Main Content




Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice

Agency Copyright Notice
- Jump to topic
-
Introduction :: Svalbard
-
Background: This entry usually highlights major historic events and current issues and may include a statement about one or two key future trends.
 The archipelago may have been first discovered by Norse explorers in the 12th century; the islands served as an international whaling base during the 17th and 18th centuries. Norway's sovereignty was internationally recognized by treaty in 1920, and five years later it officially took over the territory. In the 20th century coal mining started and today a Norwegian and a Russian company are still functioning. Travel between the settlements is accomplished with snowmobiles, aircraft, and boats.
The archipelago may have been first discovered by Norse explorers in the 12th century; the islands served as an international whaling base during the 17th and 18th centuries. Norway's sovereignty was internationally recognized by treaty in 1920, and five years later it officially took over the territory. In the 20th century coal mining started and today a Norwegian and a Russian company are still functioning. Travel between the settlements is accomplished with snowmobiles, aircraft, and boats. -
Geography :: Svalbard
-
Location: This entry identifies the country's regional location, neighboring countries, and adjacent bodies of water.
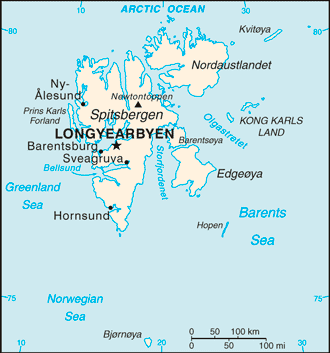
 Northern Europe, islands between the Arctic Ocean, Barents Sea, Greenland Sea, and Norwegian Sea, north of NorwayGeographic coordinates: This entry includes rounded latitude and longitude figures for the centroid or center point of a country expressed in degrees and minutes; it is based on the locations provided in the Geographic Names Server (GNS), maintained by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency on behalf of the US Board on Geographic Names.
Northern Europe, islands between the Arctic Ocean, Barents Sea, Greenland Sea, and Norwegian Sea, north of NorwayGeographic coordinates: This entry includes rounded latitude and longitude figures for the centroid or center point of a country expressed in degrees and minutes; it is based on the locations provided in the Geographic Names Server (GNS), maintained by the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency on behalf of the US Board on Geographic Names. 78 00 N, 20 00 EMap references: This entry includes the name of the Factbook reference map on which a country may be found. Note that boundary representations on these maps are not necessarily authoritative. The entry on Geographic coordinates may be helpful in finding some smaller countries.
78 00 N, 20 00 EMap references: This entry includes the name of the Factbook reference map on which a country may be found. Note that boundary representations on these maps are not necessarily authoritative. The entry on Geographic coordinates may be helpful in finding some smaller countries. Arctic RegionArea: This entry includes three subfields. Total area is the sum of all land and water areas delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Land area is the aggregate of all surfaces delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines, excluding inland water bodies (lakes, reservoirs, rivers). Water area is the sum of the surfaces of all inland water bodies, such as lakes, reservoirs, or rivers, as delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines.
Arctic RegionArea: This entry includes three subfields. Total area is the sum of all land and water areas delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. Land area is the aggregate of all surfaces delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines, excluding inland water bodies (lakes, reservoirs, rivers). Water area is the sum of the surfaces of all inland water bodies, such as lakes, reservoirs, or rivers, as delimited by international boundaries and/or coastlines. total: 62,045 sq kmland: 62,045 sq kmwater: 0 sq km
total: 62,045 sq kmland: 62,045 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmnote: includes Spitsbergen and Bjornoya (Bear Island)
country comparison to the world: 126Area - comparative: This entry provides an area comparison based on total area equivalents. Most entities are compared with the entire US or one of the 50 states based on area measurements (1990 revised) provided by the US Bureau of the Census. The smaller entities are compared with Washington, DC (178 sq km, 69 sq mi) or The Mall in Washington, DC (0.59 sq km, 0.23 sq mi, 146 acres). slightly smaller than West VirginiaLand boundaries: This entry contains the total length of all land boundaries and the individual lengths for each of the contiguous border countries. When available, official lengths published by national statistical agencies are used. Because surveying methods may differ, country border lengths reported by contiguous countries may differ.
slightly smaller than West VirginiaLand boundaries: This entry contains the total length of all land boundaries and the individual lengths for each of the contiguous border countries. When available, official lengths published by national statistical agencies are used. Because surveying methods may differ, country border lengths reported by contiguous countries may differ. 0 kmCoastline: This entry gives the total length of the boundary between the land area (including islands) and the sea.
0 kmCoastline: This entry gives the total length of the boundary between the land area (including islands) and the sea. 3,587 kmMaritime claims: This entry includes the following claims, the definitions of which are excerpted from the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which alone contains the full and definitive descriptions: territorial sea - the sovereignty of a coastal state extends beyond its land territory and internal waters to an adjacent belt of sea, described as the territorial sea in the UNCLOS (Part II); this sovereignty extends to the air space over the territorial sea as well as its underlying s . . . more
3,587 kmMaritime claims: This entry includes the following claims, the definitions of which are excerpted from the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which alone contains the full and definitive descriptions: territorial sea - the sovereignty of a coastal state extends beyond its land territory and internal waters to an adjacent belt of sea, described as the territorial sea in the UNCLOS (Part II); this sovereignty extends to the air space over the territorial sea as well as its underlying s . . . more territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmcontinental shelf: extends to depth of exploitationexclusive fishing zone: 200 nmClimate: This entry includes a brief description of typical weather regimes throughout the year; in the Word entry only, it includes four subfields that describe climate extremes:ten driest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and inches for selected countries with climate extremes. ten wettest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and i . . . more
territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmcontinental shelf: extends to depth of exploitationexclusive fishing zone: 200 nmClimate: This entry includes a brief description of typical weather regimes throughout the year; in the Word entry only, it includes four subfields that describe climate extremes:ten driest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and inches for selected countries with climate extremes. ten wettest places on earth (average annual precipitation) describes the annual average precipitation measured in both millimeters and i . . . more arctic, tempered by warm North Atlantic Current; cool summers, cold winters; North Atlantic Current flows along west and north coasts of Spitsbergen, keeping water open and navigable most of the yearTerrain: This entry contains a brief description of the topography.
