
-
Introduction :: Slovakia
-
Background:Slovakia traces its roots to the 9th century state of Great Moravia. Subsequently, the Slovaks became part of the Hungarian Kingdom, where they remained for the next 1,000 years. After the formation of the dual Austro-Hungarian monarchy in 1867, backlash to language and education policies favoring the use of Hungarian (Magyarization) encouraged the strengthening of Slovak nationalism and a cultivation of cultural ties with the closely related Czechs, who fell administratively under the Austrian half of the empire. After the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire at the close of World War I, the Slovaks joined the Czechs to form Czechoslovakia. The new state was envisioned as a nation with Czech and Slovak branches. During the interwar period, Slovak nationalist leaders pushed for autonomy within Czechoslovakia, and in 1939 Slovakia became an independent state created by and allied with Nazi Germany. Following World War II, Czechoslovakia was reconstituted and came under communist rule within Soviet-dominated Eastern Europe. In 1968, an invasion by Warsaw Pact troops ended the efforts of Czechoslovakia's leaders to liberalize communist rule and create "socialism with a human face," ushering in a period of repression known as "normalization." The peaceful "Velvet Revolution" swept the Communist Party from power at the end of 1989 and inaugurated a return to democratic rule and a market economy. On 1 January 1993, Czechoslovakia underwent a nonviolent "velvet divorce" into its two national components, Slovakia and the Czech Republic. Slovakia joined both NATO and the EU in the spring of 2004 and the euro zone on 1 January 2009.
-
Geography :: Slovakia
-
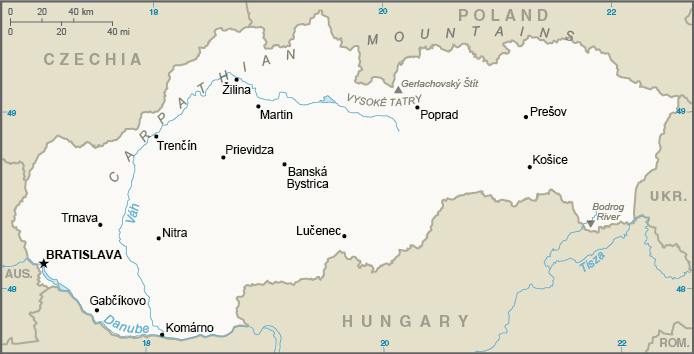
Location:Central Europe, south of PolandGeographic coordinates:48 40 N, 19 30 EMap references:EuropeArea:total: 49,035 sq kmland: 48,105 sq kmwater: 930 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 131Area - comparative:about one and a half times the size of Maryland; about twice the size of New HampshireArea comparison map:
 The World Factbook Field Image ModalEurope :: Slovakia Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalEurope :: Slovakia Print Image Description
Image Descriptionabout one and a half times the size of Maryland; about twice the size of New Hampshire
Land boundaries:total: 1,611 kmborder countries (5): Austria 105 km, Czech Republic 241 km, Hungary 627 km, Poland 541 km, Ukraine 97 kmCoastline:0 km (landlocked)Maritime claims:none (landlocked)Climate:temperate; cool summers; cold, cloudy, humid wintersTerrain:rugged mountains in the central and northern part and lowlands in the southElevation:mean elevation: 458 mlowest point: Bodrok River 94 mhighest point: Gerlachovsky Stit 2,655 mNatural resources:lignite, small amounts of iron ore, copper and manganese ore; salt; arable landLand use:agricultural land: 40.1% (2011 est.)arable land: 28.9% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0.4% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 10.8% (2011 est.)forest: 40.2% (2011 est.)other: 19.7% (2011 est.)Irrigated land:869 sq km (2012)Population distribution:a fairly even distribution throughout most of the country; slightly larger concentration in the west in proximity to the Czech borderNatural hazards:floodingEnvironment - current issues:air pollution and acid rain present human health risks and damage forests; land erosion caused by agricultural and mining practices; water pollutionEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:landlocked; most of the country is rugged and mountainous; the Tatra Mountains in the north are interspersed with many scenic lakes and valleys -
People and Society :: Slovakia
-
Population:5,445,040 (July 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 118Nationality:noun: Slovak(s)adjective: SlovakEthnic groups:Slovak 80.7%, Hungarian 8.5%, Romani 2%, other 1.8% (includes Czech, Ruthenian, Ukrainian, Russian, German, Polish), unspecified 7% (2011 est.)
