Introduction :: LATVIA
-
The name "Latvia" originates from the ancient Latgalians, one of four eastern Baltic tribes that formed the ethnic core of the Latvian people (ca. 8th-12th centuries A.D.). The region subsequently came under the control of Germans, Poles, Swedes, and finally, Russians. A Latvian republic emerged following World War I, but it was annexed by the USSR in 1940 - an action never recognized by the US and many other countries. Latvia reestablished its independence in 1991 following the breakup of the Soviet Union. Although the last Russian troops left in 1994, the status of the Russian minority (some 28% of the population) remains of concern to Moscow. Latvia acceded to both NATO and the EU in the spring of 2004; it joined the euro zone in 2014.
Geography :: LATVIA
-
Eastern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, between Estonia and Lithuania
57 00 N, 25 00 E
Europe
total: 64,589 sq km
land: 62,249 sq km
water: 2,340 sq km
country comparison to the world: 124
slightly larger than West Virginia
Area comparison map:

total: 1,370 km
border countries (4): Belarus 161 km, Estonia 333 km, Lithuania 544 km, Russia 332 km
498 km
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: limits as agreed to by Estonia, Finland, Latvia, Sweden, and Russia
continental shelf: 200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
maritime; wet, moderate winters
low plain
lowest point: Baltic Sea 0 m
highest point: Gaizina Kalns 312 m
peat, limestone, dolomite, amber, hydropower, timber, arable land
agricultural land: 29.2%
arable land 18.6%; permanent crops 0.1%; permanent pasture 10.5%
forest: 54.1%
other: 16.7% (2011 est.)
8.3 sq km
note: land in Latvia is often too wet and in need of drainage not irrigation; approximately 16,000 sq km or 85% of agricultural land has been improved by drainage (2007)
35.45 cu km (2011)
total: 0.42 cu km/yr (42%/45%/13%)
per capita: 177.9 cu m/yr (2007)
NA
Latvia's environment has benefited from a shift to service industries after the country regained independence; improvements have occurred in drinking water quality, sewage treatment, household and hazardous waste management, as well as reduction of air pollution
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
most of the country is composed of fertile low-lying plains with some hills in the east
People and Society :: LATVIA
-
noun: Latvian(s)
adjective: Latvian
Latvian 61.1%, Russian 26.2%, Belarusian 3.5%, Ukrainian 2.3%, Polish 2.2%, Lithuanian 1.3%, other 3.4% (2013 est.)
Latvian (official) 56.3%, Russian 33.8%, other 0.6% (includes Polish, Ukrainian, and Belarusian), unspecified 9.4%
note: percentages represent lanugage usually spoken at home (2011 est.)
Lutheran 19.6%, Orthodox 15.3%, other Christian 1%, other 0.4%, unspecified 63.7% (2006)
1,986,705 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144
0-14 years: 14.86% (male 151,296/female 143,968)
15-24 years: 10.47% (male 107,301/female 100,779)
25-54 years: 42.25% (male 414,648/female 424,745)
55-64 years: 13.44% (male 117,851/female 149,063)
65 years and over: 18.98% (male 122,507/female 254,547) (2015 est.)
population pyramid:

total dependency ratio: 52.2%
youth dependency ratio: 22.7%
elderly dependency ratio: 29.5%
potential support ratio: 3.4% (2015 est.)
total: 42.9 years
male: 39.2 years
female: 46.3 years (2015 est.)