arctic, tempered by warm North Atlantic Current; cool summers, cold winters; North Atlantic Current flows along west and north coasts of Spitsbergen, keeping water open and navigable most of the yearTerrain: This entry contains a brief description of the topography. rugged mountains; much of the upland areas are ice covered; west coast clear of ice about half the year; fjords along west and north coastsElevation: This entry includes the mean elevation and elevation extremes, lowest point and highest point.
rugged mountains; much of the upland areas are ice covered; west coast clear of ice about half the year; fjords along west and north coastsElevation: This entry includes the mean elevation and elevation extremes, lowest point and highest point. lowest point: Arctic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Newtontoppen 1,717 mNatural resources: This entry lists a country's mineral, petroleum, hydropower, and other resources of commercial importance, such as rare earth elements (REEs). In general, products appear only if they make a significant contribution to the economy, or are likely to do so in the future.
lowest point: Arctic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Newtontoppen 1,717 mNatural resources: This entry lists a country's mineral, petroleum, hydropower, and other resources of commercial importance, such as rare earth elements (REEs). In general, products appear only if they make a significant contribution to the economy, or are likely to do so in the future. coal, iron ore, copper, zinc, phosphate, wildlife, fishLand use: This entry contains the percentage shares of total land area for three different types of land use: agricultural land, forest, and other; agricultural land is further divided into arable land - land cultivated for crops like wheat, maize, and rice that are replanted after each harvest, permanent crops - land cultivated for crops like citrus, coffee, and rubber that are not replanted after each harvest, and includes land under flowering shrubs, fruit trees, nut trees, and vines, and permane . . . more
coal, iron ore, copper, zinc, phosphate, wildlife, fishLand use: This entry contains the percentage shares of total land area for three different types of land use: agricultural land, forest, and other; agricultural land is further divided into arable land - land cultivated for crops like wheat, maize, and rice that are replanted after each harvest, permanent crops - land cultivated for crops like citrus, coffee, and rubber that are not replanted after each harvest, and includes land under flowering shrubs, fruit trees, nut trees, and vines, and permane . . . more agricultural land: 0% (2011 est.)arable land: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 0% (2011 est.)forest: 0% (2011 est.)other: 100% (2011 est.)Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures.
agricultural land: 0% (2011 est.)arable land: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent crops: 0% (2011 est.) / permanent pasture: 0% (2011 est.)forest: 0% (2011 est.)other: 100% (2011 est.)Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures. the small population is primarily concentrated on the island of Spitsbergen in a handful of settlements on the south side of the Isfjorden, with Longyearbyen being the largestNatural hazards: This entry lists potential natural disasters. For countries where volcanic activity is common, a volcanism subfield highlights historically active volcanoes.
the small population is primarily concentrated on the island of Spitsbergen in a handful of settlements on the south side of the Isfjorden, with Longyearbyen being the largestNatural hazards: This entry lists potential natural disasters. For countries where volcanic activity is common, a volcanism subfield highlights historically active volcanoes. ice floes often block the entrance to Bellsund (a transit point for coal export) on the west coast and occasionally make parts of the northeastern coast inaccessible to maritime trafficEnvironment - current issues: This entry lists the most pressing and important environmental problems. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: Acidification - the lowering of soil and water pH due to acid precipitation and deposition usually through precipitation; this process disrupts ecosystem nutrient flows and may kill freshwater fish and plants dependent on more neutral or alkaline conditions (see acid rain). Acid rain - characterized as containing harmful levels of sulfur dioxi . . . more
ice floes often block the entrance to Bellsund (a transit point for coal export) on the west coast and occasionally make parts of the northeastern coast inaccessible to maritime trafficEnvironment - current issues: This entry lists the most pressing and important environmental problems. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: Acidification - the lowering of soil and water pH due to acid precipitation and deposition usually through precipitation; this process disrupts ecosystem nutrient flows and may kill freshwater fish and plants dependent on more neutral or alkaline conditions (see acid rain). Acid rain - characterized as containing harmful levels of sulfur dioxi . . . more ice floes are a maritime hazard; past exploitation of mammal species (whale, seal, walrus, and polar bear) severely depleted the populations, but a gradual recovery seems to be occurringGeography - note: This entry includes miscellaneous geographic information of significance not included elsewhere.
ice floes are a maritime hazard; past exploitation of mammal species (whale, seal, walrus, and polar bear) severely depleted the populations, but a gradual recovery seems to be occurringGeography - note: This entry includes miscellaneous geographic information of significance not included elsewhere. northernmost part of the Kingdom of Norway; consists of nine main islands; glaciers and snowfields cover 60% of the total area; Spitsbergen Island is the site of the Svalbard Global Seed Vault, a seed repository established by the Global Crop Diversity Trust and the Norwegian Government
northernmost part of the Kingdom of Norway; consists of nine main islands; glaciers and snowfields cover 60% of the total area; Spitsbergen Island is the site of the Svalbard Global Seed Vault, a seed repository established by the Global Crop Diversity Trust and the Norwegian Government -
People and Society :: Svalbard
-
Population: This entry gives an estimate from the US Bureau of the Census based on statistics from population censuses, vital statistics registration systems, or sample surveys pertaining to the recent past and on assumptions about future trends. The total population presents one overall measure of the potential impact of the country on the world and within its region. Note: Starting with the 1993 Factbook, demographic estimates for some countries (mostly African) have explicitly taken into account t . . . more
 2,583 (July 2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 230Ethnic groups: This entry provides an ordered listing of ethnic groups starting with the largest and normally includes the percent of total population.
