
-
Introduction :: Eswatini
-
Background:Autonomy for Eswatini was guaranteed by the British in the late 19th century; independence was granted in 1968. A new constitution came into effect in 2006, which included provisions for a more independent parliament and judiciary, but the legal status of political parties remains unclear. King MSWATI III renamed the country from Swaziland to Eswatini in April 2018. Despite its classification as a lower-middle income country, Eswatini has one of the lowest GDP growth rates in Sub-Saharan Africa and suffers from severe poverty and high unemployment. Eswatini has the world's highest known HIV/AIDS prevalence rate, although recent years have shown marked declines in new infections.
-
Geography :: Eswatini
-
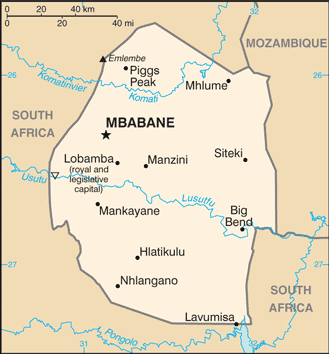
Location:Southern Africa, between Mozambique and South AfricaGeographic coordinates:26 30 S, 31 30 EMap references:AfricaArea:total: 17,364 sq kmland: 17,204 sq kmwater: 160 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 159Area - comparative:slightly smaller than New JerseyArea comparison map:
 The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: Eswatini Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: Eswatini Print Image Description
Image Descriptionslightly smaller than New Jersey
Land boundaries:total: 546 kmborder countries (2): Mozambique 108 km, South Africa 438 kmCoastline:0 km (landlocked)Maritime claims:none (landlocked)Climate:varies from tropical to near temperateTerrain:mostly mountains and hills; some moderately sloping plainsElevation:mean elevation: 305 mlowest point: Great Usutu River 21 mhighest point: Emlembe 1,862 mNatural resources:asbestos, coal, clay, cassiterite, hydropower, forests, small gold and diamond deposits, quarry stone, and talcLand use:agricultural land: 68.3% (2011 est.)arable land: 9.8% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0.8% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 57.7% (2011 est.)forest: 31.7% (2011 est.)other: 0% (2011 est.)Irrigated land:500 sq km (2012)Population distribution:because of its mountainous terrain, the population distribution is uneven throughout the country, concentrating primarily in valleys and plainsNatural hazards:droughtEnvironment - current issues:limited supplies of potable water; wildlife populations being depleted because of excessive hunting; population growth, deforestation, and overgrazing lead to soil erosion and soil degradationEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protectionsigned, but not ratified: Law of the SeaGeography - note:landlocked; almost completely surrounded by South Africa -
People and Society :: Eswatini
-
Population:1,087,200 (July 2018 est.)
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected
country comparison to the world: 160Nationality:noun: liSwati (singular), emaSwati (plural); note - former term, Swazi(s), still used among English speakersadjective: Swati; note - former term, Swazi, still used among English speakersEthnic groups:African 97%, European 3%Languages:English (official, used for government business), siSwati (official)Religions:Christian 90% (Zionist - a blend of Christianity and indigenous ancestral worship - 40%, Roman Catholic 20%, other 30% - includes Anglican, Methodist, Mormon, Jehovah's Witness), Muslim 2%, other 8% (includes Baha'i, Buddhist, Hindu, indigenous, Jewish) (2015 est.)Demographic profile:Eswatini, a small, predominantly rural, landlocked country surrounded by South Africa and Mozambique, suffers from severe poverty and the world’s highest HIV/AIDS prevalence rate. A weak and deteriorating economy, high unemployment, rapid population growth, and an uneven distribution of resources all combine to worsen already persistent poverty and food insecurity, especially in rural areas. Erratic weather (frequent droughts and intermittent heavy rains and flooding), overuse of small plots, the overgrazing of cattle, and outdated agricultural practices reduce crop yields and further degrade the environment, exacerbating Eswatini's poverty and subsistence problems. Eswatini's extremely high HIV/AIDS prevalence rate – more than 28% of adults have the disease – compounds these issues. Agricultural production has declined due to HIV/AIDS, as the illness causes households to lose manpower and to sell livestock and other assets to pay for medicine and funerals.