note: data represent population by nationality; Romani populations are usually underestimated in official statistics and may represent 7–11% of Slovakia's population
Languages:Slovak (official) 78.6%, Hungarian 9.4%, Roma 2.3%, Ruthenian 1%, other or unspecified 8.8% (2011 est.)Religions:Roman Catholic 62%, Protestant 8.2%, Greek Catholic 3.8%, other or unspecified 12.5%, none 13.4% (2011 est.)Age structure:0-14 years: 15.2% (male 424,921 /female 402,483)15-24 years: 10.48% (male 293,573 /female 277,041)25-54 years: 45.04% (male 1,239,670 /female 1,212,687)55-64 years: 13.32% (male 345,114 /female 380,077)65 years and over: 15.97% (male 339,350 /female 530,124) (2018 est.)population pyramid: The World Factbook Field Image ModalEurope :: Slovakia Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalEurope :: Slovakia Print Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Slovakia. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Slovakia. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 41.5 (2015 est.)youth dependency ratio: 21.6 (2015 est.)elderly dependency ratio: 19.9 (2015 est.)potential support ratio: 5 (2015 est.)Median age:total: 41 years (2018 est.)male: 39.3 yearsfemale: 42.7 yearscountry comparison to the world: 46Population growth rate:-0.02% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 197Birth rate:9.6 births/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 198Death rate:9.9 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 38Net migration rate:0.1 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 73Population distribution:a fairly even distribution throughout most of the country; slightly larger concentration in the west in proximity to the Czech borderUrbanization:urban population: 53.7% of total population (2019)rate of urbanization: 0% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:433,000 BRATISLAVA (capital) (2019)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.06 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.91 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.64 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.94 male(s)/female (2018 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:27.6 years (2014 est.)Maternal mortality rate:5 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 170Infant mortality rate:total: 5 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)male: 5.7 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 4.4 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 176Life expectancy at birth:total population: 77.4 years (2018 est.)male: 73.9 yearsfemale: 81.2 yearscountry comparison to the world: 74Total fertility rate:1.42 children born/woman (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 210Drinking water source:improved: urban: 100% of populationrural: 100% of populationtotal: 100% of populationunimproved: urban: 0% of populationrural: 0% of populationtotal: 0% of population (2015 est.)Current Health Expenditure:7.1% (2016)Physicians density:2.46 physicians/1,000 population (2016)Hospital bed density:5.8 beds/1,000 population (2015)Sanitation facility access:improved: urban: 99.4% of population (2015 est.)rural: 98.2% of population (2015 est.)total: 98.8% of population (2015 est.)unimproved: urban: 0.6% of population (2015 est.)rural: 1.8% of population (2015 est.)total: 1.2% of population (2015 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:<.1% (2018 est.)HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:1,200 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 141HIV/AIDS - deaths:<100 (2018 est.)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:20.5% (2016)country comparison to the world: 98Education expenditures:3.9% of GDP (2016)country comparison to the world: 109School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 15 yearsmale: 14 yearsfemale: 16 years (2016)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 18.9%male: 18.1%female: 20.2% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 72 -
Government :: Slovakia
-
