Introduction :: GUYANA
-
Originally a Dutch colony in the 17th century, by 1815 Guyana had become a British possession. The abolition of slavery led to settlement of urban areas by former slaves and the importation of indentured servants from India to work the sugar plantations. The resulting ethnocultural divide has persisted and has led to turbulent politics. Guyana achieved independence from the UK in 1966, and since then it has been ruled mostly by socialist-oriented governments. In 1992, Cheddi JAGAN was elected president in what is considered the country's first free and fair election since independence. After his death five years later, his wife, Janet JAGAN, became president but resigned in 1999 due to poor health. Her successor, Bharrat JAGDEO, was reelected in 2001 and again in 2006. Donald RAMOTAR was elected president in 2011.
Geography :: GUYANA
-
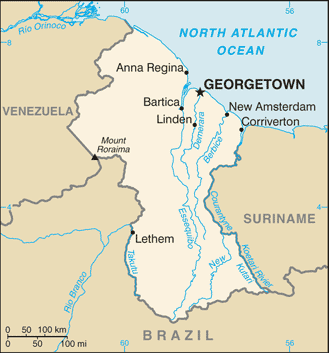
Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Suriname and Venezuela
5 00 N, 59 00 W
South America
total: 214,969 sq km
land: 196,849 sq km
water: 18,120 sq km
country comparison to the world: 85
slightly smaller than Idaho
total: 2,933 km
border countries (3): Brazil 1,308 km, Suriname 836 km, Venezuela 789 km
459 km
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or to the outer edge of the continental margin
tropical; hot, humid, moderated by northeast trade winds; two rainy seasons (May to August, November to January)
mostly rolling highlands; low coastal plain; savanna in south
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point: Mount Roraima 2,835 m
bauxite, gold, diamonds, hardwood timber, shrimp, fish
agricultural land: 8.4%
arable land 2.1%; permanent crops 0.1%; permanent pasture 6.2%
forest: 77.4%
other: 14.2% (2011 est.)
1,501 sq km (2003)
241 cu km (2011)
total: 1.64 cu km/yr (4%/1%/94%)
per capita: 2,222 cu m/yr (2010)
flash flood threat during rainy seasons
water pollution from sewage and agricultural and industrial chemicals; deforestation
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
the third-smallest country in South America after Suriname and Uruguay; substantial portions of its western and eastern territories are claimed by Venezuela and Suriname respectively
People and Society :: GUYANA
-
noun: Guyanese (singular and plural)
adjective: Guyanese
East Indian 43.5%, black (African) 30.2%, mixed 16.7%, Amerindian 9.1%, other 0.5% (includes Portuguese, Chinese, white) (2002 est.)
English (official), Guyanese Creole, Amerindian languages (including Caribbean and Arawak languages), Indian languages (including Caribbean Hindustani, a dialect of Hindi), Chinese (2014 est.)
Protestant 30.5% (Pentecostal 16.9%, Anglican 6.9%, Seventh Day Adventist 5%, Methodist 1.7%), Hindu 28.4%, Roman Catholic 8.1%, Muslim 7.2%, Jehovah's Witness 1.1%, other Christian 17.7%, other 1.9%, none 4.3%, unspecified 0.9% (2002 est.)
Guyana is the only English-speaking country in South America and shares cultural and historical bonds with the Anglophone Caribbean. Guyana's two largest ethnic groups are the Afro-Guyanese (descendants of African slaves) and the Indo-Guyanese (descendants of Indian indentured laborers), which together comprise about three quarters of Guyana's population. Tensions periodically have boiled over between the two groups, which back ethnically based political parties and vote along ethnic lines. Poverty reduction has stagnated since the late 1990s. About one-third of the Guyanese population lives below the poverty line; indigenous people are disproportionately affected. Although Guyana's literacy rate is reported to be among the highest in the Western Hemisphere, the level of functional literacy is considerably lower, which has been attributed to poor education quality, teacher training, and infrastructure.
Guyana's emigration rate is among the highest in the world - more than 55% of its citizens reside abroad - and it is one of the largest recipients of remittances relative to GDP among Latin American and Caribbean counties. Although remittances are a vital source of income for most citizens, the pervasive emigration of skilled workers deprives Guyana of professionals in healthcare and other key sectors. More than 80% of Guyanese nationals with tertiary level educations have emigrated. Brain drain and the concentration of limited medical resources in Georgetown hamper Guyana's ability to meet the health needs of its predominantly rural population. Guyana has one of the highest HIV prevalence rates in the region and continues to rely on international support for its HIV treatment and prevention programs.
