Introduction :: HAITI
-
The native Taino - who inhabited the island of Hispaniola when it was discovered by Christopher COLUMBUS in 1492 - were virtually annihilated by Spanish settlers within 25 years. In the early 17th century, the French established a presence on Hispaniola. In 1697, Spain ceded to the French the western third of the island, which later became Haiti. The French colony, based on forestry and sugar-related industries, became one of the wealthiest in the Caribbean but only through the heavy importation of African slaves and considerable environmental degradation. In the late 18th century, Haiti's nearly half million slaves revolted under Toussaint L'OUVERTURE. After a prolonged struggle, Haiti became the first post-colonial black-led nation in the world, declaring its independence in 1804. Currently the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere, Haiti has experienced political instability for most of its history. After an armed rebellion led to the forced resignation and exile of President Jean-Bertrand ARISTIDE in February 2004, an interim government organized new elections under the auspices of the UN. Continued instability and technical delays prompted repeated postponements, but Haiti inaugurated a democratically elected president and parliament in May 2006. This was followed by contested elections in 2010 that resulted in the election of Haiti's current President, Michel MARTELLY. A massive magnitude 7.0 earthquake struck Haiti in January 2010 with an epicenter about 25 km (15 mi) west of the capital, Port-au-Prince. Estimates are that over 300,000 people were killed and some 1.5 million left homeless. The earthquake was assessed as the worst in this region over the last 200 years.
Geography :: HAITI
-
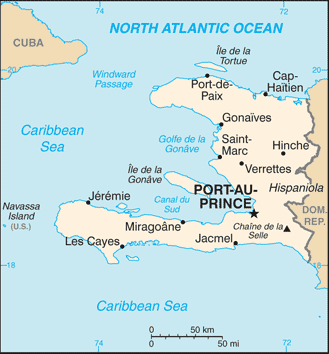
Caribbean, western one-third of the island of Hispaniola, between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, west of the Dominican Republic
19 00 N, 72 25 W
Central America and the Caribbean
total: 27,750 sq km
land: 27,560 sq km
water: 190 sq km
country comparison to the world: 148
slightly smaller than Maryland
total: 376 km
border countries (1): Dominican Republic 376 km
1,771 km
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: to depth of exploitation
tropical; semiarid where mountains in east cut off trade winds
mostly rough and mountainous
lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 m
highest point: Chaine de la Selle 2,680 m
bauxite, copper, calcium carbonate, gold, marble, hydropower, arable land
agricultural land: 66.4%
arable land 38.5%; permanent crops 10.2%; permanent pasture 17.7%
forest: 3.6%
other: 30% (2011 est.)
970 sq km (2009)
14.03 cu km (2011)
total: 1.2 cu km/yr (17%/3%/80%)
per capita: 134.3 cu m/yr (2009)
lies in the middle of the hurricane belt and subject to severe storms from June to October; occasional flooding and earthquakes; periodic droughts
extensive deforestation (much of the remaining forested land is being cleared for agriculture and used as fuel); soil erosion; inadequate supplies of potable water
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified: Hazardous Wastes
shares island of Hispaniola with Dominican Republic (western one-third is Haiti, eastern two-thirds is the Dominican Republic)
People and Society :: HAITI
-
noun: Haitian(s)
adjective: Haitian
black 95%, mulatto and white 5%
French (official), Creole (official)
Roman Catholic (official) 54.7%, Protestant 28.5% (Baptist 15.4%, Pentecostal 7.9%, Adventist 3%, Methodist 1.5%, other .7%), voodoo (official) 2.1%, other 4.6%, none 10.2%
note: many Haitians practice elements of voodoo in addition to another religion, most often Roman Catholicism; voodoo was recognized as an official religion in 2003
10,110,019
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
0-14 years: 33.28% (male 1,686,647/female 1,678,156)
15-24 years: 21.64% (male 1,093,024/female 1,094,591)
25-54 years: 35.78% (male 1,801,988/female 1,815,819)
55-64 years: 5.11% (male 247,588/female 269,103)
65 years and over: 4.18% (male 188,952/female 234,151) (2015 est.)
population pyramid:

total dependency ratio: 62.3%
youth dependency ratio: 54.8%
elderly dependency ratio: 7.5%
potential support ratio: 13.3% (2015 est.)
total: 22.5 years
male: 22.3 years
female: 22.7 years (2015 est.)
