-
Introduction :: Greenland
-
Background:Greenland, the world's largest island, is about 80% ice-capped. Vikings reached the island in the 10th century from Iceland; Danish colonization began in the 18th century, and Greenland became an integral part of the Danish Realm in 1953. It joined the European Community (now the EU) with Denmark in 1973 but withdrew in 1985 over a dispute centered on stringent fishing quotas. Greenland remains a member of the Overseas Countries and Territories Association of the EU. Greenland was granted self-government in 1979 by the Danish parliament; the law went into effect the following year. Greenland voted in favor of increased self-rule in November 2008 and acquired greater responsibility for internal affairs when the Act on Greenland Self-Government was signed into law in June 2009. Denmark, however, continues to exercise control over several policy areas on behalf of Greenland, including foreign affairs, security, and financial policy in consultation with Greenland's Self-Rule Government.
-
Geography :: Greenland
-
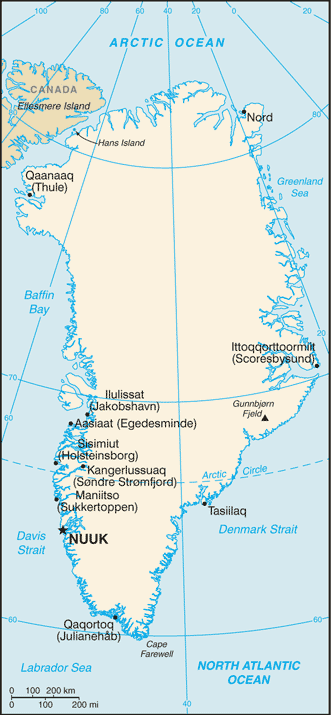
Location:Northern North America, island between the Arctic Ocean and the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of CanadaGeographic coordinates:72 00 N, 40 00 WMap references:Arctic RegionArea:total: 2,166,086 sq kmland: 2,166,086 sq km (approximately 1,710,000 sq km ice-covered)country comparison to the world: 13Area - comparative:slightly more than three times the size of TexasLand boundaries:0 kmCoastline:44,087 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 3 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or agreed boundaries or median lineexclusive fishing zone: 200 nm or agreed boundaries or median lineClimate:arctic to subarctic; cool summers, cold wintersTerrain:flat to gradually sloping icecap covers all but a narrow, mountainous, barren, rocky coastElevation:mean elevation: 1,792 mlowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Gunnbjorn Fjeld 3,694 mNatural resources:coal, iron ore, lead, zinc, molybdenum, diamonds, gold, platinum, niobium, tantalite, uranium, fish, seals, whales, hydropower, possible oil and gasLand use:agricultural land: 0.6% (2011 est.)arable land: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 0.6% (2011 est.)forest: 0% (2011 est.)other: 99.4% (2011 est.)Irrigated land:NAPopulation distribution:settlement concentrated on the southwest shoreline, with limited settlements scattered along the remaining coast; interior is uninhabitedNatural hazards:continuous permafrost over northern two-thirds of the islandEnvironment - current issues:especially vulnerable to climate change and disruption of the Arctic environment; preservation of the Inuit traditional way of life, including whaling and seal huntingGeography - note:dominates North Atlantic Ocean between North America and Europe; sparse population confined to small settlements along coast; close to one-quarter of the population lives in the capital, Nuuk; world's second largest ice sheet after that of Antarctica covering an area of 1.71 million sq km (660,000 sq mi) or about 79% of the island, and containing 2.85 million cu km (684 thousand cu mi) of ice (this is almost 7% of all of the world's fresh water); if all this ice were converted to liquid water, one estimate is that it would be sufficient to raise the height of the world's oceans by 7.2 m (24 ft)
-
People and Society :: Greenland
-
Population:57,691 (July 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 206Nationality:noun: Greenlander(s)adjective: GreenlandicEthnic groups:Greenlandic 89.7%, Danish 7.8%, other Nordic 1.1%, and other 1.4% (2018 est.)note: data represent population by country of birthLanguages:Greenlandic (West Greenlandic or Kalaallisut is the official language), Danish, EnglishReligions:Evangelical Lutheran, traditional Inuit spiritual beliefsAge structure:0-14 years: 21% (male 6,151 /female 5,962)15-24 years: 15.1% (male 4,388 /female 4,321)25-54 years: 40.83% (male 12,349 /female 11,209)55-64 years: 13.5% (male 4,259 /female 3,529)65 years and over: 9.57% (male 2,944 /female 2,579) (2018 est.)population pyramid:
 The World Factbook Field Image ModalNorth America :: Greenland Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalNorth America :: Greenland Print Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Greenland. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Greenland. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Median age:total: 34 years (2018 est.)male: 35 yearsfemale: 32.9 yearscountry comparison to the world: 89Population growth rate:-0.04% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 200Birth rate:14.3 births/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 133Death rate:8.8 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 69Net migration rate:-6 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 201Population distribution:settlement concentrated on the southwest shoreline, with limited settlements scattered along the remaining coast; interior is uninhabitedUrbanization:urban population: 87.1% of total population (2019)rate of urbanization: 0.42% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:18,000 NUUK (capital) (2018)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.02 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.1 male(s)/female55-64 years: 1.21 male(s)/female65 years and over: 1.14 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1.09 male(s)/female (2018 est.)Infant mortality rate:total: 8.7 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)male: 9.9 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 7.4 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 147Life expectancy at birth:total population: 72.9 years (2018 est.)male: 70.2 yearsfemale: 75.8 yearscountry comparison to the world: 145Total fertility rate:1.97 children born/woman (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 122Drinking water source:improved: urban: 100% of populationrural: 100% of populationtotal: 100% of populationunimproved: urban: 0% of populationrural: 0% of populationtotal: 0% of population (2015 est.)Physicians density:1.87 physicians/1,000 population (2016)Hospital bed density:8.2 beds/1,000 population (2015)Sanitation facility access:improved: urban: 100% of population (2015 est.)rural: 100% of population (2015 est.)total: 100% of population (2015 est.)unimproved: urban: 0% of population (2015 est.)rural: 0% of population (2015 est.)total: 0% of population (2015 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:NAHIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:NAHIV/AIDS - deaths:NAEducation expenditures:NALiteracy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 100%male: 100%female: 100% (2015) -
Government :: Greenland
-
Country name:conventional long form: noneconventional short form: Greenlandlocal long form: nonelocal short form: Kalaallit Nunaat
note: named by Norwegian adventurer Erik THORVALDSSON (Erik the Red) in A.D. 985 in order to entice settlers to the island
Dependency status:part of the Kingdom of Denmark; self-governing overseas administrative division of Denmark since 1979Government type:parliamentary democracy (Parliament of Greenland or Inatsisartut)Capital:name: Nuuk (Godthaab)geographic coordinates: 64 11 N, 51 45 Wtime difference: UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in Octobernote: Greenland has four time zones
etymology: "nuuk" is the Inuit word for "cape" and refers to the city's position at the end of the Nuup Kangerlua fjordAdministrative divisions:5 municipalities (kommuner, singular kommune); Avannaata, Kujalleq, Qeqertalik, Qeqqata, Sermersooqnote: Northeast Greenland National Park (Kalaallit Nunaanni Nuna Eqqissisimatitaq) and the Thule Air Base in Pituffik (in northwest Greenland) are two unincorporated areas; the national park's 972,000 sq km - about 46% of the island - makes it the largest national park in the world and also the most northerly
Independence:none (extensive self-rule as part of the Kingdom of Denmark; foreign affairs is the responsibility of Denmark, but Greenland actively participates in international agreements relating to Greenland)National holiday:National Day, June 21; note - marks the summer solstice and the longest day of the year in the Northern HemisphereConstitution:history: previous 1953 (Greenland established as a constituency in the Danish constitution), 1979 (Greenland Home Rule Act); latest 21 June 2009 (Greenland Self-Government Act)Legal system:the laws of Denmark apply where applicable and Greenlandic law applies to other areasCitizenship:see DenmarkSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: Queen MARGRETHE II of Denmark (since 14 January 1972), represented by High Commissioner Mikaela ENGELL (since April 2011)head of government: Premier Kim KIELSEN (since 30 September 2014)cabinet: Self-rule Government (Naalakkersuisut) elected by the Parliament (Inatsisartut) on the basis of the strength of partieselections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; high commissioner appointed by the monarch; premier indirectly elected by Parliament for a 4-year termelection results: Kim KIELSEN elected premier; Parliament vote - Kim KIELSEN (S) 27.2%, Sara OLSVIG (IA) 25.5%, Randi Vestergaard EVALDSEN (D) 19.5%, other 27.8%Legislative branch:description: unicameral Parliament or Inatsisartut (31 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote to serve 4-year terms)