-1.06% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 231
10 births/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 194
14.31 deaths/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
-6.26 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200
urban population: 67.4% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: -0.67% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
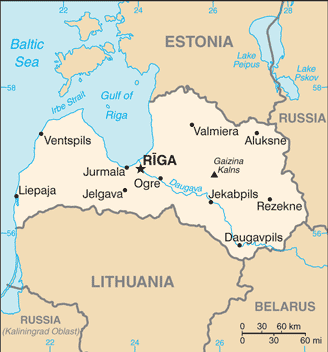
RIGA (capital) 621,000 (2015)
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.79 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.48 male(s)/female
total population: 0.85 male(s)/female (2015 est.)
total: 5.36 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 5.76 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 4.95 deaths/1,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
total population: 74.23 years
male: 69.62 years
female: 79.07 years (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
1.5 children born/woman (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
5.7% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 110
3.58 physicians/1,000 population (2012)
5.9 beds/1,000 population (2011)
improved:
urban: 99.8% of population
rural: 98.3% of population
total: 99.3% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0.2% of population
rural: 1.7% of population
total: 0.7% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 90.8% of population
rural: 81.5% of population
total: 87.8% of population
unimproved:
urban: 9.2% of population
rural: 18.5% of population
total: 12.2% of population (2015 est.)
NA
NA
NA
degree of risk: intermediate
vectorborne diseases: tickborne encephalitis (2013)
25.6% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 62
4.9% of GDP (2011)
country comparison to the world: 77
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99.9%
male: 99.9%
female: 99.9% (2015 est.)
total: 15 years
male: 15 years
female: 16 years (2012)
total: 28.4%
male: 27.6%
female: 29.3% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
Government :: LATVIA
-
conventional long form: Republic of Latvia
conventional short form: Latvia
local long form: Latvijas Republika
local short form: Latvija
former: Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic
parliamentary democracy
name: Riga
geographic coordinates: 56 57 N, 24 06 E
time difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
110 municipalities (novadi, singular - novads) and 9 cities
municipalities: Adazu Novads, Aglonas Novads, Aizkraukles Novads, Aizputes Novads, Aknistes Novads, Alojas Novads, Alsungas Novads, Aluksnes Novads, Amatas Novads, Apes Novads, Auces Novads, Babites Novads, Baldones Novads, Baltinavas Novads, Balvu Novads, Bauskas Novads, Beverinas Novads, Brocenu Novads, Burtnieku Novads, Carnikavas Novads, Cesu Novads, Cesvaines Novads, Ciblas Novads, Dagdas Novads, Daugavpils Novads, Dobeles Novads, Dundagas Novads, Durbes Novads, Engures Novads, Erglu Novads, Garkalnes Novads, Grobinas Novads, Gulbenes Novads, Iecavas Novads, Ikskiles Novads, Ilukstes Novads, Incukalna Novads, Jaunjelgavas Novads, Jaunpiebalgas Novads, Jaunpils Novads, Jekabpils Novads, Jelgavas Novads, Kandavas Novads, Karsavas Novads, Keguma Novads, Kekavas Novads, Kocenu Novads, Kokneses Novads, Kraslavas Novads, Krimuldas Novads, Krustpils Novads, Kuldigas Novads, Lielvardes Novads, Ligatnes Novads, Limbazu Novads, Livanu Novads, Lubanas Novads, Ludzas Novads, Madonas Novads, Malpils Novads, Marupes Novads, Mazsalacas Novads, Mersraga Novads, Nauksenu Novads, Neretas Novads, Nicas Novads, Ogres Novads, Olaines Novads, Ozolnieku Novads, Pargaujas Novads, Pavilostas Novads, Plavinu Novads, Preilu Novads, Priekules Novads, Priekulu Novads, Raunas Novads, Rezeknes Novads, Riebinu Novads, Rojas Novads, Ropazu Novads, Rucavas Novads, Rugaju Novads, Rujienas Novads, Rundales Novads, Salacgrivas Novads, Salas Novads, Salaspils Novads, Saldus Novads, Saulkrastu Novads, Sejas Novads, Siguldas Novads, Skriveru Novads, Skrundas Novads, Smiltenes Novads, Stopinu Novads, Strencu Novads, Talsu Novads, Tervetes Novads, Tukuma Novads, Vainodes Novads, Valkas Novads, Varaklanu Novads, Varkavas Novads, Vecpiebalgas Novads, Vecumnieku Novads, Ventspils Novads, Viesites Novads, Vilakas Novads, Vilanu Novads, Zilupes Novads
cities: Daugavpils, Jekabpils, Jelgava, Jurmala, Liepaja, Rezekne, Riga, Valmiera, Ventspils
4 May 1990 (declared); 6 September 1991 (recognized by the Soviet Union)
Independence Day, 18 November (1918); note - 18 November 1918 was the date Latvia declared independence from Soviet Russia and established its statehood; 4 May 1990 was the date it declared its independence from the Soviet Union
