-
Introduction :: Nauru
-
Background:The exact origins of the Nauruans are unclear since their language does not resemble any other in the Pacific region. Germany annexed the island in 1888. A German-British consortium began mining the island's phosphate deposits early in the 20th century. Australian forces occupied Nauru in World War I; it subsequently became a League of Nations mandate. After the Second World War - and a brutal occupation by Japan - Nauru became a UN trust territory. It achieved independence in 1968 and joined the UN in 1999 as the world's smallest independent republic.
-
Geography :: Nauru
-
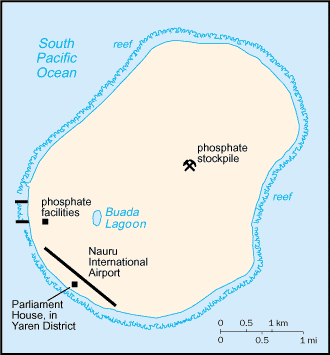
Location:Oceania, island in the South Pacific Ocean, south of the Marshall IslandsGeographic coordinates:0 32 S, 166 55 EMap references:OceaniaArea:total: 21 sq kmland: 21 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 240Area - comparative:about 0.1 times the size of Washington, DCLand boundaries:0 kmCoastline:30 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmClimate:tropical with a monsoonal pattern; rainy season (November to February)Terrain:sandy beach rises to fertile ring around raised coral reefs with phosphate plateau in centerElevation:lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 mhighest point: Command Ridge 70 mNatural resources:phosphates, fishLand use:agricultural land: 20% (2011 est.)arable land: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 20% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 0% (2011 est.)forest: 0% (2011 est.)other: 80% (2011 est.)Irrigated land:0 sq km (2012)Population distribution:extensive phosphate mining made approximately 90% of the island unsuitable for farming; most people live in the fertile coastal areas, especially along the southwest coastNatural hazards:periodic droughtsEnvironment - current issues:limited natural freshwater resources, roof storage tanks that collect rainwater and desalination plants provide water; a century of intensive phosphate mining beginning in 1906 left the central 90% of Nauru a wasteland; cadmium residue, phosphate dust, and other contaminants have caused air and water pollution with negative impacts on health; climate change has brought on rising sea levels and inland water shortagesEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:world's smallest island country; situated just 53 km south of the Equator; Nauru is one of the three great phosphate rock islands in the Pacific Ocean - the others are Banaba (Ocean Island) in Kiribati and Makatea in French Polynesia
-
People and Society :: Nauru
-
Population:9,692 (July 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 223Nationality:noun: Nauruan(s)adjective: NauruanEthnic groups:Nauruan 88.9%, part Nauruan 6.6%, I-Kiribati 2%, other 2.5% (2007 est.)Languages:Nauruan 93% (official, a distinct Pacific Island language), English 2% (widely understood, spoken, and used for most government and commercial purposes), other 5% (includes I-Kiribati 2% and Chinese 2%) (2011 est.)
note: percentages represent main language spoken at home; Nauruan is spoken by 95% of the population, English by 66%, and other languages by 12%
Religions:Protestant 60.4% (includes Nauru Congregational 35.7%, Assembly of God 13%, Nauru Independent Church 9.5%, Baptist 1.5%, and Seventh Day Adventist 0.7%), Roman Catholic 33%, other 3.7%, none 1.8%, unspecified 1.1% (2011 est.)Age structure:0-14 years: 31.18% (male 1,323 /female 1,699)15-24 years: 16.37% (male 764 /female 823)25-54 years: 43.08% (male 2,112 /female 2,063)55-64 years: 6.51% (male 249 /female 382)65 years and over: 2.86% (male 101 /female 176) (2018 est.)population pyramid: The World Factbook Field Image ModalAustralia - Oceania :: Nauru Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalAustralia - Oceania :: Nauru Print Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Nauru. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Nauru. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Median age:total: 26.7 years (2018 est.)male: 27.4 yearsfemale: 25.8 yearscountry comparison to the world: 149Population growth rate:0.51% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 153Birth rate:23.2 births/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Death rate:5.9 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 168Net migration rate:-12.3 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 218Population distribution:extensive phosphate mining made approximately 90% of the island unsuitable for farming; most people live in the fertile coastal areas, especially along the southwest coastUrbanization:urban population: 100% of total population (2019)rate of urbanization: -0.06% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Sex ratio:at birth: 0.84 male(s)/female0-14 years: 0.78 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.93 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.65 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.57 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.88 male(s)/female (2018 est.)Infant mortality rate:total: 7.7 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)male: 9.8 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 5.9 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 156Life expectancy at birth:total population: 67.8 years (2018 est.)male: 63.6 yearsfemale: 71.2 yearscountry comparison to the world: 170Total fertility rate:2.76 children born/woman (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Drinking water source:improved: urban: 96.5% of populationtotal: 96.5% of populationunimproved: urban: 3.5% of populationtotal: 3.5% of population (2015 est.)Current Health Expenditure:11.1% (2016)Physicians density:1.24 physicians/1,000 population (2015)Hospital bed density:5 beds/1,000 population (2010)Sanitation facility access:improved: urban: 65.6% of population (2015 est.)total: 65.6% of population (2015 est.)unimproved: urban: 34.4% of population (2015 est.)total: 34.4% of population (2015 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:NAHIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:NAHIV/AIDS - deaths:NAObesity - adult prevalence rate:61% (2016)country comparison to the world: 1Education expenditures:NASchool life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 9 yearsmale: 9 yearsfemale: 10 years (2008)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 26.6%male: 20.9%female: 37.5% (2013)country comparison to the world: 43 -