Swazis, mainly men from the country’s rural south, have been migrating to South Africa to work in coal, and later gold, mines since the late 19th century. Although the number of miners abroad has never been high in absolute terms because of Eswatini's small population, the outflow has had important social and economic repercussions. The peak of mining employment in South Africa occurred during the 1980s. Cross-border movement has accelerated since the 1990s, as increasing unemployment has pushed more Swazis to look for work in South Africa (creating a "brain drain" in the health and educational sectors); southern Swazi men have continued to pursue mining, although the industry has downsized. Women now make up an increasing share of migrants and dominate cross-border trading in handicrafts, using the proceeds to purchase goods back in Eswatini. Much of today’s migration, however, is not work-related but focuses on visits to family and friends, tourism, and shopping.
Age structure:0-14 years: 34.41% (male 186,747 /female 187,412)15-24 years: 19.31% (male 99,192 /female 110,770)25-54 years: 38.22% (male 193,145 /female 222,405)55-64 years: 4.28% (male 19,915 /female 26,663)65 years and over: 3.77% (male 15,470 /female 25,481) (2018 est.)population pyramid: The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: Eswatini Print
The World Factbook Field Image ModalAfrica :: Eswatini Print Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Eswatini. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
Image DescriptionThis is the population pyramid for Eswatini. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 68.8 (2015 est.)youth dependency ratio: 63.5 (2015 est.)elderly dependency ratio: 5.2 (2015 est.)potential support ratio: 19.1 (2015 est.)Median age:total: 23.2 years (2018 est.)male: 22.2 yearsfemale: 24 yearscountry comparison to the world: 175Population growth rate:0.82% (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 128Birth rate:25.8 births/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 48Death rate:10.7 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 24Net migration rate:-6.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 207Population distribution:because of its mountainous terrain, the population distribution is uneven throughout the country, concentrating primarily in valleys and plainsUrbanization:urban population: 24% of total population (2019)rate of urbanization: 2.46% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)Major urban areas - population:68,000 MBABANE (capital) (2018)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.9 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.87 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.75 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.61 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.9 male(s)/female (2018 est.)Maternal mortality rate:437 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 25Infant mortality rate:total: 46.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2018 est.)male: 51.4 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 41.7 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 33Life expectancy at birth:total population: 57.2 years (2018)male: 55.1 yearsfemale: 59.3 yearscountry comparison to the world: 215Total fertility rate:2.63 children born/woman (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Contraceptive prevalence rate:66.1% (2014)Drinking water source:improved: urban: 93.6% of populationrural: 68.9% of populationtotal: 74.1% of populationunimproved: urban: 6.4% of populationrural: 31.1% of populationtotal: 25.9% of population (2015 est.)Current Health Expenditure:7.7% (2016)Physicians density:0.08 physicians/1,000 population (2016)Hospital bed density:2.1 beds/1,000 population (2011)Sanitation facility access:improved: urban: 63.1% of population (2015 est.)rural: 56% of population (2015 est.)total: 57.5% of population (2015 est.)unimproved: urban: 36.9% of population (2015 est.)rural: 44% of population (2015 est.)total: 42.5% of population (2015 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:27.3% (201 est.)country comparison to the world: 1HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:210,000 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 28HIV/AIDS - deaths:2,400 (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 42Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: intermediate (2016)food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever (2016)vectorborne diseases: malaria (2016)water contact diseases: schistosomiasis (2016)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:16.5% (2016)country comparison to the world: 124Children under the age of 5 years underweight:5.8% (2014)country comparison to the world: 79Education expenditures:7.1% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 13Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 87.5%male: 87.4%female: 87.5% (2015)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 11 yearsmale: 12 yearsfemale: 11 years (2013)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 47.1%male: 44.2%female: 50.1% (2016)country comparison to the world: 5 -
Government :: Eswatini
-
Country name:conventional long form: Kingdom of Eswatiniconventional short form: Eswatinilocal long form: Umbuso weSwatinilocal short form: eSwatiniformer: Swazilandetymology: the country name derives from 19th century King MSWATI II, under whose rule Swati territory was expanded and unified
note: pronounced ay-swatini or eh-swatini