several previous (preindependence); note - at independence in 1990, parts of the 1922 constitution were reinforced and fully reinforced 6 July 1993; amended several times, last in 2014 (2015)
civil law system with traces of socialist legal traditions and practices
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
18 years of age; universal
chief of state: President Raimonds VEJONIS (since 8 July 2015)
head of government: Prime Minister Laimdota STRAUJUMA (since 22 January 2014)
cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers nominated by the prime minister, appointed by Parliament
elections/appointments: president indirectly elected by Parliament for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 3 June 2015 (next to be held in 2019); prime minister appointed by the president, confirmed by Parliament
election results: Andris BERZINS (ZZS) elected president; Parliament vote - Raimonds VEJONIS 55 of 100
description: unicameral Parliament or Saeima (100 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)
elections: last held on 4 October 2014 (next to be held in October 2018)
election results: percent of vote by party - SC 23%, Unity 21.9%, ZZS 19.5%, National Alliance 16.6%, NSL 6.8%, LRA 6.7%, other 5.5%; seats by party - SC 24, Unity 23, ZZS 21, National Alliance 17, LRA 8, NSL 7
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the Senate with 27 judges and Supreme Court of Chambers with 22 judges); Constitutional Court (consists of 7 judges)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges nominated by chief justice and confirmed by the Saeima; judges serve until age 70, but term can be extended 2 years; Constitutional Court judges - 3 nominated by Saeima members, 2 by Cabinet ministers, and 2 by plenum of Supreme Court; all judges confirmed by Saeima majority vote; Constitutional Court president and vice president serve in their positions for 3 years; all judges serve 10-year terms; mandatory retirement at age 70
subordinate courts: district (city) and regional courts
Alliance of Regions or LRA [Martins BONDARS, Dainis LIEPINS]
For Latvia from the Heart or NSL [Inguna SUDRABA]
Social Democratic Party "Harmony" or SC [Janis URBANOVICS, Nils USAKOVS]
National Alliance "All For Latvia!"-"For Fatherland and Freedom/LNNK" or NA [Gaidis BERZINS, Raivis DZINTARS]
Union of Greens and Farmers or ZZS [Augusts BRIGMANIS, Raimonds VEJONIS]
Unity [Solvita ABOLTINA]
Employers' Confederation of Latvia [Vitalijs GAVRILOVS]
Farmers' Parliament [Juris LAZDINS]
Free Trade Union Confederation of Latvia [Peteris KRIGERS]
Australia Group, BA, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA (cooperating state), EU, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NATO, NIB, NSG, OAS (observer), OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
chief of mission: Ambassador Andris RAZANS (since 27 July 2012)
chancery: 2306 Massachusetts Ave. NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 328-2840
FAX: [1] (202) 328-2860
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge D'Affaires Sharon HUDSON-DEAN (since 2015)
embassy: 1 Samnera Velsa St, Riga LV-1510
mailing address: Embassy of the United States of America, 1 Samnera Velsa St, Riga, LV-1510, Latvia
telephone: [371] 6710-7000
FAX: [371] 6710-7050
three horizontal bands of maroon (top), white (half-width), and maroon; the flag is one of the older banners in the world; a medieval chronicle mentions a red standard with a white stripe being used by Latvian tribes in about 1280
white wagtail (bird); national colors: maroon, white
name: "Dievs, sveti Latviju!" (God Bless Latvia)
lyrics/music: Karlis BAUMANIS
note: adopted 1920, restored 1990; first performed in 1873 while Latvia was a part of Russia; banned during the Soviet occupation from 1940 to 1990
Economy :: LATVIA
-