Government :: Nauru
-
Country name:conventional long form: Republic of Nauruconventional short form: Naurulocal long form: Republic of Naurulocal short form: Nauruformer: Pleasant Islandetymology: the island name may derive from the Nauruan word "anaoero" meaning "I go to the beach"Government type:parliamentary republicCapital:name: no official capital; government offices in the Yaren Districttime difference: UTC+12 (17 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:14 districts; Aiwo, Anabar, Anetan, Anibare, Baitsi, Boe, Buada, Denigomodu, Ewa, Ijuw, Meneng, Nibok, Uaboe, YarenIndependence:31 January 1968 (from the Australia-, NZ-, and UK-administered UN trusteeship)National holiday:Independence Day, 31 January (1968)Constitution:history: effective 29 January 1968amendments: proposed by Parliament; passage requires two-thirds majority vote of Parliament; amendments to constitutional articles, such as the republican form of government, protection of fundamental rights and freedoms, the structure and authorities of the executive and legislative branches, also requires two-thirds majority of votes in a referendum; amended 1968, 2009, 2014 (2018)Legal system:mixed legal system of common law based on the English model and customary lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictionSuffrage:20 years of age; universal and compulsoryExecutive branch:chief of state: President Lionel AINGIMEA (since 27 August 2019); note - the president is both chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President Lionel AINGIMEA (since 27 August 2019)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president from among members of Parliamentelections/appointments: president indirectly elected by Parliament (eligible for a second term); election last held on 27 August 2019 (next to be held in 2022)election results: Lionel AINGIMEA elected president; Parliament vote - Lionel AINGIMEA (independent) 12, David ADEANG (Nauru First) 6Legislative branch:description: unicameral parliament (19 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by majority vote using the "Dowdall" counting system by which voters rank candidates on their ballots; members serve 3-year terms)elections: last held on 24 August 2019 (next to be held in 2022)election results: percent of vote - NA; seats - independent 19; composition - men 17, women 2, percent of women 10.5%Judicial branch:highest courts: Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice and several justices); note - in late 2017, the Nauruan Government revoked the 1976 High Court Appeals Act, which had allowed appeals beyond the Nauruan Supreme Court, and in early 2018, the government formed its own appeals courtjudge selection and term of office: judges appointed by the president to serve until age 65subordinate courts: District Court, Family CourtPolitical parties and leaders:Democratic Party [Kennan ADEANG]
Nauru First (Naoero Amo) Party
Nauru Party (informal)note: loose multiparty system
International organization participation:ACP, ADB, AOSIS, C, FAO, G-77, ICAO, ICCt, IFAD, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ITU, OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UPU, WHODiplomatic representation in the US:Ambassador Marlene Inemwin MOSES (since 13 March 2006)chancery: 800 2nd Avenue, Suite 400 D, New York, NY 10017telephone: [1] (212) 937-0074FAX: [1] (212) 937-0079Diplomatic representation from the US:the US does not have an embassy in Nauru; the US Ambassador to Fiji is accredited to NauruFlag description:blue with a narrow, horizontal, gold stripe across the center and a large white 12-pointed star below the stripe on the hoist side; blue stands for the Pacific Ocean, the star indicates the country's location in relation to the Equator (the gold stripe) and the 12 points symbolize the 12 original tribes of Nauru; the star's white color represents phosphate, the basis of the island's wealthNational symbol(s):frigatebird, calophyllum flower; national colors: blue, yellow, whiteNational anthem:name: "Nauru Bwiema" (Song of Nauru)lyrics/music: Margaret HENDRIE/Laurence Henry HICKSnote: adopted 1968
-
Economy :: Nauru
-
Economy - overview:
Revenues of this tiny island - a coral atoll with a land area of 21 square kilometers - traditionally have come from exports of phosphates. Few other resources exist, with most necessities being imported, mainly from Australia, its former occupier and later major source of support. Primary reserves of phosphates were exhausted and mining ceased in 2006, but mining of a deeper layer of "secondary phosphate" in the interior of the island began the following year. The secondary phosphate deposits may last another 30 years. Earnings from Nauru’s export of phosphate remains an important source of income. Few comprehensive statistics on the Nauru economy exist; estimates of Nauru's GDP vary widely.