735,222
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
0-14 years: 28.07% (male 105,078/female 101,296)
15-24 years: 21.26% (male 80,303/female 76,022)
25-54 years: 37.42% (male 143,490/female 131,644)
55-64 years: 7.72% (male 25,426/female 31,304)
65 years and over: 5.53% (male 16,877/female 23,782) (2015 est.)
population pyramid:

total dependency ratio: 51.1%
youth dependency ratio: 43.5%
elderly dependency ratio: 7.6%
potential support ratio: 13.2% (2015 est.)
total: 25.4 years
male: 25 years
female: 25.8 years (2015 est.)
0.02% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
15.59 births/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
7.32 deaths/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
-8.06 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 207
urban population: 28.6% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: 0.76% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
GEORGETOWN (capital) 124,000 (2014)
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.09 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.81 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.71 male(s)/female
total population: 1.02 male(s)/female (2015 est.)
total: 32.56 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 36.52 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 28.4 deaths/1,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
total population: 68.09 years
male: 65.1 years
female: 71.24 years (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 164
2.08 children born/woman (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
42.5% (2009)
6.5% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 93
0.21 physicians/1,000 population (2010)
2 beds/1,000 population (2009)
improved:
urban: 98.2% of population
rural: 98.3% of population
total: 98.3% of population
unimproved:
urban: 1.8% of population
rural: 1.7% of population
total: 1.7% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 87.9% of population
rural: 82% of population
total: 83.7% of population
unimproved:
urban: 12.1% of population
rural: 18% of population
total: 16.3% of population (2015 est.)
1.81% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
9,700 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
100 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria (2013)
21.9% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 113
11.1% (2009)
country comparison to the world: 67
3.2% of GDP (2012)
country comparison to the world: 136
definition: age 15 and over has ever attended school
total population: 88.5%
male: 87.2%
female: 89.8% (2015 est.)
total: 10 years
male: 9 years
female: 11 years (2012)
total number: 30,255
percentage: 16% (2006 est.)
total: 46.05%
male: 43.59%
female: 50% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
Government :: GUYANA
-
conventional long form: Cooperative Republic of Guyana
conventional short form: Guyana
former: British Guiana
republic
name: Georgetown
geographic coordinates: 6 48 N, 58 09 W
time difference: UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
10 regions; Barima-Waini, Cuyuni-Mazaruni, Demerara-Mahaica, East Berbice-Corentyne, Essequibo Islands-West Demerara, Mahaica-Berbice, Pomeroon-Supenaam, Potaro-Siparuni, Upper Demerara-Berbice, Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo
26 May 1966 (from the UK)
Republic Day, 23 February (1970)
several previous; latest promulgated 6 October 1980; amended many times, last in 2007 (2013)
common law system, based on the English model, with some Roman-Dutch civil law influence
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
18 years of age; universal
chief of state: President Donald RAMOTAR (since 03 December 2011)
head of government: Prime Minister Samuel HINDS (since October 1992, except for a period as chief of state after the death of President Cheddi JAGAN on 6 March 1997)
cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers appointed by the president, responsible to the National Assembly
elections/appointments: president indirectly elected by the National Assembly from party lists to serve a 5-year term (no term limits); election last held on 28 November 2011 (next to be held by December 2016); prime minister appointed by the president
election results: Donald RAMOTAR (PPP/C) elected president by National Assembly; percent of vote - 48.6%
description: unicameral National Assembly (65 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies and a single nationwide constituency by proportional representation vote; members serve 5-year terms)
elections: last held on 11 May 2015 (next to be held by May 2020)
election results: percent of vote by party - APNU 50.3%, PPP/C 49.19%, other 0.51%; seats by party - APNU 33, PPP/C 32
highest court(s): Supreme Court of Judicature (consists of the Court of Appeal with a chief justice and 3 justices, and the High Court with a chief justice and 10 justices organized into 3- or 5-judge panels); note - in 2009, Guyana ceased final appeals in civil and criminal cases to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (in London), replacing it with the Caribbean Court of Justice, the judicial organ of the Caribbean Community
judge selection and term of office: Court of Appeal and High Court chief justices appointed by the president; other judges of both courts appointed by the Judicial Service Commission, a body appointed by the president; judges appointed for life with retirement at age 65
subordinate courts: Land Court; magistrates' courts
A Partnership for National Unity or APNU [David A. GRANGER]
Alliance for Change or AFC [Khemraj RAMJATTAN]
Justice for All Party [C.N. SHARMA]
People's Progressive Party/Civic or PPP/C [Donald RAMOTAR]