2,583 (July 2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 230Ethnic groups: This entry provides an ordered listing of ethnic groups starting with the largest and normally includes the percent of total population. Norwegian 58%, foreign population 42% (consists primarily of Russians, Thais, Swedes, Filipinos, and Ukrainians) (2019 est.)note: foreigners account for almost one third of the population of the Norwegian settlements, Longyearbyen and Ny-Alesund (where the majority of Svalbard's resident population lives), as of mid-2019Languages: This entry provides a listing of languages spoken in each country and specifies any that are official national or regional languages. When data is available, the languages spoken in each country are broken down according to the percent of the total population speaking each language as a first language. For those countries without available data, languages are listed in rank order based on prevalence, starting with the most-spoken language.
Norwegian 58%, foreign population 42% (consists primarily of Russians, Thais, Swedes, Filipinos, and Ukrainians) (2019 est.)note: foreigners account for almost one third of the population of the Norwegian settlements, Longyearbyen and Ny-Alesund (where the majority of Svalbard's resident population lives), as of mid-2019Languages: This entry provides a listing of languages spoken in each country and specifies any that are official national or regional languages. When data is available, the languages spoken in each country are broken down according to the percent of the total population speaking each language as a first language. For those countries without available data, languages are listed in rank order based on prevalence, starting with the most-spoken language. Norwegian, RussianPopulation growth rate: The average annual percent change in the population, resulting from a surplus (or deficit) of births over deaths and the balance of migrants entering and leaving a country. The rate may be positive or negative. The growth rate is a factor in determining how great a burden would be imposed on a country by the changing needs of its people for infrastructure (e.g., schools, hospitals, housing, roads), resources (e.g., food, water, electricity), and jobs. Rapid population growth can be seen as . . . more
Norwegian, RussianPopulation growth rate: The average annual percent change in the population, resulting from a surplus (or deficit) of births over deaths and the balance of migrants entering and leaving a country. The rate may be positive or negative. The growth rate is a factor in determining how great a burden would be imposed on a country by the changing needs of its people for infrastructure (e.g., schools, hospitals, housing, roads), resources (e.g., food, water, electricity), and jobs. Rapid population growth can be seen as . . . more -0.03% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 198Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures.
-0.03% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 198Population distribution: This entry provides a summary description of the population dispersion within a country. While it may suggest population density, it does not provide density figures. the small population is primarily concentrated on the island of Spitsbergen in a handful of settlements on the south side of the Isfjorden, with Longyearbyen being the largestSex ratio: This entry includes the number of males for each female in five age groups - at birth, under 15 years, 15-64 years, 65 years and over, and for the total population. Sex ratio at birth has recently emerged as an indicator of certain kinds of sex discrimination in some countries. For instance, high sex ratios at birth in some Asian countries are now attributed to sex-selective abortion and infanticide due to a strong preference for sons. This will affect future marriage patterns and fertilit . . . more
the small population is primarily concentrated on the island of Spitsbergen in a handful of settlements on the south side of the Isfjorden, with Longyearbyen being the largestSex ratio: This entry includes the number of males for each female in five age groups - at birth, under 15 years, 15-64 years, 65 years and over, and for the total population. Sex ratio at birth has recently emerged as an indicator of certain kinds of sex discrimination in some countries. For instance, high sex ratios at birth in some Asian countries are now attributed to sex-selective abortion and infanticide due to a strong preference for sons. This will affect future marriage patterns and fertilit . . . more NAInfant mortality rate: This entry gives the number of deaths of infants under one year old in a given year per 1,000 live births in the same year. This rate is often used as an indicator of the level of health in a country.
NAInfant mortality rate: This entry gives the number of deaths of infants under one year old in a given year per 1,000 live births in the same year. This rate is often used as an indicator of the level of health in a country. total: NA (2018)male: NAfemale: NALife expectancy at birth: This entry contains the average number of years to be lived by a group of people born in the same year, if mortality at each age remains constant in the future. Life expectancy at birth is also a measure of overall quality of life in a country and summarizes the mortality at all ages. It can also be thought of as indicating the potential return on investment in human capital and is necessary for the calculation of various actuarial measures.
total: NA (2018)male: NAfemale: NALife expectancy at birth: This entry contains the average number of years to be lived by a group of people born in the same year, if mortality at each age remains constant in the future. Life expectancy at birth is also a measure of overall quality of life in a country and summarizes the mortality at all ages. It can also be thought of as indicating the potential return on investment in human capital and is necessary for the calculation of various actuarial measures. total population: NA (2017 est.)male: NAfemale: NATotal fertility rate: This entry gives a figure for the average number of children that would be born per woman if all women lived to the end of their childbearing years and bore children according to a given fertility rate at each age. The total fertility rate (TFR) is a more direct measure of the level of fertility than the crude birth rate, since it refers to births per woman. This indicator shows the potential for population change in the country. A rate of two children per woman is considered the replaceme . . . more
total population: NA (2017 est.)male: NAfemale: NATotal fertility rate: This entry gives a figure for the average number of children that would be born per woman if all women lived to the end of their childbearing years and bore children according to a given fertility rate at each age. The total fertility rate (TFR) is a more direct measure of the level of fertility than the crude birth rate, since it refers to births per woman. This indicator shows the potential for population change in the country. A rate of two children per woman is considered the replaceme . . . more NAEducation expenditures: This entry provides the public expenditure on education as a percent of GDP.