Government type:absolute monarchyCapital:name: Mbabane (administrative capital); Lobamba (royal and legislative capital)geographic coordinates: 26 19 S, 31 08 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)etymology: named after a Swati chief, Mbabane Kunene, who lived in the area at the onset of British settlementAdministrative divisions:4 regions; Hhohho, Lubombo, Manzini, ShiselweniIndependence:6 September 1968 (from the UK)National holiday:Independence Day (Somhlolo Day), 6 September (1968)Constitution:history: previous 1968, 1978; latest signed by the king 26 July 2005, effective 8 February 2006amendments: proposed at a joint sitting of both houses of Parliament; passage requires majority vote by both houses and/or majority vote in a referendum, and assent of the king; passage of amendments affecting "specially entrenched" constitutional provisions requires at least three-fourths majority vote by both houses, passage by simple majority vote in a referendum, and assent of the king; passage of "entrenched" provisions requires at least two-thirds majority vote of both houses, passage in a referendum, and assent of the king (2017)Legal system:mixed legal system of civil, common, and customary lawInternational law organization participation:accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; non-party state to the ICCtCitizenship:citizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: both parents must be citizens of Eswatinidual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 5 yearsSuffrage:18 years of ageExecutive branch:chief of state: King MSWATI III (since 25 April 1986)head of government: Prime Minister Ambrose Mandvulo DLAMINI (since 27 October 2018); Deputy Prime Minister Themba MASUKU (since 6 November 2018)cabinet: Cabinet recommended by the prime minister, confirmed by the monarch; at least one-half of the cabinet membership must be appointed from among elected members of the House of Assemblyelections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; prime minister appointed by the monarch from among members of the House of AssemblyLegislative branch:description: bicameral Parliament (Libandla) consists of:
Senate (30 seats; 20 members appointed by the monarch and 10 indirectly elected by simple majority vote by the House of Assembly; members serve 5-year terms)
House of Assembly (73 seats; 59 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies or tinkhundla by absolute majority vote in 2 rounds if needed, 10 members appointed by the monarch, 4 women elected by the members if representation of elected women is less than 30%; members serve 5-year terms)elections: Senate - last held on 23 October 2018 (next to be held - 31 October 2023)
House of Assembly - last held on 21 September 2018 (next to be held in 2023)election results: Senate - percent of seats by party - NA; seats by party - NA; composition - men 20, women 10, percent of women 33.3%
House of Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - independent 59; composition - men 60, women 5, percent of women 7.7%; note - total Parliament percent of women 15.8%Judicial branch:highest courts: Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice and at least 4 justices) and the High Court (consists of the chief justice - ex officio - and 4 justices); note - the Supreme Court has jurisdiction in all constitutional mattersjudge selection and term of office: justices of the Supreme Court and High Court appointed by the monarch on the advice of the Judicial Service Commission (JSC), a judicial advisory body consisting of the Supreme Court Chief Justice, 4 members appointed by the monarch, and the chairman of the Civil Service Commission; justices of both courts eligible for retirement at age 65 with mandatory retirement at age 75subordinate courts: magistrates' courts; National Swazi Courts for administering customary/traditional laws (jurisdiction restricted to customary law for Swazi citizens)Political parties and leaders:political parties exist, but conditions for their operations, particularly in elections, are undefined, legally unclear, or culturally restricted; the following are considered political associations:
African United Democratic Party or AUDP [Sibusiso DLAMINI]
Ngwane National Liberatory Congress or NNLC [Dr. Alvit DLAMINI]
People's United Democratic Movement or PUDEMO [Mario MASUKU]
Swazi Democratic Party or SWADEPA [Jan SITHOLE]International organization participation:ACP, AfDB, AU, C, COMESA, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PCA, SACU, SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:Ambassador Njabuliso Busisiwe Sikhulile GWEBU (since 24 April 2017)chancery: 1712 New Hampshire Avenue, NW, Washington, DC 20009telephone: [1] (202) 234-5002FAX: [1] (202) 234-8254Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Lisa J. PETERSON (since February 2016)telephone: [268] 2417-9000embassy: corner of MR 103 and Cultural Center Drive, Ezulwini,
P.O. Box 0202,The Gables, H106, Eswatinimailing address: P.O. Box D202, The Gables, H106FAX: [268] 2416-3344Flag description:three horizontal bands of blue (top), red (triple width), and blue; the red band is edged in yellow; centered in the red band is a large black and white shield covering two spears and a staff decorated with feather tassels, all placed horizontally; blue stands for peace and stability, red represents past struggles, and yellow the mineral resources of the country; the shield, spears, and staff symbolize protection from the country's enemies, while the black and white of the shield are meant to portray black and white people living in peaceful coexistenceNational symbol(s):lion, elephant; national colors: blue, yellow, redNational anthem:name: "Nkulunkulu Mnikati wetibusiso temaSwati" (Oh God, Bestower of the Blessings of the Swazi)lyrics/music: Andrease Enoke Fanyana SIMELANE/David Kenneth RYCROFTnote: adopted 1968; uses elements of both ethnic Swazi and Western music styles
-
Economy :: Eswatini
-
Economy - overview:
A small, landlocked kingdom, Eswatini is bordered in the north, west and south by the Republic of South Africa and by Mozambique in the east. Eswatini depends on South Africa for a majority of its exports and imports. Eswatini's currency is pegged to the South African rand, effectively relinquishing Eswatini's monetary policy to South Africa. The government is dependent on customs duties from the Southern African Customs Union (SACU) for almost half of its revenue. Eswatini is a lower middle income country. As of 2017, more than one-quarter of the adult population was infected by HIV/AIDS; Eswatini has the world’s highest HIV prevalence rate, a financial strain and source of economic instability.
