
-
Introduction :: Indonesia
-
Background:The Dutch began to colonize Indonesia in the early 17th century; Japan occupied the islands from 1942 to 1945. Indonesia declared its independence shortly before Japan's surrender, but it required four years of sometimes brutal fighting, intermittent negotiations, and UN mediation before the Netherlands agreed to transfer sovereignty in 1949. A period of sometimes unruly parliamentary democracy ended in 1957 when President SOEKARNO declared martial law and instituted "Guided Democracy." After an abortive coup in 1965 by alleged communist sympathizers, SOEKARNO was gradually eased from power. From 1967 until 1998, President SUHARTO ruled Indonesia with his "New Order" government. After street protests toppled SUHARTO in 1998, free and fair legislative elections took place in 1999. Indonesia is now the world's third most populous democracy, the world's largest archipelagic state, and the world's largest Muslim-majority nation. Current issues include: alleviating poverty, improving education, preventing terrorism, consolidating democracy after four decades of authoritarianism, implementing economic and financial reforms, stemming corruption, reforming the criminal justice system, addressing climate change, and controlling infectious diseases, particularly those of global and regional importance. In 2005, Indonesia reached a historic peace agreement with armed separatists in Aceh, which led to democratic elections in Aceh in December 2006. Indonesia continues to face low intensity armed resistance in Papua by the separatist Free Papua Movement.
-
Geography :: Indonesia
-
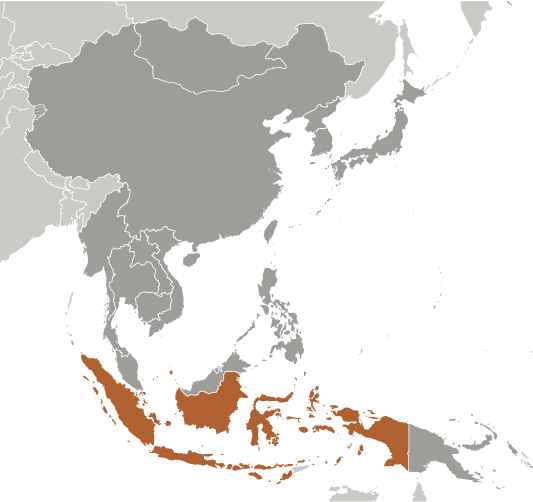
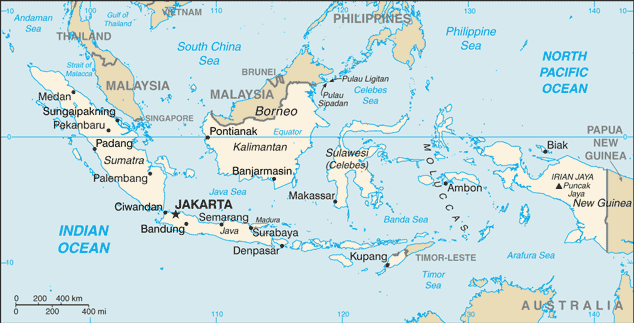
Location:Southeastern Asia, archipelago between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific OceanGeographic coordinates:5 00 S, 120 00 EMap references:Southeast AsiaArea:total: 1,904,569 sq kmland: 1,811,569 sq kmwater: 93,000 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 16Area - comparative:slightly less than three times the size of TexasArea comparison map:
 The World Factbook Field Image ModalEast Asia/Southeast Asia :: Indonesia Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalEast Asia/Southeast Asia :: Indonesia Print Image Description
Image Descriptionslightly less than three times the size of Texas
Land boundaries:total: 2,958 kmborder countries (3): Malaysia 1881 km, Papua New Guinea 824 km, Timor-Leste 253 kmCoastline:54,716 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmmeasured from claimed archipelagic straight baselinesClimate:tropical; hot, humid; more moderate in highlandsTerrain:mostly coastal lowlands; larger islands have interior mountainsElevation:mean elevation: 367 mlowest point: Indian Ocean 0 mhighest point: Puncak Jaya 4,884 mNatural resources:petroleum, tin, natural gas, nickel, timber, bauxite, copper, fertile soils, coal, gold, silverLand use:agricultural land: 31.2% (2011 est.)arable land: 13% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 12.1% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 6.1% (2011 est.)forest: 51.7% (2011 est.)other: 17.1% (2011 est.)Irrigated land:67,220 sq km (2012)Population distribution:major concentration on the island of Java, which is considered one of the most densely populated places on earth; of the outer islands (those surrounding Java and Bali), Sumatra contains some of the most significant clusters, particularly in the south near the Selat Sunda, and along the northeastern coast near Medan; the cities of Makasar (Sulawesi), Banjarmasin (Kalimantan) are also heavily populatedNatural hazards:occasional floods; severe droughts; tsunamis; earthquakes; volcanoes; forest fires
volcanism: Indonesia contains the most volcanoes of any country in the world - some 76 are historically active; significant volcanic activity occurs on Java, Sumatra, the Sunda Islands, Halmahera Island, Sulawesi Island, Sangihe Island, and in the Banda Sea; Merapi (2,968 m), Indonesia's most active volcano and in eruption since 2010, has been deemed a Decade Volcano by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to its explosive history and close proximity to human populations; other notable historically active volcanoes include Agung, Awu, Karangetang, Krakatau (Krakatoa), Makian, Raung, and Tambora; see note 2 under "Geography - note"