1.17%
note: the preliminary 2011 numbers differ significantly from those of 2010, which were strongly influenced by the demographic effect of the January 2010 earthquake; the latest figures more closely correspond to those of 2009 (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
22.31 births/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
7.83 deaths/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
-2.76 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 177
urban population: 58.6% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: 3.78% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
PORT-AU-PRINCE (capital) 2.44 million (2015)
at birth: 1.01 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.92 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.81 male(s)/female
total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2015 est.)
359 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
total: 47.98 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 51.71 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 44.21 deaths/1,000 live births
note: the preliminary 2011 numbers differ significantly from those of 2010, which were strongly influenced by the demographic effect of the January 2010 earthquake; the latest figures more closely correspond to those of 2009 (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
total population: 63.51 years
male: 62.07 years
female: 64.95 years (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 187
2.69 children born/woman (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
34.5% (2012)
9.4% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 96
1.3 beds/1,000 population (2007)
improved:
urban: 64.9% of population
rural: 47.6% of population
total: 57.7% of population
unimproved:
urban: 35.1% of population
rural: 52.4% of population
total: 42.3% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 33.6% of population
rural: 19.2% of population
total: 27.6% of population
unimproved:
urban: 66.4% of population
rural: 80.8% of population
total: 72.4% of population (2015 est.)
1.93% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
141,300 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
3,800 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria (2013)
10.7% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 137
11.6% (2012)
country comparison to the world: 64
NA
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 60.7%
male: 64.3%
female: 57.3% (2015 est.)
total number: 2,587,205
percentage: 21% (2006 est.)
Government :: HAITI
-
conventional long form: Republic of Haiti
conventional short form: Haiti
local long form: Republique d'Haiti/Repiblik d Ayiti
local short form: Haiti/Ayiti
republic
name: Port-au-Prince
geographic coordinates: 18 32 N, 72 20 W
time difference: UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins second Sunday in March; ends first Sunday in November
10 departments (departements, singular - departement); Artibonite, Centre, Grand'Anse, Nippes, Nord, Nord-Est, Nord-Ouest, Ouest, Sud, Sud-Est
1 January 1804 (from France)
Independence Day, 1 January (1804)
many previous (23 total); latest adopted 10 March 1987; amended 2012 (2015)
civil law system strongly influenced by Napoleonic Code
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; non-party state to the ICCt
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a native-born citizen of Haiti
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
18 years of age; universal
chief of state: President Michel MARTELLY (since 14 May 2011)
head of government: Prime Minister Evans PAUL (since 16 January 2015)
cabinet: Cabinet chosen by the prime minister in consultation with the president
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a single non-consecutive term); election last held on 25 November 2015 with a runoff on 27 December 2015 (next tentatively scheduled for late 2020); prime minister chosen by the president from among members of the majority party in the National Assembly
election results: 2010 election - Michel MARTELLY elected president in runoff; percent of vote - Michel MARTELLY (Peasant's Response) 68%, Mirlande MANIGAT (RDNP) 32%; 2015 election - results are pending
description: bicameral legislature or "le Corps Legislatif ou parlement" consists of le Senat or Senate (30 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by absolute majority vote in two rounds if needed; members serve 6-year terms with one-third of the membership renewed every 2 years) and la Chambre de deputes or Chamber of Deputies (118 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by absolute majority vote in two rounds if needed; members serve 4-year terms); note - when the two chambers meet collectively it is known as L'Assemblee Nationale or the National Assembly that is convened for specific purposes spelled out in the constitution
elections: Senate - last held on 9 August 2015 with run-off election on 25 October 2015 (next possible election in 2017); Chamber of Deputies - last held on 9 August 2015 with run-off election on 25 October 2015 (next regular election may be held in 2017)
election results: 2015 Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; 2015 Chamber of Deputies - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; note - official results pending
highest court(s): Supreme Court or Cour de Cassation (consists of a chief judge and other judges); note - Haiti is a member of the Caribbean Court of Justice
judge selection and term of office: judges appointed by the president from candidate lists submitted by the Senate of the National Assembly; note - Article 174 of the Haiti Constitution states "Judges of the Supreme Court.... are appointed for 10 years." whereas Article 177 states "Judges of the Supreme Court..... are appointed for life."