NAEducation expenditures: This entry provides the public expenditure on education as a percent of GDP. NA
NA -
Government :: Svalbard
-
Country name: This entry includes all forms of the country's name approved by the US Board on Geographic Names (Italy is used as an example): conventional long form (Italian Republic), conventional short form (Italy), local long form (Repubblica Italiana), local short form (Italia), former (Kingdom of Italy), as well as the abbreviation. Also see the Terminology note.
 conventional long form: noneconventional short form: Svalbard (sometimes referred to as Spitsbergen, the largest island in the archipelago)etymology: 12th century Norse accounts speak of the discovery of a "Svalbard" - literally "cold shores" - but they may have referred to Jan Mayen Island or eastern Greenland; the archipelago was traditionally known as Spitsbergen, but Norway renamed it Svalbard in the 1920s when it assumed sovereignty of the islandsDependency status: This entry describes the formal relationship between a particular nonindependent entity and an independent state.
conventional long form: noneconventional short form: Svalbard (sometimes referred to as Spitsbergen, the largest island in the archipelago)etymology: 12th century Norse accounts speak of the discovery of a "Svalbard" - literally "cold shores" - but they may have referred to Jan Mayen Island or eastern Greenland; the archipelago was traditionally known as Spitsbergen, but Norway renamed it Svalbard in the 1920s when it assumed sovereignty of the islandsDependency status: This entry describes the formal relationship between a particular nonindependent entity and an independent state. territory of Norway; administered by the Polar Department of the Ministry of Justice, through a governor (sysselmann) residing in Longyearbyen, Spitsbergen; by treaty (9 February 1920), sovereignty was awarded to NorwayGovernment type: This entry gives the basic form of government. Definitions of the major governmental terms are as follows. (Note that for some countries more than one definition applies.): Absolute monarchy - a form of government where the monarch rules unhindered, i.e., without any laws, constitution, or legally organized opposition. Anarchy - a condition of lawlessness or political disorder brought about by the absence of governmental authority. Authoritarian - a form of government in whic . . . more
territory of Norway; administered by the Polar Department of the Ministry of Justice, through a governor (sysselmann) residing in Longyearbyen, Spitsbergen; by treaty (9 February 1920), sovereignty was awarded to NorwayGovernment type: This entry gives the basic form of government. Definitions of the major governmental terms are as follows. (Note that for some countries more than one definition applies.): Absolute monarchy - a form of government where the monarch rules unhindered, i.e., without any laws, constitution, or legally organized opposition. Anarchy - a condition of lawlessness or political disorder brought about by the absence of governmental authority. Authoritarian - a form of government in whic . . . more non-self-governing territory of NorwayCapital: This entry gives the name of the seat of government, its geographic coordinates, the time difference relative to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and the time observed in Washington, DC, and, if applicable, information on daylight saving time (DST). Where appropriate, a special note has been added to highlight those countries that have multiple time zones.
non-self-governing territory of NorwayCapital: This entry gives the name of the seat of government, its geographic coordinates, the time difference relative to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and the time observed in Washington, DC, and, if applicable, information on daylight saving time (DST). Where appropriate, a special note has been added to highlight those countries that have multiple time zones. name: Longyearbyengeographic coordinates: 78 13 N, 15 38 Etime difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in Octoberetymology: the name in Norwegian means Longyear Town; the site was established by and named after John LONGYEAR, whose Arctic Coal Company began mining operations there in 1906Independence: For most countries, this entry gives the date that sovereignty was achieved and from which nation, empire, or trusteeship. For the other countries, the date given may not represent "independence" in the strict sense, but rather some significant nationhood event such as the traditional founding date or the date of unification, federation, confederation, establishment, fundamental change in the form of government, or state succession. For a number of countries, the establishment of statehood . . . more
name: Longyearbyengeographic coordinates: 78 13 N, 15 38 Etime difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in Octoberetymology: the name in Norwegian means Longyear Town; the site was established by and named after John LONGYEAR, whose Arctic Coal Company began mining operations there in 1906Independence: For most countries, this entry gives the date that sovereignty was achieved and from which nation, empire, or trusteeship. For the other countries, the date given may not represent "independence" in the strict sense, but rather some significant nationhood event such as the traditional founding date or the date of unification, federation, confederation, establishment, fundamental change in the form of government, or state succession. For a number of countries, the establishment of statehood . . . more none (territory of Norway)Legal system: This entry provides the description of a country's legal system. A statement on judicial review of legislative acts is also included for a number of countries. The legal systems of nearly all countries are generally modeled upon elements of five main types: civil law (including French law, the Napoleonic Code, Roman law, Roman-Dutch law, and Spanish law); common law (including United State law); customary law; mixed or pluralistic law; and religious law (including Islamic law). An addition . . . more
none (territory of Norway)Legal system: This entry provides the description of a country's legal system. A statement on judicial review of legislative acts is also included for a number of countries. The legal systems of nearly all countries are generally modeled upon elements of five main types: civil law (including French law, the Napoleonic Code, Roman law, Roman-Dutch law, and Spanish law); common law (including United State law); customary law; mixed or pluralistic law; and religious law (including Islamic law). An addition . . . more the laws of Norway where applicable apply; only the laws of Norway made explicitly applicable to Svalbard have effect there; the Svalbard Act and the Svalbard Environmental Protection Act, and certain regulations, apply only to Svalbard; the Spitsbergen Treaty and the Svalbard Treaty grant certain rights to citizens and corporations of signatory nations; as of June 2017, 45 nations had ratified the Svalbard TreatyCitizenship: This entry provides information related to the acquisition and exercise of citizenship; it includes four subfields: citizenship by birth describes the acquisition of citizenship based on place of birth, known as Jus soli, regardless of the citizenship of parents. citizenship by descent only describes the acquisition of citizenship based on the principle of Jus sanguinis, or by descent, where at least one parent is a citizen of the state and being born within the territorial limits of the s . . . more