Environment - current issues:large-scale deforestation (much of it illegal) and related wildfires cause heavy smog; over-exploitation of marine resources; environmental problems associated with rapid urbanization and economic development, including air pollution, traffic congestion, garbage management, and reliable water and waste water services; water pollution from industrial wastes, sewageEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: Marine Life ConservationGeography - note:note 1: according to Indonesia's National Coordinating Agency for Survey and Mapping, the total number of islands in the archipelago is 13,466, of which 922 are permanently inhabited (Indonesia is the world's largest country comprised solely of islands); the country straddles the equator and occupies a strategic location astride or along major sea lanes from the Indian Ocean to the Pacific Ocean
note 2: Indonesia is one of the countries along the Ring of Fire, a belt of active volcanoes and earthquake epicenters bordering the Pacific Ocean; up to 90% of the world's earthquakes and some 75% of the world's volcanoes occur within the Ring of Fire
note 3: despite having the fourth largest population in the world, Indonesia is the most heavily forested region on earth after the Amazon
-
People and Society :: Indonesia
-
Population:262,787,403 (July 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Nationality:noun: Indonesian(s)adjective: IndonesianEthnic groups:Javanese 40.1%, Sundanese 15.5%, Malay 3.7%, Batak 3.6%, Madurese 3%, Betawi 2.9%, Minangkabau 2.7%, Buginese 2.7%, Bantenese 2%, Banjarese 1.7%, Balinese 1.7%, Acehnese 1.4%, Dayak 1.4%, Sasak 1.3%, Chinese 1.2%, other 15% (2010 est.)Languages:Bahasa Indonesia (official, modified form of Malay), English, Dutch, local dialects (of which the most widely spoken is Javanese)
note: more than 700 languages are used in Indonesia
Religions:Muslim 87.2%, Protestant 7%, Roman Catholic 2.9%, Hindu 1.7%, other 0.9% (includes Buddhist and Confucian), unspecified 0.4% (2010 est.)Age structure:0-14 years: 24.63% (male 32,967,727 /female 31,757,882)15-24 years: 16.94% (male 22,661,264 /female 21,852,006)25-54 years: 42.44% (male 57,097,131 /female 54,433,239)55-64 years: 8.73% (male 10,447,365 /female 12,494,036)65 years and over: 7.26% (male 8,326,858 /female 10,749,895) (2018 est.)population pyramid: The World Factbook Field Image ModalEast Asia/Southeast Asia :: Indonesia Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalEast Asia/Southeast Asia :: Indonesia Print Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Indonesia. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Indonesia. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 49.2 (2015 est.)youth dependency ratio: 41.6 (2015 est.)elderly dependency ratio: 7.6 (2015 est.)potential support ratio: 13.2 (2015 est.)Median age:total: 30.5 years (2018 est.)male: 29.9 yearsfemale: 31.1 yearscountry comparison to the world: 116Population growth rate:0.83% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 127Birth rate:15.9 births/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 113Death rate:6.5 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 143Net migration rate:-1.1 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 143Population distribution:major concentration on the island of Java, which is considered one of the most densely populated places on earth; of the outer islands (those surrounding Java and Bali), Sumatra contains some of the most significant clusters, particularly in the south near the Selat Sunda, and along the northeastern coast near Medan; the cities of Makasar (Sulawesi), Banjarmasin (Kalimantan) are also heavily populatedUrbanization:urban population: 56% of total population (2019)rate of urbanization: 2.27% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:10.639 million JAKARTA (capital), 3.277 million Bekasi, 2.922 million Surabaya, 2.558 million Bandung, 2.311 million Medan, 2.28 million Tangerang (2019)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.05 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.84 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.77 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1 male(s)/female (2018 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:22.8 years (2012 est.)note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
Maternal mortality rate:177 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 52Infant mortality rate:total: 21.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)male: 25.7 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 17.9 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 73Life expectancy at birth:total population: 73.2 years (2018 est.)male: 70.6 yearsfemale: 76 yearscountry comparison to the world: 142Total fertility rate:2.08 children born/woman (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 104Contraceptive prevalence rate:61% (2016/17)Drinking water source:improved: urban: 94.2% of populationrural: 79.5% of populationtotal: 87.4% of populationunimproved: urban: 5.8% of populationrural: 20.5% of populationtotal: 12.6% of population (2015 est.)Current Health Expenditure:3.1% (2016)Physicians density:0.38 physicians/1,000 population (2017)Hospital bed density:1.2 beds/1,000 population (2015)Sanitation facility access:improved: urban: 72.3% of population (2015 est.)rural: 47.5% of population (2015 est.)total: 60.8% of population (2015 est.)unimproved: urban: 27.7% of population (2015 est.)rural: 52.5% of population (2015 est.)total: 39.2% of population (2015 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.4% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 81HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:640,000 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 14HIV/AIDS - deaths:38,000 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 5Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: very high (2016)food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever (2016)vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria (2016)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:6.9% (2016)country comparison to the world: 162Children under the age of 5 years underweight:19.9% (2013)country comparison to the world: 28Education expenditures:3.6% of GDP (2015)country comparison to the world: 120Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 95.4%male: 97.2%female: 93.6% (2016)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 13 yearsmale: 13 yearsfemale: 13 years (2017)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 15.6%male: 15.6%female: 15.6% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 86 -
Government :: Indonesia
-
Country name:conventional long form: Republic of Indonesiaconventional short form: Indonesialocal long form: Republik Indonesialocal short form: Indonesiaformer: Netherlands East Indies, Dutch East Indiesetymology: the name is an 18th-century construct of two Greek words, "Indos" (India) and "nesoi" (islands), meaning "Indian islands"Government type:presidential republicCapital:name: Jakartageographic coordinates: 6 10 S, 106 49 Etime difference: UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
note: Indonesia has three time zones