Greenland elects 2 members to the Danish Parliament to serve 4-year termselections: Greenland Parliament - last held on 24 April 2018 (next to be held by 2022)
Greenland members to Danish Parliament - last held on 18 June 2015 (next to be held by June 2019)election results: Greenland Parliament percent of vote by party - S 27.2%, IA 25.5%, D 19.5%, PN 13.4%, A 5.9%, SA 4.1%, NQ 3.4% other 1%; seats by party - S 9, IA 8, D 6, PN 4, A 2, SA 1, NQ 1; composition - men 19, women 12, percent of women 38.7%
Greenland members in Danish Parliament - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - IA 1, S 1; composition - 2 womenJudicial branch:highest courts: High Court of Greenland (consists of the presiding professional judge and 2 lay assessors); note - appeals beyond the High Court of Greenland can be heard by the Supreme Court (in Copenhagen)judge selection and term of office: judges appointed by the monarch upon the recommendation of the Judicial Appointments Council, a 6-member independent body of judges and lawyers; judges appointed for life with retirement at age 70subordinate courts: Court of Greenland; 18 district or magistrates' courtsPolitical parties and leaders:Cooperation Party (Suleqatigiissitsisut or Samarbejdspartiet) or SA [Michael ROSING]
Democrats Party (Demokraatit) or D [Niels THOMSEN]
Forward Party (Siumut) or S [Kim KIELSEN]
Inuit Community (Inuit Ataqatigiit) or IA [Sara OLSVIG]
Our Country's Future (Nunatta Qitornai) or NQ [Vittus QUJAUKITSOQ]
Signpost Party (Partii Naleraq) or PN [Hans ENOKSEN]
Fellowship Party (Atassut) or A [Siverth Karl HEILMANN]International organization participation:Arctic Council, ICC, NC, NIB, UPUDiplomatic representation in the US:none (self-governing overseas administrative division of Denmark); note - Greenland has an office in the Danish Embassy in the US; it also has offices in the Danish consulates in Chicago and New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:none (self-governing overseas administrative division of Denmark)Flag description:two equal horizontal bands of white (top) and red with a large disk slightly to the hoist side of center - the top half of the disk is red, the bottom half is white; the design represents the sun reflecting off a field of ice; the colors are the same as those of the Danish flag and symbolize Greenland's links to the Kingdom of DenmarkNational symbol(s):polar bear; national colors: red, whiteNational anthem:name: "Nunarput utoqqarsuanngoravit" ("Our Country, Who's Become So Old" also translated as "You Our Ancient Land")lyrics/music: Henrik LUND/Jonathan PETERSENnote: adopted 1916; the government also recognizes "Nuna asiilasooq" as a secondary anthem
-
Economy :: Greenland
-
Economy - overview:
Greenland’s economy depends on exports of shrimp and fish, and on a substantial subsidy from the Danish Government. Fish account for over 90% of its exports, subjecting the economy to price fluctuations. The subsidy from the Danish Government is budgeted to be about $535 million in 2017, more than 50% of government revenues, and 25% of GDP.
The economy is expanding after a period of decline. The economy contracted between 2012 and 2014, grew by 1.7% in 2015 and by 7.7%in 2016. The expansion has been driven by larger quotas for shrimp, the predominant Greenlandic export, and also by increased activity in the construction sector, especially in Nuuk, the capital. Private consumption and tourism also are contributing to GDP growth more than in previous years. Tourism in Greenland grew annually around 20% in 2015 and 2016, largely a result of increasing numbers of cruise lines now operating in Greenland's western and southern waters during the peak summer tourism season.
The public sector, including publicly owned enterprises and the municipalities, plays a dominant role in Greenland's economy. During the last decade the Greenland Self Rule Government pursued conservative fiscal and monetary policies, but public pressure has increased for better schools, health care, and retirement systems. The budget was in deficit in 2014 and 2016, but public debt remains low at about 5% of GDP. The government plans a balanced budget for the 2017–20 period.
Significant challenges face the island, including low levels of qualified labor, geographic dispersion, lack of industry diversification, the long-term sustainability of the public budget, and a declining population due to emigration. Hydrocarbon exploration has ceased with declining oil prices. The island has potential for natural resource exploitation with rare-earth, uranium, and iron ore mineral projects proposed, but a lack of infrastructure hinders development.