the laws of Norway where applicable apply; only the laws of Norway made explicitly applicable to Svalbard have effect there; the Svalbard Act and the Svalbard Environmental Protection Act, and certain regulations, apply only to Svalbard; the Spitsbergen Treaty and the Svalbard Treaty grant certain rights to citizens and corporations of signatory nations; as of June 2017, 45 nations had ratified the Svalbard TreatyCitizenship: This entry provides information related to the acquisition and exercise of citizenship; it includes four subfields: citizenship by birth describes the acquisition of citizenship based on place of birth, known as Jus soli, regardless of the citizenship of parents. citizenship by descent only describes the acquisition of citizenship based on the principle of Jus sanguinis, or by descent, where at least one parent is a citizen of the state and being born within the territorial limits of the s . . . more see NorwayExecutive branch: This entry includes five subentries: chief of state; head of government; cabinet; elections/appointments; election results. Chief of state includes the name, title, and beginning date in office of the titular leader of the country who represents the state at official and ceremonial functions but may not be involved with the day-to-day activities of the government. Head of government includes the name, title of the top executive designated to manage the executive branch of the government, a . . . more
see NorwayExecutive branch: This entry includes five subentries: chief of state; head of government; cabinet; elections/appointments; election results. Chief of state includes the name, title, and beginning date in office of the titular leader of the country who represents the state at official and ceremonial functions but may not be involved with the day-to-day activities of the government. Head of government includes the name, title of the top executive designated to manage the executive branch of the government, a . . . more chief of state: King HARALD V of Norway (since 17 January 1991); Heir Apparent Crown Prince Haakon MAGNUS (son of the king, born 20 July 1973)head of government: Governor Kjerstin ASKHOLT (since 1 October 2015); Assistant Governor Berit SAGFOSSEN (since 1 April 2016)elections/appointments: none; the monarchy is hereditary; governor and assistant governor responsible to the Polar Department of the Ministry of JusticeLegislative branch: This entry has three subfields. The description subfield provides the legislative structure (unicameral – single house; bicameral – an upper and a lower house); formal name(s); number of member seats; types of constituencies or voting districts (single seat, multi-seat, nationwide); electoral voting system(s); and member term of office. The elections subfield includes the dates of the last election and next election. The election results subfield lists percent of vote by party/coalition an . . . more
chief of state: King HARALD V of Norway (since 17 January 1991); Heir Apparent Crown Prince Haakon MAGNUS (son of the king, born 20 July 1973)head of government: Governor Kjerstin ASKHOLT (since 1 October 2015); Assistant Governor Berit SAGFOSSEN (since 1 April 2016)elections/appointments: none; the monarchy is hereditary; governor and assistant governor responsible to the Polar Department of the Ministry of JusticeLegislative branch: This entry has three subfields. The description subfield provides the legislative structure (unicameral – single house; bicameral – an upper and a lower house); formal name(s); number of member seats; types of constituencies or voting districts (single seat, multi-seat, nationwide); electoral voting system(s); and member term of office. The elections subfield includes the dates of the last election and next election. The election results subfield lists percent of vote by party/coalition an . . . more description: unicameral Longyearbyen Community Council (15 seats; members directly elected by majority vote to serve 4-year-terms); note - the Council acts very much like a Norwegian municipality, responsible for infrastructure and utilities, including power, land-use and community planning, education, and child welfare; however, healthcare services are provided by the stateelections: last held on 6 October 2015 (next to be held in October 2019)election results: seats by party - Conservatives 5, Labor Party 5, Liberals 3, Green Party 2; composition - men 10, women 5, percent of women 33.3%Judicial branch: This entry includes three subfields. The highest court(s) subfield includes the name(s) of a country's highest level court(s), the number and titles of the judges, and the types of cases heard by the court, which commonly are based on civil, criminal, administrative, and constitutional law. A number of countries have separate constitutional courts. The judge selection and term of office subfield includes the organizations and associated officials responsible for nominating and appointing j . . . more
description: unicameral Longyearbyen Community Council (15 seats; members directly elected by majority vote to serve 4-year-terms); note - the Council acts very much like a Norwegian municipality, responsible for infrastructure and utilities, including power, land-use and community planning, education, and child welfare; however, healthcare services are provided by the stateelections: last held on 6 October 2015 (next to be held in October 2019)election results: seats by party - Conservatives 5, Labor Party 5, Liberals 3, Green Party 2; composition - men 10, women 5, percent of women 33.3%Judicial branch: This entry includes three subfields. The highest court(s) subfield includes the name(s) of a country's highest level court(s), the number and titles of the judges, and the types of cases heard by the court, which commonly are based on civil, criminal, administrative, and constitutional law. A number of countries have separate constitutional courts. The judge selection and term of office subfield includes the organizations and associated officials responsible for nominating and appointing j . . . more none; note - Svalbard is subordinate to Norway's Nord-Troms District Court and Halogaland Court of Appeal, both located in TromsoPolitical parties and leaders: This entry includes a listing of significant political parties, coalitions, and electoral lists as of each country's last legislative election, unless otherwise noted.