etymology: "Jakarta" derives from the Sanscrit "Jayakarta" meaning "victorious city" and refers to a successful defeat and expulsion of the Portuguese in 1527; previously the port had been named "Sunda Kelapa"Administrative divisions:31 provinces (provinsi-provinsi, singular - provinsi), 1 autonomous province*, 1 special region** (daerah-daerah istimewa, singular - daerah istimewa), and 1 national capital district*** (daerah khusus ibukota); Aceh*, Bali, Banten, Bengkulu, Gorontalo, Jakarta***, Jambi, Jawa Barat (West Java), Jawa Tengah (Central Java), Jawa Timur (East Java), Kalimantan Barat (West Kalimantan), Kalimantan Selatan (South Kalimantan), Kalimantan Tengah (Central Kalimantan), Kalimantan Timur (East Kalimantan), Kalimantan Utara (North Kalimantan), Kepulauan Bangka Belitung (Bangka Belitung Islands), Kepulauan Riau (Riau Islands), Lampung, Maluku, Maluku Utara (North Maluku), Nusa Tenggara Barat (West Nusa Tenggara), Nusa Tenggara Timur (East Nusa Tenggara), Papua, Papua Barat (West Papua), Riau, Sulawesi Barat (West Sulawesi), Sulawesi Selatan (South Sulawesi), Sulawesi Tengah (Central Sulawesi), Sulawesi Tenggara (Southeast Sulawesi), Sulawesi Utara (North Sulawesi), Sumatera Barat (West Sumatra), Sumatera Selatan (South Sumatra), Sumatera Utara (North Sumatra), Yogyakarta**note: following the implementation of decentralization beginning on 1 January 2001, regencies and municipalities have become the key administrative units responsible for providing most government services
Independence:17 August 1945 (declared independence from the Netherlands)National holiday:Independence Day, 17 August (1945)Constitution:history: drafted July to August 1945, effective 18 August 1945, abrogated by 1949 and 1950 constitutions; 1945 constitution restored 5 July 1959amendments: proposed by the People’s Consultative Assembly, with at least two thirds of its members present; passage requires simple majority vote by the Assembly membership; constitutional articles on the unitary form of the state cannot be amended; amended several times, last in 2002 (2017)Legal system:civil law system based on the Roman-Dutch model and influenced by customary lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtCitizenship:citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Indonesiadual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 5 continuous yearsSuffrage:17 years of age; universal and married persons regardless of ageExecutive branch:chief of state: President Joko WIDODO (since 20 October 2014, reelected 17 April 2019, inauguration 19 October 2019); Vice President Ma'ruf AMIN (since 20 October 2019); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government (2019)head of government: President Joko WIDODO (since 20 October 2014); Vice President Ma'ruf AMIN (since 20 October 2019) (2019)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the presidentelections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 17 April 2019 (next election 2024)election results: Joko WIDODO elected president; percent of vote - Joko WIDODO (PDI-P) 55.5%, PRABOWO Subianto Djojohadikusumo (GERINDRA) 44.5%Legislative branch:description: bicameral People's Consultative Assembly or Majelis Permusyawaratan Rakyat consists of:
Regional Representative Council or Dewan Perwakilan Daerah (136 seats; non-partisan members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies - 4 each from the country's 34 electoral districts - by proportional representation vote to serve 5-year terms); note - the Regional Representative Council has no legislative authority
House of Representatives or Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat (575 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by single non-transferable vote to serve 5-year terms) (2019)elections: Regional Representative Council - last held 17 April 2019 (next to be held 2024)
House of Representatives - last held on 17 April 2019 (next to be held 2024) (2019)election results: Regional Representative Council - all seats elected on a non-partisan basis
House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - PDI-P 19.3%, Gerindra 12.6%, Golkar 12.3%, PKB 9.7%, Nasdem 9.1%, PKS 8.2%, PD 7.8%, PAN 6.8%, PPP 4.5%, other 9.6%; seats by party - PDI-P 128, Golkar 85, Gerindra 78, Nasdem 59, PKB 58, PD 54, PKS 50, PAN 44, PPP 19; composition - men 475, women 100, percent of women 17.9%; total People's Consultative Assembly percent of women 28% (2019)Judicial branch:highest courts: Supreme Court or Mahkamah Agung (51 judges divided into 8 chambers); Constitutional Court or Mahkamah Konstitusi (consists of 9 judges)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges nominated by Judicial Commission, appointed by president with concurrence of parliament; judges serve until retirement at age 65; Constitutional Court judges - 3 nominated by president, 3 by Supreme Court, and 3 by parliament; judges appointed by the president; judges serve until mandatory retirement at age 70subordinate courts: High Courts of Appeal, district courts, religious courtsPolitical parties and leaders:Democrat Party or PD [Susilo Bambang YUDHOYONO]