Country name:conventional long form: Slovak Republicconventional short form: Slovakialocal long form: Slovenska republikalocal short form: Slovenskoetymology: related to the Slavic autonym (self-designation) "Slovenin," a derivation from "slovo" (meaning "word"), denoting "people who speak (the same language)" (i.e., people who understand each other)Government type:parliamentary republicCapital:name: Bratislavageographic coordinates: 48 09 N, 17 07 Etime difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in Octoberetymology: "slava" means glory, so the city's name literally means "Braslav's glory"; Braslav was a ninth century Slavic dukeAdministrative divisions:8 regions (kraje, singular - kraj); Banskobystricky, Bratislavsky, Kosicky, Nitriansky, Presovsky, Trenciansky, Trnavsky, ZilinskyIndependence:1 January 1993 (Czechoslovakia split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia)National holiday:Constitution Day, 1 September (1992)Constitution:history: several previous (preindependence); latest passed by the National Council 1 September 1992, signed 3 September 1992, effective 1 October 1992amendments: proposed by the National Council; passage requires at least three-fifths majority vote of Council members; amended many times, last in 2017 (2017)Legal system:civil law system based on Austro-Hungarian codes; note - legal code modified to comply with the obligations of Organization on Security and Cooperation in EuropeInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictionCitizenship:citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Slovakiadual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 5 yearsSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Zuzana CAPUTOVA (since 15 June 2014)head of government: Prime Minister Peter PELLIGRINI (since 22 March 2018); Deputy Prime Ministers Richard RASI (since 22 March 2018), Laszlo SOLYMOS (since 22 March 2018), Gabriela MATECNA (since 29 November 2017)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime ministerelections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 16 March and 30 March 2019 (next to be held March 2024); following National Council elections (every 4 years), the president designates a prime minister candidate, usually the leader of the party or coalition that wins the most votes, who must win a vote of confidence in the National Councilelection results: Zuzana CAPUTOVA elected president in second round; percent of vote - Zuzana CAPUTOVA (PS) 58.4%, Maros SEFCOVIC (independent) 41.6%Legislative branch:description: unicameral National Council or Narodna Rada (150 seats; members directly elected in a single- and multi-seat constituencies by closed, party-list proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)elections: last held on 5 March 2016 (next to be held in March 2020)election results: percent of vote by party - Smer-SD 28.3%, SaS 12.1%, OLaNO-NOVA 11%, SNS 8.6%, LSNS 8%, Sme-Rodina 6.6%, Most-Hid 6.5%, Siet 5.6%, other 13.3%; seats by party - Smer-SD 49, SaS 21, OLaNO-NOVA 19, SNS 15, LSNS 14, Sme-Rodina 11, Most-Hid 11, Siet 10; composition - men 120, women 30, percent of women 20%
note - seats by party as of May 2019 - Smer-SD 48, SaS 20, OLaNO-NOVA 16, SNS 15, LSNS 13, Sme-Rodina 8, Most-Hid 13, independent 17; composition as of May 2019 - men 118, women 32, percent of women 21.3%Judicial branch:highest courts: Supreme Court of the Slovak Republic (consists of the court president, vice president, and approximately 80 judges organized into criminal, civil, commercial, and administrative divisions with 3- and 5-judge panels); Constitutional Court of the Slovak Republic (consists of 13 judges organized into 3-judge panels)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judge candidates nominated by the Judicial Council of the Slovak Republic, an 18-member self-governing body that includes the Supreme Court chief justice and presidential, governmental, parliamentary, and judiciary appointees; judges appointed by the president serve for life subject to removal by the president at age 65; Constitutional Court judges nominated by the National Council of the Republic and appointed by the president; judges serve 12-year termssubordinate courts: regional and district civil courts; Special Criminal Court; Higher Military Court; military district courts; Court of Audit;Political parties and leaders:Christian Democratic Movement or KDH [Alojz HLINA]
