmann) of Nordland; however, authority has been delegated to a station commander of the Norwegian Defense Communication Service; in 2010, Norway designated the majority of Jan Mayen as a nature reserveLegal system: This entry provides the description of a country's legal system. A statement on judicial review of legislative acts is also included for a number of countries. The legal systems of nearly all countries are generally modeled upon elements of five main types: civil law (including French law, the Napoleonic Code, Roman law, Roman-Dutch law, and Spanish law); common law (including United State law); customary law; mixed or pluralistic law; and religious law (including Islamic law). An addition . . . more the laws of Norway apply where applicableFlag description: This entry provides a written flag description produced from actual flags or the best information available at the time the entry was written. The flags of independent states are used by their dependencies unless there is an officially recognized local flag. Some disputed and other areas do not have flags.
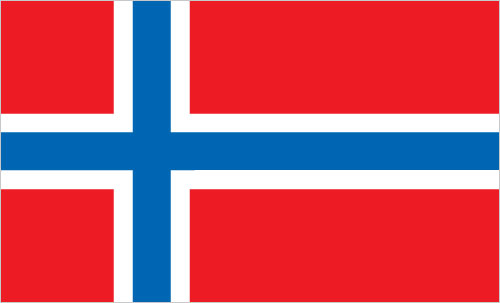
the laws of Norway apply where applicableFlag description: This entry provides a written flag description produced from actual flags or the best information available at the time the entry was written. The flags of independent states are used by their dependencies unless there is an officially recognized local flag. Some disputed and other areas do not have flags. the flag of Norway is used
the flag of Norway is used -
Economy :: Jan Mayen
-
Economy - overview: This entry briefly describes the type of economy, including the degree of market orientation, the level of economic development, the most important natural resources, and the unique areas of specialization. It also characterizes major economic events and policy changes in the most recent 12 months and may include a statement about one or two key future macroeconomic trends.
 Jan Mayen is a volcanic island with no exploitable natural resources, although surrounding waters contain substantial fish stocks and potential untapped petroleum resources. Economic activity is limited to providing services for employees of Norway's radio and meteorological stations on the island.
Jan Mayen is a volcanic island with no exploitable natural resources, although surrounding waters contain substantial fish stocks and potential untapped petroleum resources. Economic activity is limited to providing services for employees of Norway's radio and meteorological stations on the island. -
Communications :: Jan Mayen
-
Broadcast media: This entry provides information on the approximate number of public and private TV and radio stations in a country, as well as basic information on the availability of satellite and cable TV services.
 a coastal radio station has been remotely operated since 1994
a coastal radio station has been remotely operated since 1994 -
Military and Security :: Jan Mayen
-
Military - note: This entry includes miscellaneous military information of significance not included elsewhere.
 defense is the responsibility of Norway
defense is the responsibility of Norway -
Transportation :: Jan Mayen
-
Airports: This entry gives the total number of airports or airfields recognizable from the air. The runway(s) may be paved (concrete or asphalt surfaces) or unpaved (grass, earth, sand, or gravel surfaces) and may include closed or abandoned installations. Airports or airfields that are no longer recognizable (overgrown, no facilities, etc.) are not included. Note that not all airports have accommodations for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control.
 1 (2013)country comparison to the world: 225Airports - with unpaved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with unpaved runways (grass, dirt, sand, or gravel surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listin . . . more
1 (2013)country comparison to the world: 225Airports - with unpaved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with unpaved runways (grass, dirt, sand, or gravel surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listin . . . more total: 1 (2013)1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2013)Roadways: This entry gives the total length of the road network and includes the length of the paved and unpaved portions.
total: 1 (2013)1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2013)Roadways: This entry gives the total length of the road network and includes the length of the paved and unpaved portions. Ports and terminals: This entry lists major ports and terminals primarily on the basis of the amount of cargo tonnage shipped through the facilities on an annual basis. In some instances, the number of containers handled or ship visits were also considered. Most ports service multiple classes of vessels including bulk carriers (dry and liquid), break bulk cargoes (goods loaded individually in bags, boxes, crates, or drums; sometimes palletized), containers, roll-on/roll-off, and passenger ships. The listing le . . . more
Ports and terminals: This entry lists major ports and terminals primarily on the basis of the amount of cargo tonnage shipped through the facilities on an annual basis. In some instances, the number of containers handled or ship visits were also considered. Most ports service multiple classes of vessels including bulk carriers (dry and liquid), break bulk cargoes (goods loaded individually in bags, boxes, crates, or drums; sometimes palletized), containers, roll-on/roll-off, and passenger ships. The listing le . . . more none; offshore anchorage only
none; offshore anchorage only -
Transnational Issues :: Jan Mayen
-
Disputes - international: This entry includes a wide variety of situations that range from traditional bilateral boundary disputes to unilateral claims of one sort or another. Information regarding disputes over international terrestrial and maritime boundaries has been reviewed by the US Department of State. References to other situations involving borders or frontiers may also be included, such as resource disputes, geopolitical questions, or irredentist issues; however, inclusion does not necessarily constitute . . . more

none