Latvia is a small, open economy with exports contributing nearly a third of GDP. Due to its geographical location, transit services are highly-developed, along with timber and wood-processing, agriculture and food products, and manufacturing of machinery and electronics industries. Corruption continues to be an impediment to attracting foreign direct investment and Latvia's low birth rate and decreasing population are major challenges to its long-term economic vitality. Latvia's economy experienced GDP growth of more than 10% per year during 2006-07, but entered a severe recession in 2008 as a result of an unsustainable current account deficit and large debt exposure amid the softening world economy. Triggered by the collapse of the second largest bank, GDP plunged 18% in 2009. The economy has not returned to pre-crisis levels despite strong growth, especially in the export sector in 2011-14. The IMF, EU, and other international donors provided substantial financial assistance to Latvia as part of an agreement to defend the currency's peg to the euro in exchange for the government's commitment to stringent austerity measures. The IMF/EU program successfully concluded in December 2011. The majority of companies, banks, and real estate have been privatized, although the state still holds sizable stakes in a few large enterprises, including 99.8% ownership of the Latvian national airline. Latvia officially joined the World Trade Organization in February 1999 and the EU in May 2004. Latvia joined the euro zone in 2014.
$48.19 billion (2014 est.)
$47.07 billion (2013 est.)
$45.16 billion (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 110
$31.97 billion (2014 est.)
2.4% (2014 est.)
4.2% (2013 est.)
4.8% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
$23,700 (2014 est.)
$23,200 (2013 est.)
$22,200 (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 75
20.8% of GDP (2014 est.)
21.1% of GDP (2013 est.)
22.7% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
household consumption: 61.1%
government consumption: 16.2%
investment in fixed capital: 20.9%
investment in inventories: 1.6%
exports of goods and services: 58.9%
imports of goods and services: -58.7%
(2014 est.)
agriculture: 4.8%
industry: 24.8%
services: 70.4% (2014 est.)
grain, rapeseed, potatoes, vegetables; pork, poultry, milk, eggs; fish
processed foods, processed wood products, textiles, processed metals, pharmaceuticals, railroad cars, synthetic fibers, electronics
1.5% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
1.014 million (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
agriculture: 8.8%
industry: 24%
services: 67.2% (2010 est.)
10.8% (2014 est.)
9.9% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
NA%
lowest 10%: 2.7%
highest 10%: 27.6% (2008)
35.2 (2010)
32 (1999)
country comparison to the world: 89
revenues: $11.96 billion
expenditures: $11.97 billion (2014 est.)
36.4% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
0% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
36.5% of GDP (2014 est.)
38.1% of GDP (2013 est.)
note: data cover general government debt, and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities, including sub-sectors of central government, state government, local government, and social security funds
country comparison to the world: 106
calendar year
0.7% (2014 est.)
0% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
3.5% (31 December 2011)
3.5% (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 102
6% (31 December 2014 est.)
5.92% (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
$10.15 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$10.24 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
$12.88 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$13.41 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
$15.98 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$18 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
$1.115 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
$1.076 billion (31 December 2011)
$1.252 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
-$996 million (2014 est.)
-$249.6 million (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
$13.38 billion (2014 est.)
$13.06 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
foodstuffs, wood and wood products, metals, machinery and equipment, textiles
Lithuania 17.7%, Russia 14.7%, Estonia 11.2%, Germany 6.6%, Poland 6.2%, Sweden 5.1%, UK 4.7% (2014)
$16.56 billion (2014 est.)
$15.98 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
machinery and equipment, consumer goods, chemicals, fuels, vehicles
Lithuania 17%, Germany 11.7%, Poland 10.9%, Russia 7.7%, Estonia 7.7%, Finland 5.8%, Italy 4.1% (2014)
$7.507 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$7.893 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
$38.54 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$38.28 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
$17.92 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$16.62 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
$2.731 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$2.431 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
lati (LVL) per US dollar -
0.7489 (2014 est.)