Bridge or Most-Hid [Bela BUGAR]
Direction-Social Democracy or Smer-SD [Robert FICO]
Freedom and Solidarity or SaS [Richard SULIK]
Kotleba-People's Party Our Slovakia or LSNS [Marian KOTLEBA]
Ordinary People and Independent Personalities - New Majority or OLaNO-NOVA [Igor MATOVIC]
Party of the Hungarian Community or SMK [Jozsef MENYHART]
Progressive Slovakia or PS [Michal TRUBAN]
Slovak National Party or SNS [Andrej DANKO]
Together or Spolu [Miroslav BEBLAVY]
We Are Family or Sme-Rodina [Boris KOLLAR]International organization participation:Australia Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CBSS (observer), CD, CE, CEI, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, EU, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, SELEC (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNIDO, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZCDiplomatic representation in the US:Ambassador Ivan KORCOK (since 17 September 2018)chancery: 3523 International Court NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 237-1054FAX: [1] (202) 237-6438consulate(s) general: Los Angeles, New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Bridget A. BRINK (since 20 August 2019)telephone: [421] (2) 5443-3338embassy: P.O. Box 309, 814 99 Bratislavamailing address: P.O. Box 309, 814 99 BratislavaFAX: [421] (2) 5441-5148Flag description:three equal horizontal bands of white (top), blue, and red derive from the Pan-Slav colors; the Slovakian coat of arms (consisting of a red shield bordered in white and bearing a white double-barred cross of St. Cyril and St. Methodius surmounting three blue hills) is centered over the bands but offset slightly to the hoist sidenote: the Pan-Slav colors were inspired by the 19th-century flag of Russia
National symbol(s):double-barred cross (Cross of St. Cyril and St. Methodius) surmounting three peaks; national colors: white, blue, redNational anthem:name: "Nad Tatrou sa blyska" (Lightning Over the Tatras)lyrics/music: Janko MATUSKA/traditionalnote: adopted 1993, in use since 1844; music based on the Slovak folk song "Kopala studienku"
-
Economy :: Slovakia
-
Economy - overview:
Slovakia’s economy suffered from a slow start in the first years after its separation from the Czech Republic in 1993, due to the country’s authoritarian leadership and high levels of corruption, but economic reforms implemented after 1998 have placed Slovakia on a path of strong growth. With a population of 5.4 million, the Slovak Republic has a small, open economy driven mainly by automobile and electronics exports, which account for more than 80% of GDP. Slovakia joined the EU in 2004 and the euro zone in 2009. The country’s banking sector is sound and predominantly foreign owned.
Slovakia has been a regional FDI champion for several years, attractive due to a relatively low-cost yet skilled labor force, and a favorable geographic location in the heart of Central Europe. Exports and investment have been key drivers of Slovakia’s robust growth in recent years. The unemployment rate fell to historical lows in 2017, and rising wages fueled increased consumption, which played a more prominent role in 2017 GDP growth. A favorable outlook for the Eurozone suggests continued strong growth prospects for Slovakia during the next few years, although inflation is also expected to pick up.
Among the most pressing domestic issues potentially threatening the attractiveness of the Slovak market are shortages in the qualified labor force, persistent corruption issues, and an inadequate judiciary, as well as a slow transition to an innovation-based economy. The energy sector in particular is characterized by unpredictable regulatory oversight and high costs, in part driven by government interference in regulated tariffs. Moreover, the government’s attempts to maintain low household energy prices could harm the profitability of domestic energy firms while undercutting energy efficiency initiatives.