Functional Groups Party or GOLKAR [Airlangga HARTARTO]
Great Indonesia Movement Party or GERINDRA [PRABOWO Subianto Djojohadikusumo]
Indonesia Democratic Party-Struggle or PDI-P [MEGAWATI Sukarnoputri]
National Awakening Party or PKB [Muhaiman ISKANDAR]
National Democratic Party or NasDem [Surya PALOH]
National Mandate Party or PAN [Zulkifli HASAN]
Party of the Functional Groups or Golkar [Airlangga HARTARTO]
People's Conscience Party or HANURA [Oesman Sapta ODANG]
Prosperous Justice Party or PKS [Muhammad Sohibul IMAN]
United Development Party or PPP [Muhammad ROMAHURMUZIY] (2019)International organization participation:ADB, APEC, ARF, ASEAN, BIS, CD, CICA (observer), CP, D-8, EAS, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-11, G-15, G-20, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IORA, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, MSG (associate member), NAM, OECD (enhanced engagement), OIC, OPCW, PIF (partner), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:Ambassador Mahendra SIREGAR (since 8 April 2019)chancery: 2020 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036telephone: [1] (202) 775-5200FAX: [1] (202) 775-5365consulate(s) general: Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, New York, San FranciscoDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Joseph R. DONOVAN, Jr. (since 12 January 2017)telephone: [62] (21) 5083-1000 (2018)embassy: Jalan Medan Merdeka Selatan 3-5, Jakarta 10110mailing address: Unit 8129, Box 1, FPO AP 96520FAX: [62] (21) 2395-1697 (2018)consulate(s) general: Surabayaconsulate(s): MedanFlag description:two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and white; the colors derive from the banner of the Majapahit Empire of the 13th-15th centuries; red symbolizes courage, white represents puritynote: similar to the flag of Monaco, which is shorter; also similar to the flag of Poland, which is white (top) and red
National symbol(s):garuda (mythical bird); national colors: red, whiteNational anthem:name: "Indonesia Raya" (Great Indonesia)lyrics/music: Wage Rudolf SOEPRATMANnote: adopted 1945
-
Economy :: Indonesia
-
Economy - overview:
Indonesia, the largest economy in Southeast Asia, has seen a slowdown in growth since 2012, mostly due to the end of the commodities export boom. During the global financial crisis, Indonesia outperformed its regional neighbors and joined China and India as the only G20 members posting growth. Indonesia’s annual budget deficit is capped at 3% of GDP, and the Government of Indonesia lowered its debt-to-GDP ratio from a peak of 100% shortly after the Asian financial crisis in 1999 to 34% today. In May 2017 Standard & Poor’s became the last major ratings agency to upgrade Indonesia’s sovereign credit rating to investment grade.
Poverty and unemployment, inadequate infrastructure, corruption, a complex regulatory environment, and unequal resource distribution among its regions are still part of Indonesia’s economic landscape. President Joko WIDODO - elected in July 2014 – seeks to develop Indonesia’s maritime resources and pursue other infrastructure development, including significantly increasing its electrical power generation capacity. Fuel subsidies were significantly reduced in early 2015, a move which has helped the government redirect its spending to development priorities. Indonesia, with the nine other ASEAN members, will continue to move towards participation in the ASEAN Economic Community, though full implementation of economic integration has not yet materialized.