The manufacturing sector diversified in the 1980s and 1990s, but manufacturing has grown little in the last decade. Sugar and soft drink concentrate are the largest foreign exchange earners, although a drought in 2015-16 decreased sugar production and exports. Overgrazing, soil depletion, drought, and floods are persistent problems. Mining has declined in importance in recent years. Coal, gold, diamond, and quarry stone mines are small scale, and the only iron ore mine closed in 2014. With an estimated 28% unemployment rate, Eswatini's need to increase the number and size of small and medium enterprises and to attract foreign direct investment is acute.
Eswatini's national development strategy, which expires in 2022, prioritizes increases in infrastructure, agriculture production, and economic diversification, while aiming to reduce poverty and government spending. Eswatini's revenue from SACU receipts are likely to continue to decline as South Africa pushes for a new distribution scheme, making it harder for the government to maintain fiscal balance without introducing new sources of revenue.
GDP (purchasing power parity):$11.6 billion (2017 est.)$11.41 billion (2016 est.)$11.26 billion (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 157GDP (official exchange rate):$4.417 billion (2017 est.)GDP - real growth rate:1.6% (2017 est.)1.4% (2016 est.)0.4% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 168GDP - per capita (PPP):$10,100 (2017 est.)$10,100 (2016 est.)$10,100 (2015 est.)note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 139Gross national saving:25.4% of GDP (2017 est.)29.7% of GDP (2016 est.)23.3% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 59GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 64% (2017 est.)government consumption: 21.3% (2017 est.)investment in fixed capital: 13.4% (2017 est.)investment in inventories: -0.1% (2017 est.)exports of goods and services: 47.9% (2017 est.)imports of goods and services: -46.3% (2017 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 6.5% (2017 est.)industry: 45% (2017 est.)services: 48.6% (2017 est.)Agriculture - products:sugarcane, corn, cotton, citrus, pineapples, cattle, goatsIndustries:soft drink concentrates, coal, forestry, sugar processing, textiles, and apparelIndustrial production growth rate:5.6% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 48Labor force:427,900 (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 157Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 10.7%industry: 30.4%services: 58.9% (2014 est.)Unemployment rate:28% (2014 est.)28% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Population below poverty line:63% (2010 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 1.7%highest 10%: 40.1% (2010 est.)Distribution of family income - Gini index:50.4 (2001)country comparison to the world: 16Budget:revenues: 1.263 billion (2017 est.)expenditures: 1.639 billion (2017 est.)Taxes and other revenues:28.6% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 94Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-8.5% (of GDP) (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 201Public debt:28.4% of GDP (2017 est.)25.5% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 168Fiscal year:1 April - 31 MarchInflation rate (consumer prices):6.2% (2017 est.)7.8% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 188Central bank discount rate:7.25% (31 December 2016)6.5% (31 December 2015)country comparison to the world: 43Commercial bank prime lending rate:10.75% (31 December 2017 est.)10.25% (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 77Stock of narrow money:$554.3 million (31 December 2017 est.)$439 million (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 168Stock of broad money:$554.3 million (31 December 2017 est.)$439 million (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 172Stock of domestic credit:$1.144 billion (31 December 2017 est.)$891.3 million (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 166Market value of publicly traded shares:$203.1 million (31 December 2007)$199.9 million (31 December 2006)NA
country comparison to the world: 117Current account balance:$604 million (2017 est.)$642 million (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 55Exports:$1.83 billion (2017 est.)$1.577 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 146Exports - partners:South Africa 94% (2017)Exports - commodities:soft drink concentrates, sugar, timber, cotton yarn, refrigerators, citrus, and canned fruitImports:$1.451 billion (2017 est.)$1.266 billion (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 175Imports - commodities:motor vehicles, machinery, transport equipment, foodstuffs, petroleum products, chemicalsImports - partners:South Africa 81.6%, China 5.2% (2017)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$563.1 million (31 December 2017 est.)$564.4 million (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 147Debt - external:$526.3 million (31 December 2017 est.)$468.9 million (31 December 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 178Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:NA
Stock of direct foreign investment - abroad:NA