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; Courts of First Instance; magistrates' courts; special courts
Assembly of Progressive National Democrats or RDNP [Mirlande MANIGAT]
Christian and Citizen For Haiti's Reconstruction or ACCRHA [Chavannes JEUNE]
Christian Movement for a New Haiti or MCNH [Luc MESADIEU]
Convention for Democratic Unity or KID [Evans PAUL]
Cooperative Action to Rebuild Haiti or KONBA [Jean William JEANTY]
December 16 Platform or Platfom 16 Desanm [Dr. Gerard BLOT]
Democratic Alliance or ALYANS [Evans PAUL] (coalition composed of KID and PPRH)
Democratic Centers's National Council or CONACED [Osner FEVRY]
Democratic Movement for the Liberation of Haiti-Revolutionary Party of Haiti or MODELH-PRDH
Effort and Solidarity to Create an Alternative for the People or ESKAMP [Joseph JASME]
Fanmi Lavalas or FL [Jean-Bertrand ARISTIDE]
For Us All or PONT [Jean-Marie CHERESTAL]
Fusion of Haitian Social Democrats or FHSD [Edmonde Supplice BEAUZILE]
Grouping of Citizens for Hope or RESPE [Charles-Henri BAKER]
Haiti in Action or AAA [Youri LATORTUE]
Haitian Tet Kale Party or PHTK [Ann Valerie Timothee MILFORT]
Haitians for Haiti [Yvon NEPTUNE]
Independent Movement for National Reconstruction or MIRN [Luc FLEURINORD]
Konbit Pou refe Ayiti or KONBIT
Lavni Organization or LAVNI [Yves CRISTALIN]
Liberal Party of Haiti or PLH [Jean Andre VICTOR]
Liberation Platform or PLATFORME LIBERATION
Love Haiti or Renmen Ayiti [Jean-Henry CEANT and Camille LEBLANC]
Merging of Haitian Social Democratics or FUSION [Edmonde Supplice BEAUZILE] (coalition of Ayiti Capable, Haitian National Revolutionary Party, and National Congress of Democratic Movements)
Mobilization for National Development or MDN [Hubert de RONCERAY]
National Front for the Reconstruction of Haiti or FRN [Guy PHILIPPE]
New Christian Movement for a New Haiti or MOCHRENA [Luc MESADIEU]
Patriotic Movement of the Democratic Opposition or MOPOD
Patriotic Unity or IP [Marie Denise CLAUDE]
Peasant Platform or PP
Peasant's Response or Repons Peyizan [Michel MARTELLY]
Platform Alternative for Progress and Democracy or ALTENATIV [Victor BENOIT and Evans PAUL]
Platform of Haitian Patriots or PLAPH [Dejean BELISAIRE and Himmler REBU]
Platform Pitit Dessalines or PPD [Moise JEAN-CHARLES]
Pont
Popular Party for the Renewal of Haiti or PPRH [Claude ROMAIN]
PPG18
Rally or RASAMBLE
Renmen Ayiti or RA [Jean-Henry CEANT]
Respect or RESPE
Socialist Action Movement or MAS
Strength in Unity or Ansanm Nou Fo [Leslie VOLTAIRE]
Struggling People's Organization or OPL [Sauveur PIERRE-ETIENNE]
Truth (Verite)
Union [Chavannes JEUNE]
Union of Haitian Citizens for Democracy, Development, and Education or UCADDE [Jeantel JOSEPH]
Union of Nationalist and Progressive Haitians or UNPH [Edouard FRANCISQUE]
Unity or Inite [Levaillant LOUIS-JEUNE] (coalition that includes Front for Hope or L'ESPWA)
Vigilance or Veye Yo [Lavarice GAUDIN]
Youth for People's Power or JPP [Rene CIVIL]
Autonomous Organizations of Haitian Workers or CATH [Fignole ST-CYR]
Confederation of Haitian Workers or CTH
Economic Forum of the Private Sector or EF [Reginald BOULOS]
Federation of Workers Trade Unions or FOS
General Organization of Independent Haitian Workers [Patrick NUMAS]
Grand-Anse Resistance Committee or KOREGA
Haitian Association of Industries or ADIH [Georges SASSINE]
National Popular Assembly or APN
Papaye Peasants Movement or MPP [Chavannes JEAN-BAPTISTE]
Popular Organizations Gathering Power or PROP
Protestant Federation of Haiti
Roman Catholic Church
ACP, AOSIS, Caricom, CD, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OIF, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, Petrocaribe, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
chief of mission: Ambassador Paul Getty ALTIDOR (since 17 April 2012)
chancery: 2311 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 332-4090
FAX: [1] (202) 745-7215
consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Miami, Orlando (FL), New York, San Juan (Puerto Rico)
chief of mission: Ambassador Pamela A. WHITE (since 18 July 2012)
embassy: Tabarre 41, Route de Tabarre, Port-au-Prince
mailing address: (in Haiti) P.O. Box 1634, Port-au-Prince, Haiti; (from abroad) 3400 Port-au-Prince, State Department, Washington, DC 20521-3400
telephone: [509] 2229-8000
FAX: [509] 229-8028
two equal horizontal bands of blue (top) and red with a centered white rectangle bearing the coat of arms, which contains a palm tree flanked by flags and two cannons above a scroll bearing the motto L'UNION FAIT LA FORCE (Union Makes Strength); the colors are taken from the French Tricolor and represent the union of blacks and mulattoes
Hispaniolan trogon (bird), hibiscus flower; national colors: blue, red