GDP (purchasing power parity):$3.25 trillion (2017 est.)$3.093 trillion (2016 est.)$2.945 trillion (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 7GDP (official exchange rate):$1.015 trillion (2017 est.)GDP - real growth rate:5.1% (2017 est.)5% (2016 est.)4.9% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 47GDP - per capita (PPP):$12,400 (2017 est.)$12,000 (2016 est.)$11,500 (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 127Gross national saving:31.7% of GDP (2017 est.)32% of GDP (2016 est.)32% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 27GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 57.3% (2017 est.)government consumption: 9.1% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 32.1% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: 0.3% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 20.4% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -19.2% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 13.7% (2017 est.)industry: 41% (2017 est.)services: 45.4% (2017 est.)Agriculture - products:rubber and similar products, palm oil, poultry, beef, forest products, shrimp, cocoa, coffee, medicinal herbs, essential oil, fish and its similar products, and spicesIndustries:petroleum and natural gas, textiles, automotive, electrical appliances, apparel, footwear, mining, cement, medical instruments and appliances, handicrafts, chemical fertilizers, plywood, rubber, processed food, jewelry, and tourismIndustrial production growth rate:4.1% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 73Labor force:125 million (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 4Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 32%industry: 21%services: 47% (2016 est.)Unemployment rate:5.4% (2017 est.)5.6% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 79Population below poverty line:10.9% (2016 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 3.4%highest 10%: 28.2% (2010)Distribution of family income - Gini index:36.8 (2009)39.4 (2005)country comparison to the world: 84Budget:revenues: 131.7 billion (2017 est.)expenditures: 159.6 billion (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues:13% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 208Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-2.7% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 121Public debt:28.8% of GDP (2017 est.)28.3% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 166Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):3.8% (2017 est.)3.5% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 150Central bank discount rate:6.37% (31 December 2010)6.46% (31 December 2009)note: this figure represents the 3-month SBI rate; the Bank of Indonesia has not employed the one-month SBI since September 2010
country comparison to the world: 65Commercial bank prime lending rate:11.07% (31 December 2017 est.)11.89% (31 December 2016 est.)note: these figures represent the average annualized rate on working capital loanscountry comparison to the world: 74Stock of narrow money:$102.7 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$92.11 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 40Stock of broad money:$102.7 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$92.11 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 40Stock of domestic credit:$422.4 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$397.7 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 29Market value of publicly traded shares:$523.8 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$426 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$353.3 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 22Current account balance:-$17.33 billion (2017 est.)-$16.95 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 197Exports:$168.9 billion (2017 est.)$144.4 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 29Exports - partners:China 13.6%, US 10.6%, Japan 10.5%, India 8.4%, Singapore 7.6%, Malaysia 5.1%, South Korea 4.8% (2017)Exports - commodities:mineral fuels, animal or vegetable fats (includes palm oil), electrical machinery, rubber, machinery and mechanical appliance partsImports:$150.1 billion (2017 est.)$129.2 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 31Imports - commodities:mineral fuels, boilers, machinery, and mechanical parts, electric machinery, iron and steel, foodstuffsImports - partners:China 23.2%, Singapore 10.9%, Japan 10%, Thailand 6%, Malaysia 5.6%, South Korea 5.3%, US 5.2% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$130.2 billion (31 December 2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 19Debt - external:$344.4 billion (31 December 2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 30Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$251.5 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$229.1 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 26Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$20.5 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$18.42 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 53Exchange rates:Indonesian rupiah (IDR) per US dollar -13,385 (2017 est.)13,308.3 (2016 est.)13,308.3 (2015 est.)13,389.4 (2014 est.)11,865.2 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Indonesia