Exchange rates:emalangeni per US dollar -14.44 (2017 est.)14.6924 (2016 est.)14.6924 (2015 est.)12.7581 (2014 est.)10.8469 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Eswatini
-
Electricity access:population without electricity: 900,000 (2017)electrification - total population: 65.8% (2016)electrification - urban areas: 82.8% (2016)electrification - rural areas: 61.2% (2016)Electricity - production:381 million kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 173Electricity - consumption:1.431 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 149Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2016)country comparison to the world: 132Electricity - imports:1.077 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 69Electricity - installed generating capacity:295,900 kW (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 160Electricity - from fossil fuels:39% of total installed capacity (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 172Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:20% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Electricity - from other renewable sources:41% of total installed capacity (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 6Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2018 est.)country comparison to the world: 133Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 124Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2018)country comparison to the world: 129Refined petroleum products - production:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 142Refined petroleum products - consumption:5,300 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 175Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 152Refined petroleum products - imports:5,279 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 169Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 129Natural gas - consumption:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 143Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 101Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 122Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 133Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:1.14 million Mt (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 166
-
Communications :: Eswatini
-
Telephones - fixed lines:total subscriptions: 42,000subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 3 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 160Telephones - mobile cellular:total subscriptions: 995,000subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 68 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 160Telephone system:general assessment: earlier government monopoly in telecommunications hindered its growth; new regulatory authority established in 2013 has aided expansion in the telecom sector; 2G, 3G, 4G and LTE services (2018)domestic: Eswatini has 2 mobile-cellular providers; communication infrastructure has a geographic coverage of about 90% and a rising subscriber base; fixed-line stands at 3 per 100 and mobile-cellular teledensity roughly 68 telephones per 100 persons; telephone system consists of carrier-equipped, open-wire lines and low-capacity, microwave radio relay (2018)international: country code - 268; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean)Broadcast media:1 state-owned TV station; satellite dishes are able to access South African providers; state-owned radio network with 3 channels; 1 private radio station (2019)Internet country code:.szInternet users:total: 414,724percent of population: 28.6% (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 152Broadband - fixed subscriptions:total: 7,000subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 173
-
Military and Security :: Eswatini
-
Military expenditures:1.5% of GDP (2018)1.8% of GDP (2017)1.81% of GDP (2016)1.78% of GDP (2015)1.81% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 77Military and security forces:Umbutfo Eswatini Defense Force (UEDF): Ground Force (includes Air Wing (no operational aircraft)) (2019)Military service age and obligation:18-30 years of age for male and female voluntary military service; no conscription; compulsory HIV testing required, only HIV-negative applicants accepted (2012)
-
Transportation :: Eswatini
-
National air transport system:number of registered air carriers: 1 (2015)inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 1 (2015)annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 89,791 (2015)annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 0 mt-km (2015)Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:3 (2016)Airports:14 (2013)country comparison to the world: 148Airports - with paved runways:total: 2 (2019)over 3,047 m: 12,438 to 3,047 m: 1Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 12 (2013)914 to 1,523 m: 5 (2013)under 914 m: 7 (2013)Railways:total: 301 km (2014)narrow gauge: 301 km 1.067-m gauge (2014)country comparison to the world: 122Roadways:total: 3,769 km (2019)country comparison to the world: 153
-
Transnational Issues :: Eswatini
-
Disputes - international:
in 2006, Swati king advocated resorting to ICJ to claim parts of Mpumalanga and KwaZulu-Natal from South Africa