name: "La Dessalinienne" (The Dessalines Song)
lyrics/music: Justin LHERISSON/Nicolas GEFFRARD
note: adopted 1904; named for Jean-Jacques DESSALINES, a leader in the Haitian Revolution and first ruler of an independent Haiti
Economy :: HAITI
-
Haiti is a free market economy that enjoys the advantages of low labor costs and tariff-free access to the US for many of its exports. Poverty, corruption, vulnerability to natural disasters, and low levels of education for much of the population are among Haiti's most serious impediments to economic growth. Haiti's economy suffered a severe setback in January 2010 when a 7.0 magnitude earthquake destroyed much of its capital city, Port-au-Prince, and neighboring areas. Currently the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere with 80% of the population living under the poverty line and 54% in abject poverty, the earthquake further inflicted $7.8 billion in damage and caused the country's GDP to contract. In 2011, the Haitian economy began recovering from the earthquake. However, two hurricanes adversely affected agricultural output and the low public capital spending slowed the recovery in 2012. Two-fifths of all Haitians depend on the agricultural sector, mainly small-scale subsistence farming, and remain vulnerable to damage from frequent natural disasters, exacerbated by the country's widespread deforestation. US economic engagement under the Caribbean Basin Trade Preference Agreement (CBTPA) and the 2008 Haitian Hemispheric Opportunity through Partnership Encouragement (HOPE II) Act helped increase apparel exports and investment by providing duty-free access to the US. Congress voted in 2010 to extend the CBTPA and HOPE II until 2020 under the Haiti Economic Lift Program (HELP) Act; the apparel sector accounts for about 90% of Haitian exports and nearly one-twentieth of GDP. Remittances are the primary source of foreign exchange, equaling one-fifth of GDP and representing more than five times the earnings from exports in 2012. Haiti suffers from a lack of investment, partly because of weak infrastructure such as access to electricity. Haiti's outstanding external debt was cancelled by donor countries following the 2010 earthquake, but has since risen to $1.43 billion as of December 2014. The government relies on formal international economic assistance for fiscal sustainability, with over half of its annual budget coming from outside sources.
$18.38 billion (2014 est.)
$17.88 billion (2013 est.)
$17.16 billion (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 147
$8.711 billion (2014 est.)
2.8% (2014 est.)
4.2% (2013 est.)
2.9% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
$1,800 (2014 est.)
$1,700 (2013 est.)
$1,600 (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 207
24.8% of GDP (2014 est.)
23.7% of GDP (2013 est.)
23.9% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
household consumption: 104.7%
government consumption: 0%
investment in fixed capital: 29.8%
investment in inventories: -2.2%
exports of goods and services: 15.8%
imports of goods and services: -48.1%
note: figure for household consumption also includes government consumption (2014 est.)
agriculture: 23.4%
industry: 19.8%
services: 56.8% (2014 est.)
coffee, mangoes, cocoa, sugarcane, rice, corn, sorghum; wood, vetiver
textiles, sugar refining, flour milling, cement, light assembly using imported parts
4% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
4.81 million
note: shortage of skilled labor, unskilled labor abundant (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
agriculture: 38.1%
industry: 11.5%
services: 50.4% (2010)
40.6% (2010 est.)
note: widespread unemployment and underemployment; more than two-thirds of the labor force do not have formal jobs
country comparison to the world: 197
58.5% (2012 est.)
lowest 10%: 0.7%
highest 10%: 47.7% (2001)
59.2 (2001)
country comparison to the world: 8
revenues: $1.683 billion
expenditures: $2.232 billion (2014 est.)
19.3% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
-6.3% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 188
1 October - 30 September
3.9% (2014 est.)
6.8% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
10.8% (31 December 2014 est.)
8.72% (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
$1.092 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$1.132 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
$3.509 billion (31 October 2012 est.)
$3.43 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
$2.175 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$1.699 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
$NA
-$552 million (2014 est.)
-$535 million (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
$917.7 million (2014 est.)