-
Electricity access:population without electricity: 14 million (2017)electrification - total population: 97.6% (2016)electrification - urban areas: 100% (2016)electrification - rural areas: 94.8% (2016)Electricity - production:235.4 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 20Electricity - consumption:213.4 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 20Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 149Electricity - imports:693 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 76Electricity - installed generating capacity:61.43 million kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 19Electricity - from fossil fuels:85% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 110Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:9% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 118Electricity - from other renewable sources:6% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 99Crude oil - production:772,000 bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 24Crude oil - exports:302,300 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 27Crude oil - imports:498,500 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 18Crude oil - proved reserves:3.31 billion bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 28Refined petroleum products - production:950,000 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 18Refined petroleum products - consumption:1.601 million bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 14Refined petroleum products - exports:79,930 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 47Refined petroleum products - imports:591,500 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 15Natural gas - production:72.09 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 12Natural gas - consumption:42.32 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 23Natural gas - exports:29.78 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 12Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 141Natural gas - proved reserves:2.866 trillion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 12Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:540.7 million Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 12
-
Communications :: Indonesia
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 11,172,021subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 18Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 458,923,202subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 176 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 3Telephone system:general assessment: domestic service includes an interisland microwave system, an HF radio police net, and a domestic satellite communications system; international service good; Indonesia has very low fixed line and fixed broadband penetration, high mobile penetration and moderate mobile broadband penetration (2018)domestic: fixed-line 4 per 100 and mobile-cellular 175 per 100 persons; coverage provided by existing network has been expanded by use of over 200,000 telephone kiosks many located in remote areas; mobile-cellular subscribership growing rapidly (2018)international: country code - 62; landing points for the SEA-ME-WE-3 & 5, DAMAI, JASUKA, BDM, Dumai-Melaka Cable System, IGG, JIBA, Link 1, 3, 4, & 5, PGASCOM, B3J2, Tanjung Pandam-Sungai Kakap Cable System, JAKABARE, JAYABAYA, INDIGO-West, Matrix Cable System, ASC, SJJK, Jaka2LaDeMa, S-U-B Cable System, JBCS, MKCS, BALOK, Palapa Ring East, West and Middle, SMPCS Packet-1 and 2, LTCS, TSCS, SEA-US and Kamal Domestic Submarine Cable System, 35 submarine cable networks that provide links throughout Asia, the Middle East, Australia, Southeast Asia, Africa and Europe; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Indian Ocean and 1 Pacific Ocean) (2019)Broadcast media:mixture of about a dozen national TV networks - 1 public broadcaster, the remainder private broadcasters - each with multiple transmitters; more than 100 local TV stations; widespread use of satellite and cable TV systems; public radio broadcaster operates 6 national networks, as well as regional and local stations; overall, more than 700 radio stations with more than 650 privately operated (2019)Internet country code:.idInternet users:total: 65,525,226percent of population: 25.4% (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 10Broadband - fixed subscriptions:total: 6,044,712subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 2 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 25
-
Military and Security :: Indonesia
-