none; note - Svalbard is subordinate to Norway's Nord-Troms District Court and Halogaland Court of Appeal, both located in TromsoPolitical parties and leaders: This entry includes a listing of significant political parties, coalitions, and electoral lists as of each country's last legislative election, unless otherwise noted. Svalbard Conservative Party [Kjetil FIGENSCHOU]
Svalbard Conservative Party [Kjetil FIGENSCHOU]
Svalbard Green Party [Helga Bardsdatter KRISTIANSEN, Espen Klungseth ROTEVATN]
Svalbard Labor Party [Elise STROMSENG]
Svalbard Liberal Party [Erik BERGER]International organization participation: This entry lists in alphabetical order by abbreviation those international organizations in which the subject country is a member or participates in some other way. noneFlag description: This entry provides a written flag description produced from actual flags or the best information available at the time the entry was written. The flags of independent states are used by their dependencies unless there is an officially recognized local flag. Some disputed and other areas do not have flags.
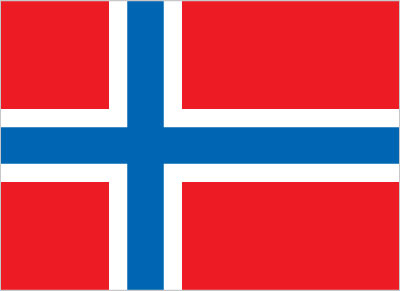
noneFlag description: This entry provides a written flag description produced from actual flags or the best information available at the time the entry was written. The flags of independent states are used by their dependencies unless there is an officially recognized local flag. Some disputed and other areas do not have flags. the flag of Norway is usedNational anthem: A generally patriotic musical composition - usually in the form of a song or hymn of praise - that evokes and eulogizes the history, traditions, or struggles of a nation or its people. National anthems can be officially recognized as a national song by a country's constitution or by an enacted law, or simply by tradition. Although most anthems contain lyrics, some do not.
the flag of Norway is usedNational anthem: A generally patriotic musical composition - usually in the form of a song or hymn of praise - that evokes and eulogizes the history, traditions, or struggles of a nation or its people. National anthems can be officially recognized as a national song by a country's constitution or by an enacted law, or simply by tradition. Although most anthems contain lyrics, some do not.
note: as a territory of Norway, "Ja, vi elsker dette landet" is official (see Norway)
-
Economy :: Svalbard
-
Economy - overview: This entry briefly describes the type of economy, including the degree of market orientation, the level of economic development, the most important natural resources, and the unique areas of specialization. It also characterizes major economic events and policy changes in the most recent 12 months and may include a statement about one or two key future macroeconomic trends.

Coal mining, tourism, and international research are Svalbard's major industries. Coal mining has historically been the dominant economic activity, and the Spitzbergen Treaty of 9 February 1920 gives the 45 countries that so far have ratified the treaty equal rights to exploit mineral deposits, subject to Norwegian regulation. Although US, UK, Dutch, and Swedish coal companies have mined in the past, the only companies still engaging in this are Norwegian and Russian. Low coal prices have forced the Norwegian coal company, Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani, to close one of its two mines and to considerably reduce the activity of the other. Since the 1990s, the tourism and hospitality industry has grown rapidly, and Svalbard now receives 60,000 visitors annually.
The settlements on Svalbard were established as company towns, and at their height in the 1950s, the Norwegian state-owned coal company supported nearly 1,000 jobs. Today, only about 300 people work in the mining industry.
Goods such as alcohol, tobacco, and vehicles, normally highly taxed on mainland Norway, are considerably cheaper in Svalbard in an effort by the Norwegian Government to entice more people to live on the Arctic archipelago. By law, Norway collects only enough taxes to pay for the needs of the local government; none of tax proceeds go to the central government.
GDP - real growth rate: This entry gives GDP growth on an annual basis adjusted for inflation and expressed as a percent. The growth rates are year-over-year, and not compounded.