GDP (purchasing power parity):$179.7 billion (2017 est.)$173.8 billion (2016 est.)$168.2 billion (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 69GDP (official exchange rate):$95.96 billion (2017 est.)GDP - real growth rate:3.4% (2017 est.)3.3% (2016 est.)3.9% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 102GDP - per capita (PPP):$33,100 (2017 est.)$32,000 (2016 est.)$31,000 (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 61Gross national saving:20.6% of GDP (2017 est.)21.1% of GDP (2016 est.)22.5% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 92GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 54.7% (2017 est.)government consumption: 19.2% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 21.2% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: 1.2% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 96.3% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -92.9% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 3.8% (2017 est.)industry: 35% (2017 est.)services: 61.2% (2017 est.)Agriculture - products:grains, potatoes, sugar beets, hops, fruit; pigs, cattle, poultry; forest productsIndustries:automobiles; metal and metal products; electricity, gas, coke, oil, nuclear fuel; chemicals, synthetic fibers, wood and paper products; machinery; earthenware and ceramics; textiles; electrical and optical apparatus; rubber products; food and beverages; pharmaceuticalIndustrial production growth rate:2.7% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 114Labor force:2.758 million (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 110Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 3.9%industry: 22.7%services: 73.4% (2015)Unemployment rate:8.1% (2017 est.)9.7% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 119Population below poverty line:12.3% (2015 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 3.3%highest 10%: 19.3% (2015 est.)Distribution of family income - Gini index:23.7 (2015)26.1 (2014)country comparison to the world: 155Budget:revenues: 37.79 billion (2017 est.)expenditures: 38.79 billion (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues:39.4% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 47Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-1% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 81Public debt:50.9% of GDP (2017 est.)51.8% of GDP (2016 est.)note: data cover general Government Gross Debt and include debt instruments issued (or owned) by Government entities, including sub-sectors of central, state, local government, and social security funds
country comparison to the world: 98Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):1.3% (2017 est.)-0.5% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 74Central bank discount rate:0% (31 December 2017 est.)0% (31 December 2016 est.)note: this is the European Central Bank's rate on the marginal lending facility, which offers overnight credit to banks from the euro area; Slovakia became a member of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) on 1 January 2009
country comparison to the world: 160Commercial bank prime lending rate:2.44% (31 December 2017 est.)2.7% (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 182Stock of narrow money:$56.46 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$45.63 billion (31 December 2016 est.)note: see entry for the European Union for money supply for the entire euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 18 members of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own borders
country comparison to the world: 51Stock of broad money:$56.46 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$45.63 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 51Stock of domestic credit:$85.56 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$70.84 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Market value of publicly traded shares:$4.567 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$4.634 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$4.732 billion (31 December 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 86Current account balance:-$2.005 billion (2017 est.)-$1.309 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 164Exports:$80.8 billion (2017 est.)$75.53 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 40Exports - partners:Germany 20.7%, Czech Republic 11.6%, Poland 7.7%, France 6.3%, Italy 6.1%, UK 6%, Hungary 6%, Austria 6% (2017)Exports - commodities:vehicles and related parts 27%, machinery and electrical equipment 20%, nuclear reactors and furnaces 12%, iron and steel 4%, mineral oils and fuels 5% (2015 est.)Imports:$80.07 billion (2017 est.)$72.51 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 42Imports - commodities:machinery and electrical equipment 20%, vehicles and related parts 14%, nuclear reactors and furnaces 12%, fuel and mineral oils 9% (2015 est.)Imports - partners:Germany 19.1%, Czech Republic 16.3%, Austria 10.3%, Poland 6.5%, Hungary 6.4%, South Korea 4.5%, Russia 4.5%, France 4.3%, China 4.2% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$3.622 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$2.892 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 102Debt - external:$75.04 billion (31 March 2016 est.)$74.19 billion (31 March 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 58Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$69.92 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$54.03 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 53Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$21.29 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$15.06 billion (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 51Exchange rates:euros (EUR) per US dollar -0.885 (2017 est.)0.903 (2016 est.)0.9214 (2015 est.)0.885 (2014 est.)0.7634 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Slovakia
-