Rise, Organize, and Rebuild or ROAR [Ravi DEV]
The United Force or TUF [Manzoor NADIR]
The Unity Party [Joey JAGAN]
Vision Guyana [Peter RAMSAROOP]
Amerindian People's Association
Guyana Bar Association
Guyana Citizens Initiative
Guyana Human Rights Association
Guyana Public Service Union or GPSU
Private Sector Commission
Trades Union Congress
ACP, AOSIS, C, Caricom, CD, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO (correspondent), ITU, LAES, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OIC, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, Petrocaribe, UN, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
chief of mission: Ambassador Bayney KARRAN (since 4 December 2003)
chancery: 2490 Tracy Place NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 265-6900
FAX: [1] (202) 232-1297
consulate(s) general: New York
consulate(s): Houston, Miami
chief of mission: Ambassador D. Brent HARDT (since 19 August 2011)
embassy: US Embassy, 100 Young and Duke Streets, Kingston, Georgetown
mailing address: P. O. Box 10507, Georgetown; US Embassy, 3170 Georgetown Place, Washington DC 20521-3170
telephone: [592] 225-4900 through 4909
FAX: [592] 225-8497
green with a red isosceles triangle (based on the hoist side) superimposed on a long, yellow arrowhead; there is a narrow, black border between the red and yellow, and a narrow, white border between the yellow and the green; green represents forest and foliage; yellow stands for mineral resources and a bright future; white symbolizes Guyana's rivers; red signifies zeal and the sacrifice of the people; black indicates perseverance
Canje pheasant (hoatzin), jaguar, Victoria Regia water lily; national colors: red, yellow, green, black, white
name: "Dear Land of Guyana, of Rivers and Plains"
lyrics/music: Archibald Leonard LUKERL/Robert Cyril Gladstone POTTER
note: adopted 1966
Economy :: GUYANA
-
The Guyanese economy exhibited moderate economic growth in recent years and is based largely on agriculture and extractive industries. The economy is heavily dependent upon the export of six commodities - sugar, gold, bauxite, shrimp, timber, and rice - which represent nearly 60% of the country's GDP and are highly susceptible to adverse weather conditions and fluctuations in commodity prices. Guyana's entrance into the Caricom Single Market and Economy (CSME) in January 2006 has broadened the country's export market, primarily in the raw materials sector. Guyana has experienced positive growth almost every year over the past decade. Inflation has been kept under control. Recent years have seen the government's stock of debt reduced significantly - with external debt now less than half of what it was in the early 1990s. Chronic problems include a shortage of skilled labor and a deficient infrastructure. Despite recent improvements, the government is still juggling a sizable external debt against the urgent need for expanded public investment. In March 2007, the Inter-American Development Bank, Guyana's principal donor, canceled Guyana's nearly $470 million debt, equivalent to 21% of GDP, which along with other Highly Indebted Poor Country (HIPC) debt forgiveness, brought the debt-to-GDP ratio down from 183% in 2006 to 58% in 2014. Guyana had become heavily indebted as a result of the inward-looking, state-led development model pursued in the 1970s and 1980s. Much of Guyana's growth in recent years has come from a surge in gold production in response to global prices, although downward trends in gold prices may threaten future growth. In 2014, production of sugar dropped to a 24-year low.
$5.514 billion (2014 est.)
$5.311 billion (2013 est.)
$5.047 billion (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 174
$2.997 billion (2014 est.)
3.8% (2014 est.)
5.2% (2013 est.)
4.8% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
$6,900 (2014 est.)
$6,600 (2013 est.)
$6,300 (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 154
3.5% of GDP (2014 est.)
3.5% of GDP (2013 est.)
7.6% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
household consumption: 89.2%
government consumption: 11.3%
investment in fixed capital: 24.6%
investment in inventories: -12.3%
exports of goods and services: 52%
imports of goods and services: -64.8%
(2014 est.)
agriculture: 20.3%
industry: 39.2%
services: 40.5% (2014 est.)
sugarcane, rice, edible oils; beef, pork, poultry; shrimp, fish
bauxite, sugar, rice milling, timber, textiles, gold mining
12% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
313,800 (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 163
agriculture: NA%
industry: NA%
services: NA%
11.1% (2013)
11.3% (2012)
country comparison to the world: 117
35% (2006 est.)
lowest 10%: 1.3%
highest 10%: 33.8% (1999)
44.6 (2007)
43.2 (1999)
country comparison to the world: 44
revenues: $732.2 million
expenditures: $874.3 million (2014 est.)
23.3% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
-4.5% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
58% of GDP (2014 est.)
56.6% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
calendar year
1% (2014 est.)
1.9% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
5.5% (31 December 2011)
4.25% (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 66
13.2% (31 December 2014 est.)
13.5% (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
$603.4 million (31 December 2014 est.)
$558.5 million (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
$1.59 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$1.52 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
$1.495 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$1.406 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
$610.9 million (31 December 2012 est.)