NA
Labor force: This entry contains the total labor force figure. 1,590 (2013)country comparison to the world: 228Budget: This entry includes revenues, expenditures, and capital expenditures. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
1,590 (2013)country comparison to the world: 228Budget: This entry includes revenues, expenditures, and capital expenditures. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms. revenues: NAexpenditures: NATaxes and other revenues: This entry records total taxes and other revenues received by the national government during the time period indicated, expressed as a percent of GDP. Taxes include personal and corporate income taxes, value added taxes, excise taxes, and tariffs. Other revenues include social contributions - such as payments for social security and hospital insurance - grants, and net revenues from public enterprises. Normalizing the data, by dividing total revenues by GDP, enables easy comparisons acr . . . more
revenues: NAexpenditures: NATaxes and other revenues: This entry records total taxes and other revenues received by the national government during the time period indicated, expressed as a percent of GDP. Taxes include personal and corporate income taxes, value added taxes, excise taxes, and tariffs. Other revenues include social contributions - such as payments for social security and hospital insurance - grants, and net revenues from public enterprises. Normalizing the data, by dividing total revenues by GDP, enables easy comparisons acr . . . more NABudget surplus (+) or deficit (-): This entry records the difference between national government revenues and expenditures, expressed as a percent of GDP. A positive (+) number indicates that revenues exceeded expenditures (a budget surplus), while a negative (-) number indicates the reverse (a budget deficit). Normalizing the data, by dividing the budget balance by GDP, enables easy comparisons across countries and indicates whether a national government saves or borrows money. Countries with high budget deficits (relat . . . more
NABudget surplus (+) or deficit (-): This entry records the difference between national government revenues and expenditures, expressed as a percent of GDP. A positive (+) number indicates that revenues exceeded expenditures (a budget surplus), while a negative (-) number indicates the reverse (a budget deficit). Normalizing the data, by dividing the budget balance by GDP, enables easy comparisons across countries and indicates whether a national government saves or borrows money. Countries with high budget deficits (relat . . . more NAExports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise exports on an f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
NAExports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise exports on an f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
NA
Imports: This entry provides the total US dollar amount of merchandise imports on a c.i.f. (cost, insurance, and freight) or f.o.b. (free on board) basis. These figures are calculated on an exchange rate basis, i.e., not in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms.
$NA
Exchange rates: This entry provides the average annual price of a country's monetary unit for the time period specified, expressed in units of local currency per US dollar, as determined by international market forces or by official fiat. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 4217 alphabetic currency code for the national medium of exchange is presented in parenthesis. Closing daily exchange rates are not presented in The World Factbook, but are used to convert stock values - e.g., the . . . more Norwegian kroner (NOK) per US dollar -8.308 (2017 est.)8.0646 (2016 est.)8.0646 (2015)8.0646 (2014 est.)6.3021 (2013 est.)
Norwegian kroner (NOK) per US dollar -8.308 (2017 est.)8.0646 (2016 est.)8.0646 (2015)8.0646 (2014 est.)6.3021 (2013 est.) -
Energy :: Svalbard
-
Crude oil - production: This entry is the total amount of crude oil produced, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
 194,300 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 36Crude oil - exports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil exported, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
194,300 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 36Crude oil - exports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil exported, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 16,070 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 53Crude oil - imports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil imported, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
16,070 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 53Crude oil - imports: This entry is the total amount of crude oil imported, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 0 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 200Refined petroleum products - consumption: This entry is the country's total consumption of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors.
0 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 200Refined petroleum products - consumption: This entry is the country's total consumption of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). The discrepancy between the amount of refined petroleum products produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes, refinery gains, and other complicating factors. 80,250 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Refined petroleum products - exports: This entry is the country's total exports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
80,250 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Refined petroleum products - exports: This entry is the country's total exports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 4,488 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 93Refined petroleum products - imports: This entry is the country's total imports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day).
4,488 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 93Refined petroleum products - imports: This entry is the country's total imports of refined petroleum products, in barrels per day (bbl/day). 18,600 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 127Natural gas - production: This entry is the total natural gas produced in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors.
18,600 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 127Natural gas - production: This entry is the total natural gas produced in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors. 0 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Natural gas - consumption: This entry is the total natural gas consumed in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors.
0 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 203Natural gas - consumption: This entry is the total natural gas consumed in cubic meters (cu m). The discrepancy between the amount of natural gas produced and/or imported and the amount consumed and/or exported is due to the omission of stock changes and other complicating factors. 0 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 204Natural gas - exports: This entry is the total natural gas exported in cubic meters (cu m).
0 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 204Natural gas - exports: This entry is the total natural gas exported in cubic meters (cu m). 0 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 192Natural gas - imports: This entry is the total natural gas imported in cubic meters (cu m).
0 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 192Natural gas - imports: This entry is the total natural gas imported in cubic meters (cu m). 0 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 195
0 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 195 -
Communications :: Svalbard
-
Telephone system: This entry includes a brief general assessment of the system with details on the domestic and international components. The following terms and abbreviations are used throughout the entry: Arabsat - Arab Satellite Communications Organization (Riyadh, Saudi Arabia). Autodin - Automatic Digital Network (US Department of Defense). CB - citizen's band mobile radio communications. Cellular telephone system - the telephones in this system are radio transceivers, with each instrument having its o . . . more
 general assessment: modern, well-developed (2018)domestic: the Svalbard Satellite Station - connected to the mainland via the Svalbard Undersea Cable System - is the only Arctic ground station that can see low-altitude, polar-orbiting satellites; it provides ground services to more satellites than any other facility in the world (2018)international: country code - 47-790; the Svalbard Undersea Cable System is a twin communications cable that connects Svalbard to mainland Norway; the system is the sole telecommunications link to the archipelago (2019)Broadcast media: This entry provides information on the approximate number of public and private TV and radio stations in a country, as well as basic information on the availability of satellite and cable TV services.
general assessment: modern, well-developed (2018)domestic: the Svalbard Satellite Station - connected to the mainland via the Svalbard Undersea Cable System - is the only Arctic ground station that can see low-altitude, polar-orbiting satellites; it provides ground services to more satellites than any other facility in the world (2018)international: country code - 47-790; the Svalbard Undersea Cable System is a twin communications cable that connects Svalbard to mainland Norway; the system is the sole telecommunications link to the archipelago (2019)Broadcast media: This entry provides information on the approximate number of public and private TV and radio stations in a country, as well as basic information on the availability of satellite and cable TV services. the Norwegian Broadcasting Corporation (NRK) began direct TV transmission to Svalbard via satellite in 1984; Longyearbyen households have access to 3 NRK radio and 2 TV stationsInternet country code: This entry includes the two-letter codes maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in the ISO 3166 Alpha-2 list and used by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) to establish country-coded top-level domains (ccTLDs).