The rehabilitation of mined land and the replacement of income from phosphates are serious long-term problems. In anticipation of the exhaustion of Nauru's phosphate deposits, substantial amounts of phosphate income were invested in trust funds to help cushion the transition and provide for Nauru's economic future.
Although revenue sources for government are limited, the opening of the Australian Regional Processing Center for asylum seekers since 2012 has sparked growth in the economy. Revenue derived from fishing licenses under the "vessel day scheme" has also boosted government income. Housing, hospitals, and other capital plant are deteriorating. The cost to Australia of keeping the Nauruan government and economy afloat continues to climb.
GDP (purchasing power parity):$160 million (2017 est.)$153.9 million (2016 est.)$139.4 million (2015 est.)note: data are in 2015 dollars
country comparison to the world: 224GDP (official exchange rate):$114 million (2017 est.)GDP - real growth rate:4% (2017 est.)10.4% (2016 est.)2.8% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 80GDP - per capita (PPP):$12,300 (2017 est.)$11,800 (2016 est.)$11,600 (2015 est.)note: data are in 2015 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 129GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 98% (2016 est.)government consumption: 37.6% (2016 est.)investment in fixed capital: 42.2% (2016 est.)exports of goods and services: 11.2% (2016 est.)imports of goods and services: -89.1% (2016 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 6.1% (2009 est.)industry: 33% (2009 est.)services: 60.8% (2009 est.)Agriculture - products:coconutsIndustries:phosphate mining, offshore banking, coconut productsIndustrial production growth rate:NALabor force:NALabor force - by occupation:note: most of the labor force is employed in phosphate mining, public administration, education, and transportation
Unemployment rate:23% (2011 est.)90% (2004 est.)country comparison to the world: 193Population below poverty line:NAHousehold income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: NAhighest 10%: NABudget:revenues: 103 million (2017 est.)expenditures: 113.4 million (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues:90.3% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 2Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-9.2% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 206Public debt:62% of GDP (2017 est.)65% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Fiscal year:1 July - 30 JuneInflation rate (consumer prices):5.1% (2017 est.)8.2% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 172Current account balance:$5 million (2017 est.)$2 million (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 64Exports:$125 million (2013 est.)$110.3 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 194Exports - partners:Nigeria 38.6%, Japan 16.6%, Australia 15.9%, South Korea 13.7%, NZ 5.7% (2017)Exports - commodities:phosphatesImports:$64.9 million (2016 est.)$143.1 million (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 219Imports - commodities:food, fuel, manufactures, building materials, machineryImports - partners:Australia 67.5%, Fiji 9.2%, India 8.1%, Singapore 5.4% (2017)Debt - external:$33.3 million (2004 est.)country comparison to the world: 199Exchange rates:Australian dollars (AUD) per US dollar -1.311 (2017 est.)1.3452 (2016 est.)1.3452 (2015 est.)1.3291 (2014 est.)1.1094 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Nauru
-
Electricity - production:24 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 212Electricity - consumption:22.32 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 212Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 174Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 177Electricity - installed generating capacity:7,000 kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 211Electricity - from fossil fuels:86% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 151Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 188Electricity - from other renewable sources:14% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 63Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 180Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 172Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 173Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 175Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Refined petroleum products - consumption:470 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 210Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 186Refined petroleum products - imports:449 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 206Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 176Natural gas - consumption:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 180Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 158Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 163Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 174Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:76,540 Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 208
-
Communications :: Nauru
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 1,900subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 14 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 215Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 9,900subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 87 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 212Telephone system:general assessment: adequate local and international radiotelephone communication provided via Australian facilities; geography is a challenge for the islands; there is a need to service the tourism sector and thus the South Pacific Islands economy; mobile technology is booming (2018)domestic: fixed-line 14 per 100 and mobile-cellular 87 per 100 (2018)international: country code - 674; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Pacific Ocean)Broadcast media:1 government-owned TV station broadcasting programs from New Zealand sent via satellite or on videotape; 1 government-owned radio station, broadcasting on AM and FM, utilizes Australian and British programs (2019)Internet country code:.nrInternet users:total: 5,100percent of population: 53.5% (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 213
-
Military and Security :: Nauru
-
Military and security forces:no regular military forces (2019)Military - note:Nauru maintains no defense forces; under an informal agreement, defense is the responsibility of Australia
-
Transportation :: Nauru
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 1 (2015)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 5 (2015)annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 38,858 (2015)annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 7,793,474 mt-km (2015)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:C2 (2016)Airports:1 (2013)country comparison to the world: 230Airports - with paved runways:total: 1 (2017)1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2017)Roadways:total: 30 km (2002)paved: 24 km (2002)unpaved: 6 km (2002)country comparison to the world: 211Ports and terminals:major seaport(s): Nauru
-
Transnational Issues :: Nauru
-
Disputes - international:
none