$883.7 million (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 162
apparel, manufactures, oils, cocoa, mangoes, coffee
US 83.2% (2014)
$3.392 billion (2014 est.)
$3.329 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
food, manufactured goods, machinery and transport equipment, fuels, raw materials
Dominican Republic 29.2%, US 23.8%, Algeria 11.7%, Netherlands Antilles 7.8%, China 7.3% (2014)
$1.99 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$2.53 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
$1.366 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$1.271 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
$1.185 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$1.086 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
gourdes (HTG) per US dollar -
45.216 (2014 est.)
45.22 (2013 est.)
41.95 (2012 est.)
40.52 (2011 est.)
39.8 (2010 est.)
Energy :: HAITI
-
1.089 billion kWh (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
452 million kWh (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 173
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
267,800 kW (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
77.3% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
22.7% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
0 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
0 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
0 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
0 bbl (1 January 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
0 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 193
15,000 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
0 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 186
14,720 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
0 cu m (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
2.094 million Mt (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
Communications :: HAITI
-
total subscriptions: 41,000
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
total: 6.8 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 68 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
general assessment: telecommunications infrastructure is among the least-developed in Latin America and the Caribbean; domestic facilities barely adequate; international facilities slightly better
domestic: mobile-cellular telephone services are expanding rapidly due, in part, to the introduction of low-cost GSM phones; mobile-cellular teledensity exceeds 40 per 100 persons
international: country code - 509; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2010)
several TV stations, including 1 government owned; cable TV subscription service available; government-owned radio network; more than 250 private and community radio stations with about 50 FM stations in Port-au-Prince alone (2007)
AM 41, FM 53, shortwave 0 (2009)
2 (plus a cable TV service) (1997)
.ht
total: 1.2 million
percent of population: 11.6% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
Transportation :: HAITI
-
14 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 148
total: 4
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2
914 to 1,523 m: 2 (2013)
total: 10
914 to 1,523 m: 2
under 914 m:
8 (2013)
total: 4,266 km
paved: 768 km
unpaved: 3,498 km (2009)
country comparison to the world: 156
major seaport(s): Cap-Haitien, Gonaives, Jacmel, Port-au-Prince
Military :: HAITI
-
no regular military forces - small Coast Guard; a Ministry of National Defense established May 2012; the regular Haitian Armed Forces (FAdH) - Army, Navy, and Air Force - have been demobilized but still exist on paper until or unless they are constitutionally abolished (2011)
males age 16-49: 2,398,804
females age 16-49: 2,415,039 (2010 est.)
males age 16-49: 1,666,324
females age 16-49: 1,704,364 (2010 est.)
male: 115,246
female: 115,282 (2010 est.)
Transnational Issues :: HAITI
-
since 2004, peacekeepers from the UN Stabilization Mission in Haiti have assisted in maintaining civil order in Haiti; the mission currently includes 6,685 military, 2,607 police, and 443 civilian personnel; despite efforts to control illegal migration, Haitians cross into the Dominican Republic and sail to neighboring countries; Haiti claims US-administered Navassa Island
IDPs: 60,801 (includes only IDPs from the 2010 earthquake living in camps or camp-like situations; information is lacking about IDPs living outside camps or who have left camps) (2015)
current situation: Haiti is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; many of Haiti’s trafficking cases involve children recruited to live with families in other towns in the hope of going to school but who instead become forced domestic servants known as restaveks; restaveks are vulnerable to abuse and make up a large proportion of Haiti’s population of street children, who are forced into prostitution, begging, and street crime by violent gangs; Haitians are exploited in forced labor in the Dominican Republic, elsewhere in the Caribbean, South America, and the US, and some Dominican women are forced into prostitution in Haiti; women and children living in camps for internally displaced people since the 2010 earthquake are at increased risk of sex trafficking and forced labor
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – Haiti does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; the government passed a law in 2014 criminalizing human trafficking but did not prosecute or convict any trafficking offenders, despite large numbers of identified victims; a national plan to combat human trafficking was also passed in 2014; authorities did not provide direct or specialized services for trafficking victims and referred suspected victims to donor-funded NGOs; the government managed a hotline for trafficking victims and conducted a campaign to raise awareness about child labor and child trafficking (2014)
Caribbean transshipment point for cocaine en route to the US and Europe; substantial bulk cash smuggling activity; Colombian narcotics traffickers favor Haiti for illicit financial transactions; pervasive corruption; significant consumer of cannabis
 Central Intelligence Agency
Central Intelligence Agency