the Norwegian Broadcasting Corporation (NRK) began direct TV transmission to Svalbard via satellite in 1984; Longyearbyen households have access to 3 NRK radio and 2 TV stationsInternet country code: This entry includes the two-letter codes maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in the ISO 3166 Alpha-2 list and used by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) to establish country-coded top-level domains (ccTLDs). .sj
.sj -
Military and Security :: Svalbard
-
Military and security forces: This entry lists the military and security forces subordinate to defense ministries or the equivalent (typically ground, naval, air, and marine forces), as well as those belonging to interior ministries or the equivalent (typically gendarmeries, border/coast guards, paramilitary police, and other internal security forces).
 no regular military forces; military installations prohibited by treatyMilitary - note: This entry includes miscellaneous military information of significance not included elsewhere.
no regular military forces; military installations prohibited by treatyMilitary - note: This entry includes miscellaneous military information of significance not included elsewhere. Svalbard is a territory of Norway, demilitarized by treaty on 9 February 1920; Norwegian military activity is limited to fisheries surveillance by the Norwegian Coast Guard
Svalbard is a territory of Norway, demilitarized by treaty on 9 February 1920; Norwegian military activity is limited to fisheries surveillance by the Norwegian Coast Guard -
Transportation :: Svalbard
-
Airports: This entry gives the total number of airports or airfields recognizable from the air. The runway(s) may be paved (concrete or asphalt surfaces) or unpaved (grass, earth, sand, or gravel surfaces) and may include closed or abandoned installations. Airports or airfields that are no longer recognizable (overgrown, no facilities, etc.) are not included. Note that not all airports have accommodations for refueling, maintenance, or air traffic control.
 4 (2013)country comparison to the world: 190Airports - with paved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with paved runways (concrete or asphalt surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listing. Not all . . . more
4 (2013)country comparison to the world: 190Airports - with paved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with paved runways (concrete or asphalt surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listing. Not all . . . more total: 1 (2013)2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with unpaved runways (grass, dirt, sand, or gravel surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listin . . . more
total: 1 (2013)2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways: This entry gives the total number of airports with unpaved runways (grass, dirt, sand, or gravel surfaces) by length. For airports with more than one runway, only the longest runway is included according to the following five groups - (1) over 3,047 m (over 10,000 ft), (2) 2,438 to 3,047 m (8,000 to 10,000 ft), (3) 1,524 to 2,437 m (5,000 to 8,000 ft), (4) 914 to 1,523 m (3,000 to 5,000 ft), and (5) under 914 m (under 3,000 ft). Only airports with usable runways are included in this listin . . . more total: 3 (2013)under 914 m: 3 (2013)Heliports: This entry gives the total number of heliports with hard-surface runways, helipads, or landing areas that support routine sustained helicopter operations exclusively and have support facilities including one or more of the following facilities: lighting, fuel, passenger handling, or maintenance. It includes former airports used exclusively for helicopter operations but excludes heliports limited to day operations and natural clearings that could support helicopter landings and takeoffs.
total: 3 (2013)under 914 m: 3 (2013)Heliports: This entry gives the total number of heliports with hard-surface runways, helipads, or landing areas that support routine sustained helicopter operations exclusively and have support facilities including one or more of the following facilities: lighting, fuel, passenger handling, or maintenance. It includes former airports used exclusively for helicopter operations but excludes heliports limited to day operations and natural clearings that could support helicopter landings and takeoffs. 1 (2013)Ports and terminals: This entry lists major ports and terminals primarily on the basis of the amount of cargo tonnage shipped through the facilities on an annual basis. In some instances, the number of containers handled or ship visits were also considered. Most ports service multiple classes of vessels including bulk carriers (dry and liquid), break bulk cargoes (goods loaded individually in bags, boxes, crates, or drums; sometimes palletized), containers, roll-on/roll-off, and passenger ships. The listing le . . . more
1 (2013)Ports and terminals: This entry lists major ports and terminals primarily on the basis of the amount of cargo tonnage shipped through the facilities on an annual basis. In some instances, the number of containers handled or ship visits were also considered. Most ports service multiple classes of vessels including bulk carriers (dry and liquid), break bulk cargoes (goods loaded individually in bags, boxes, crates, or drums; sometimes palletized), containers, roll-on/roll-off, and passenger ships. The listing le . . . more major seaport(s): Barentsburg, Longyearbyen, Ny-Alesund, Pyramiden
major seaport(s): Barentsburg, Longyearbyen, Ny-Alesund, Pyramiden -
Transnational Issues :: Svalbard
-
Disputes - international: This entry includes a wide variety of situations that range from traditional bilateral boundary disputes to unilateral claims of one sort or another. Information regarding disputes over international terrestrial and maritime boundaries has been reviewed by the US Department of State. References to other situations involving borders or frontiers may also be included, such as resource disputes, geopolitical questions, or irredentist issues; however, inclusion does not necessarily constitute . . . more

despite recent discussions, Russia and Norway dispute their maritime limits in the Barents Sea and Russia's fishing rights beyond Svalbard's territorial limits within the Svalbard Treaty zone