GDP (purchasing power parity):$2.413 billion (2015 est.)$2.24 billion (2014 est.)$2.203 billion (2013 est.)note: data are in 2015 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 193GDP (official exchange rate):$2.221 billion (2015 est.) (2015 est.)GDP - real growth rate:7.7% (2016 est.)1.7% (2015 est.)-0.8% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 11GDP - per capita (PPP):$41,800 (2015 est.)$38,800 (2014 est.)$38,500 (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 44GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 68.1% (2015 est.)government consumption: 28% (2015 est.)investment in fixed capital: 14.3% (2015 est.)investment in inventories: -13.9% (2015 est.)exports of goods and services: 18.2% (2015 est.)imports of goods and services: -28.6% (2015 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 15.9% (2015 est.)industry: 10.1% (2015 est.)services: 73.9% (2015)Agriculture - products:sheep, cow, reindeer, fish, shellfishIndustries:fish processing (mainly shrimp and Greenland halibut); anorthosite and ruby mining; handicrafts, hides and skins, small shipyardsIndustrial production growth rate:NALabor force:26,840 (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 207Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 15.9%industry: 10.1%services: 73.9% (2015 est.)Unemployment rate:9.1% (2015 est.)10.3% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 132Population below poverty line:16.2% (2015 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: NAhighest 10%: NADistribution of family income - Gini index:33.9 (2015 est.)34.3 (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 107Budget:revenues: 1.719 billion (2016 est.)expenditures: 1.594 billion (2016 est.)Taxes and other revenues:77.4% (of GDP) (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 3Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):5.6% (of GDP) (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 5Public debt:13% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 196Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):0.3% (January 2017 est.)1.2% (January 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 19Central bank discount rate:NA
Exports:$407.1 million (2015 est.)$599.7 million (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 183Exports - partners:Denmark 82.5%, Iceland 4.4% (2017)Exports - commodities:fish and fish products 91% (2015 est.)Imports:$783.5 million (2015 est.)$866.1 million (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 191Imports - commodities:machinery and transport equipment, manufactured goods, food, petroleum productsImports - partners:Denmark 69.7%, Sweden 10.6% (2017)Debt - external:$36.4 million (2010)$58 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 197Exchange rates:Danish kroner (DKK) per US dollar -6.586 (2017 est.)6.7309 (2016 est.)6.7309 (2015 est.)6.7326 (2014 est.)5.6125 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Greenland
-
Electricity access:electrification - total population: 100% (2016)Electricity - production:538 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 163Electricity - consumption:468 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 170Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 141Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 153Electricity - installed generating capacity:187,000 kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 167Electricity - from fossil fuels:51% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 149Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 99Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:49% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 42Electricity - from other renewable sources:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 189Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 142Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 130Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 133Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 138Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 150Refined petroleum products - consumption:4,000 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 159Refined petroleum products - imports:3,973 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 177Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 138Natural gas - consumption:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 151Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 113Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 131Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 140Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:613,800 Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 179
-
Communications :: Greenland
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 16,000subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 28 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 186Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 61,000subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 106 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 199Telephone system:general assessment: adequate domestic and international service provided by satellite, cables, and microwave radio relay; the fundamental telecommunications infrastructure consists of a digital radio link from Nanortalik in south Greenland to Uummannaq in north Greenland; satellites cover north and east Greenland for domestic and foreign telecommunications; a marine cable connects south and west Greenland to the rest of the world, extending from Nuuk and Qaqortoq to Canada and Iceland (2018)domestic: 14 per 100 for fixed-line subscriptions and 111 per 100 for mobile-cellular (2018)international: country code - 299; landing points for Greenland Connect, Greenland Connect North, Nunavut Undersea Fiber System submarine cables to Greenland, Iceland, and Canada; satellite earth stations - 15 (12 Intelsat, 1 Eutelsat, 2 Americom GE-2 (all Atlantic Ocean)) (2019)Broadcast media:the Greenland Broadcasting Company provides public radio and TV services throughout the island with a broadcast station and a series of repeaters; a few private local TV and radio stations; Danish public radio rebroadcasts are available (2019)Internet country code:.glInternet users:total: 39,544percent of population: 68.5% (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 198
-
Military and Security :: Greenland
-
Military and security forces:no regular military forces or conscription. (2019)Military - note:The Danish military’s Joint Arctic Command in Nuuk is responsible for territorial defense of Greenland (2019)
-
Transportation :: Greenland
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 1 (registered in Denmark) (2015)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 8 (registered in Denmark) (2015)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:OY-H (2016)Airports:15 (2013)country comparison to the world: 146Airports - with paved runways:total: 10 (2019)2,438 to 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 1914 to 1,523 m: 1under 914 m: 6Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 5 (2013)1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2013)914 to 1,523 m: 2 (2013)under 914 m: 2 (2013)Roadways:
note: although there are short roads in towns, there are no roads between towns; inter-urban transport is either by sea or by air
Merchant marine:total: 8by type: general cargo 1, other 7 (2018)country comparison to the world: 157Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Sisimiut -
Transnational Issues :: Greenland
-
Disputes - international:
managed dispute between Canada and Denmark over Hans Island in the Kennedy Channel between Canada's Ellesmere Island and Greenland; Denmark (Greenland) and Norway have made submissions to the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS) and Russia is collecting additional data to augment its 2001 CLCS submission