Military expenditures:0.72% of GDP (2018)0.84% of GDP (2017)0.88% of GDP (2016)0.89% of GDP (2015)0.78% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 135Military and security forces:Indonesian National Armed Forces (Tentara Nasional Indonesia, TNI): Army (TNI-Angkatan Darat (TNI-AD)), Navy (TNI-Angkatan Laut (TNI-AL), includes marines (Korps Marinir, KorMar), naval air arm), Air Force (TNI-Angkatan Udara (TNI-AU)), National Air Defense Command (Komando Pertahanan Udara Nasional (Kohanudnas)), Armed Forces Special Operations Command (Koopssus), Strategic Reserve Command (Kostrad) (2019)Military service age and obligation:18-45 years of age for voluntary military service, with selective conscription authorized; 2-year service obligation, with reserve obligation to age 45 (officers); Indonesian citizens only (2013)Maritime threats:The International Maritime Bureau continues to report the territorial and offshore waters in the Strait of Malacca and South China Sea as high risk for piracy and armed robbery against ships; attacks declined for the third year in a row from 43 incidents in 2016 to 36 in 2018 due to aggressive maritime patrolling by regional authorities; in 2018, 29 commercial vessels were boarded and three crew members were taken hostage; hijacked vessels are often disguised and cargo diverted to ports in East Asia (2018)
-
Transportation :: Indonesia
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 29 (2015)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 550 (2015)annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 88,685,767 (2015)annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 747,473,207 mt-km (2015)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:PK (2016)Airports:673 (2013)country comparison to the world: 10Airports - with paved runways:total: 186 (2017)over 3,047 m: 5 (2017)2,438 to 3,047 m: 21 (2017)1,524 to 2,437 m: 51 (2017)914 to 1,523 m: 72 (2017)under 914 m: 37 (2017)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 487 (2013)1,524 to 2,437 m: 4 (2013)914 to 1,523 m: 23 (2013)under 914 m: 460 (2013)Heliports:76 (2013)Pipelines:1064 km condensate, 150 km condensate/gas, 11702 km gas, 119 km liquid petroleum gas, 7767 km oil, 77 km oil/gas/water, 728 km refined products, 53 km unknown, 44 km water (2013)Railways:total: 8,159 km (2014)narrow gauge: 8,159 km 1.067-m gauge (565 km electrified) (2014)
note: 4,816 km operational
country comparison to the world: 27Roadways:total: 496,607 km (2011)paved: 283,102 km (2011)unpaved: 213,505 km (2011)country comparison to the world: 14Waterways:21,579 km (2011)country comparison to the world: 7Merchant marine:total: 9,053by type: bulk carrier 97, container ship 205, general cargo 2203, oil tanker 567, other 5981 (2018)country comparison to the world: 1Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Banjarmasin, Belawan, Kotabaru, Krueg Geukueh, Palembang, Panjang, Sungai Pakning, Tanjung Perak, Tanjung Priokcontainer port(s) (TEUs): Tanjung Perak (3,553,370), Tanjung Priok (6,090,000) (2017)LNG terminal(s) (export): Bontang, TangguhLNG terminal(s) (import): Arun, Lampung, West Java -
Terrorism :: Indonesia
-
Terrorist groups - home based:ISIS-associated Jemaah Anshorut Daulah (JAD): aim(s): establish an Islamic caliphate in Indonesia
area(s) of operation: an ISIS-aligned coalition of cells located throughout the country (2018)Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham (ISIS) network in Indonesia: aim(s): replace the Indonesian Government with an Islamic state and implement ISIS's strict interpretation of sharia
area(s) of operation: maintains a covert operational presence (2018)Jemaah Islamiyah (JI): aim(s): overthrow the Indonesian Government and, ultimately, establish a pan-Islamic state across Southeast Asia
area(s) of operation: Indonesia (2018) -
Transnational Issues :: Indonesia
-
Disputes - international:
Indonesia has a stated foreign policy objective of establishing stable fixed land and maritime boundaries with all of its neighbors; three stretches of land borders with Timor-Leste have yet to be delimited, two of which are in the Oecussi exclave area, and no maritime or Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) boundaries have been established between the countries; all borders between Indonesia and Australia have been agreed upon bilaterally, but a 1997 treaty that would settle the last of their maritime and EEZ boundary has yet to be ratified by Indonesia's legislature; Indonesian groups challenge Australia's claim to Ashmore Reef; Australia has closed parts of the Ashmore and Cartier Reserve to Indonesian traditional fishing and placed restrictions on certain catches; land and maritime negotiations with Malaysia are ongoing, and disputed areas include the controversial Tanjung Datu and Camar Wulan border area in Borneo and the maritime boundary in the Ambalat oil block in the Celebes Sea; Indonesia and Singapore continue to work on finalizing their 1973 maritime boundary agreement by defining unresolved areas north of Indonesia's Batam Island; Indonesian secessionists, squatters, and illegal migrants create repatriation problems for Papua New Guinea; maritime delimitation talks continue with Palau; EEZ negotiations with Vietnam are ongoing, and the two countries in Fall 2011 agreed to work together to reduce illegal fishing along their maritime boundary
Refugees and internally displaced persons:refugees (country of origin): 6,098 (Afghanistan) (2018)IDPs: 16,000 (inter-communal, inter-faith, and separatist violence between 1998 and 2004 in Aceh and Papua; religious attacks and land conflicts in 2012 and 2013; most IDPs in Aceh, Maluku, East Nusa Tengarra) (2018)Illicit drugs:illicit producer of cannabis largely for domestic use; producer of methamphetamine and ecstasy; President WIDODO's war on drugs has led to an increase in death sentences and executions, particularly of foreign drug traffickers