Electricity access:electrification - total population: 100% (2016)Electricity - production:25.32 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 72Electricity - consumption:26.64 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 66Electricity - exports:10.6 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 19Electricity - imports:13.25 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 19Electricity - installed generating capacity:7.644 million kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 72Electricity - from fossil fuels:36% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 176Electricity - from nuclear fuels:27% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 3Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:24% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 81Electricity - from other renewable sources:13% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 70Crude oil - production:200 bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 95Crude oil - exports:1,022 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 74Crude oil - imports:111,200 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 42Crude oil - proved reserves:9 million bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Refined petroleum products - production:131,300 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Refined petroleum products - consumption:85,880 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 85Refined petroleum products - exports:81,100 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 46Refined petroleum products - imports:38,340 bbl/day (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Natural gas - production:104.8 million cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 81Natural gas - consumption:4.672 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Natural gas - imports:4.984 billion cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 37Natural gas - proved reserves:14.16 billion cu m (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:34.86 million Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 73
-
Communications :: Slovakia
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 758,842subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 14 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 83Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 7,117,753subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 131 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 105Telephone system:general assessment: a modern telecommunications system; near monopoly of fixed-line market; competition in mobile and fixed broadband market; poor mobile virtual network operator (MVNO); regulatory preparing for 5G; broadband growth in recent years; competition among DSL, cable and fibre platforms; wireless broadband options from mobile network operators; FttP growth in cities (2018)domestic: four companies have a license to operate cellular networks and provide nationwide cellular services (cellular operators); a few other companies provide services but do not have their own networks; fixed-line 14 per 100 and mobile-cellular 131 per 100 teledesity (2018)international: country code - 421; 3 international exchanges (1 in Bratislava and 2 in Banska Bystrica) are available; Slovakia is participating in several international telecommunications projects that will increase the availability of external services (2017)Broadcast media:state-owned public broadcaster, Radio and Television of Slovakia (RTVS), operates 2 national TV stations and multiple national and regional radio networks; roughly 50 privately owned TV stations operating nationally, regionally, and locally; about 40% of households are connected to multi-channel cable or satellite TV; 32 privately owned radio stationsInternet country code:.skInternet users:total: 4,382,558percent of population: 80.5% (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 82Broadband - fixed subscriptions:total: 1,404,751subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 26 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 62
-
Military and Security :: Slovakia
-
Military expenditures:1.74% of GDP (2019 est.)1.22% of GDP (2018)1.1% of GDP (2017)1.12% of GDP (2016)1.12% of GDP (2015)country comparison to the world: 66Military and security forces:Armed Forces of the Slovak Republic (Ozbrojene Sily Slovenskej Republiky): Land Forces, Air and Air Defense Forces, and a Joint Training and Support Command. (2019)Military service age and obligation:18-30 years of age for voluntary military service; conscription in peacetime suspended in 2006; women are eligible to serve (2012)
-
Transportation :: Slovakia
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 4 (2015)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 23 (2015)annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 11,100 (2015)annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 0 mt-km (2015)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:OM (2016)Airports:35 (2013)country comparison to the world: 111Airports - with paved runways:total: 19 (2019)over 3,047 m: 22,438 to 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 3914 to 1,523 m: 3under 914 m: 9Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 15 (2019)914 to 1,523 m: 10under 914 m: 5Heliports:1 (2019)Pipelines:2270 km gas transmission pipelines, 6278 km high-pressure gas distribution pipelines, 27023 km mid- and low-pressure gas distribution pipelines (2016), 510 km oil (2015)Railways:total: 3,580 km (2016)standard gauge: 3,435 km 1.435-m gauge (1,587 km electrified) (2016)narrow gauge: 46 km 1.000-m or 0.750-m gauge (2016)broad gauge: 99 km 1.520-m gauge (2016)country comparison to the world: 56Roadways:total: 56,926 km (includes local roads, national roads, and 464 km of highways) (2016)country comparison to the world: 80Waterways:172 km (on Danube River) (2012)country comparison to the world: 99Ports and terminals:river port(s): Bratislava, Komarno (Danube)
-
Transnational Issues :: Slovakia
-
Disputes - international:
bilateral government, legal, technical and economic working group negotiations continued between Slovakia and Hungary over Hungary's completion of its portion of the Gabcikovo-Nagymaros hydroelectric dam project along the Danube; as a member state that forms part of the EU's external border, Slovakia has implemented strict Schengen border rules
Refugees and internally displaced persons:stateless persons: 1,523 (2018)Illicit drugs:transshipment point for Southwest Asian heroin bound for Western Europe; producer of synthetic drugs for regional market; consumer of ecstasy