$440.4 million (31 December 2011)
$339.8 million (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
-$477 million (2014 est.)
-$405.4 million (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
$1.308 billion (2014 est.)
$1.343 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
sugar, gold, bauxite, alumina, rice, shrimp, molasses, rum, timber
US 31.9%, Canada 21.3%, Venezuela 10.9%, UK 6.4% (2014)
$1.981 billion (2014 est.)
$1.859 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
manufactures, machinery, petroleum, food
US 21.9%, Trinidad and Tobago 19.9%, Venezuela 12%, China 9.9%, Suriname 8% (2014)
$779.2 million (31 December 2014 est.)
$783.6 million (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
$1.846 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
Guyanese dollars (GYD) per US dollar -
206.9 (2014 est.)
205.39 (2013 est.)
204.36 (2012 est.)
204.02 (2011 est.)
203.64 (2010 est.)
Energy :: GUYANA
-
725 million kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
523 million kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 171
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
363,500 kW (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
96% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
0% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
0.3% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
3.7% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
0 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
0 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
0 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 197
0 bbl (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
0 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
10,880 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
0 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 184
10,780 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
0 cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
0 cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 153
0 cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
0 cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
0 cu m (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
1.661 million Mt (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
Communications :: GUYANA
-
total subscriptions: 160,000
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 22 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
total: 566,900
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 77 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
general assessment: fair system for long-distance service; microwave radio relay network for trunk lines; many areas still lack fixed-line telephone services
domestic: fixed-line teledensity is about 20 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular teledensity about 70 per 100 persons in 2011
international: country code - 592; tropospheric scatter to Trinidad; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2011)
government-dominated broadcast media; the National Communications Network (NCN) TV is state-owned; a few private TV stations relay satellite services; the state owns and operates 2 radio stations broadcasting on multiple frequencies capable of reaching the entire country; government limits on licensing of new private radio stations continue to constrain competition in broadcast media (2007)
AM 3, FM 3, shortwave 1 (2009)
3 (1 public station; 2 private stations which relay US satellite services) (1997)
.gy
total: 270,200
percent of population: 36.7% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
Transportation :: GUYANA
-
117 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 50
total: 11
1,524 to 2,437 m: 2
914 to 1,523 m: 1
under 914 m: 8 (2013)
total: 106
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 16
under 914 m:
89 (2013)
total: 7,970 km
paved: 590 km
unpaved: 7,380 km (2000)
country comparison to the world: 141
330 km (the Berbice, Demerara, and Essequibo Rivers are navigable by oceangoing vessels for 150 km, 100 km, and 80 km respectively) (2012)
country comparison to the world: 91
total: 10
by type: cargo 7, petroleum tanker 2, refrigerated cargo 1
registered in other countries: 3 (Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 2, unknown 1) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 114
major seaport(s): Georgetown
Military :: GUYANA
-
Guyana Defense Force: Army (includes Air Corps, Coast Guard) (2012)
18 years of age or older for voluntary military service; no conscription (2014)
males age 16-49: 189,840 (2010 est.)
males age 16-49: 133,239
females age 16-49: 147,719 (2010 est.)
male: 8,849
female: 8,460 (2010 est.)
1.09% of GDP (2012)
1.17% of GDP (2011)
1.09% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 93
Transnational Issues :: GUYANA
-
all of the area west of the Essequibo River is claimed by Venezuela preventing any discussion of a maritime boundary; Guyana has expressed its intention to join Barbados in asserting claims before UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) that Trinidad and Tobago's maritime boundary with Venezuela extends into their waters; Suriname claims a triangle of land between the New and Kutari/Koetari rivers in a historic dispute over the headwaters of the Courantyne; Guyana seeks arbitration under provisions of the UNCLOS to resolve the long-standing dispute with Suriname over the axis of the territorial sea boundary in potentially oil-rich waters
current situation: Guyana is a source and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to sex trafficking and forced labor; Guyanese and foreign women and girls are forced into prostitution in Guyana; forced labor, especially of children, is reported in mining, agriculture, forestry, domestic service, and shops; Indonesian workers are victims of forced labor on Guyanese-flagged fishing boats
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – Guyana does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however,it is making significant efforts to do so; limited efforts were made to protect and provide assistance to victims in 2013, and authorities operated a hotline for trafficking victims; the government failed to increase its efforts to hold trafficking offenders accountable with jail time, creating an enabling environment for human trafficking and further endangering victims (2014)
transshipment point for narcotics from South America - primarily Venezuela - to Europe and the US; producer of cannabis; rising money laundering related to drug trafficking and human smuggling
 Central Intelligence Agency
Central Intelligence Agency