0.7634 (2013 est.)
0.55 (2012 est.)
0.5012 (2011 est.)
0.5305 (2010 est.)
Energy :: LATVIA
-
5.891 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
6.52 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
3.65 billion kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
5.005 billion kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
2.226 million kW (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
26.5% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 185
0% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
70.8% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
2.7% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
1,000 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
0 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
0 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 209
0 bbl (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
0 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 163
33,670 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
6,146 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
35,930 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
0 cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
1.48 billion cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
0 cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
1.48 billion cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
0 cu m (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
7.897 million Mt (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
Communications :: LATVIA
-
total subscriptions: 390,000
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 19 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
total: 2.5 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 126 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
general assessment: recent efforts focused on bringing competition to the telecommunications sector; the number of fixed lines is decreasing as mobile-cellular telephone service expands
domestic: number of telecommunications operators has grown rapidly since the fixed-line market opened to competition in 2003; combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular subscribership roughly 150 per 100 persons
international: country code - 371; the Latvian network is now connected via fiber optic cable to Estonia, Finland, and Sweden (2008)
several national and regional commercial TV stations are foreign-owned, 2 national TV stations are publicly owned; system supplemented by privately owned regional and local TV stations; cable and satellite multi-channel TV services with domestic and foreign broadcasts available; publicly owned broadcaster operates 4 radio networks with dozens of stations throughout the country; dozens of private broadcasters also operate radio stations (2007)
AM 8, FM 62, shortwave 1 (2008)
37 (plus 31 repeaters) (2008)
.lv
total: 1.5 million
percent of population: 76.5% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
Transportation :: LATVIA
-
42 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 101
total: 18
over 3,047 m: 1
2,438 to 3,047 m: 3
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4
914 to 1,523 m: 3
under 914 m: 7 (2013)
total: 24
under 914 m:
24 (2013)
1 (2013)
gas 928 km; refined products 415 km (2013)
total: 2,239 km
broad gauge: 2,206 km 1.520-m gauge
narrow gauge: 33 km 0.750-m gauge (2008)
country comparison to the world: 68
total: 72,440 km
paved: 14,707 km
unpaved: 57,733 km (2013)
country comparison to the world: 64
300 km (navigable year round) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 92
total: 11
by type: cargo 3, chemical tanker 1, passenger/cargo 4, petroleum tanker 2, roll on/roll off 1
foreign-owned: 3 (Estonia 3)
registered in other countries: 79 (Antigua and Barbuda 16, Belize 9, Comoros 2, Dominica 2, Georgia 1, Liberia 5, Malta 8, Marshall Islands 19, Russia 2, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 15) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 113
major seaport(s): Riga, Ventspils
Military :: LATVIA
-
National Armed Forces (Nacionalo Brunoto Speku): Land Forces (Latvijas Sauszemes Speki), Navy (Latvijas Juras Speki; includes Coast Guard (Latvijas Kara Flotes)), Latvian Air Force (Latvijas Gaisa Speki), Latvian Home Guard (Latvijas Zemessardze) (2011)
18 years of age for voluntary male and female military service; no conscription; under current law, every citizen is entitled to serve in the armed forces for life (2012)
males age 16-49: 546,090
females age 16-49: 540,810 (2010 est.)
males age 16-49: 401,691
females age 16-49: 447,638 (2010 est.)
male: 10,482
female: 9,858 (2010 est.)
0.91% of GDP (2014)
0.99% of GDP (2013)
0.92% of GDP (2012)
1.05% of GDP (2011)
0.92% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 105
Transnational Issues :: LATVIA
-
Russia demands better Latvian treatment of ethnic Russians in Latvia; boundary demarcated with Latvia and Lithuania; the Latvian parliament has not ratified its 1998 maritime boundary treaty with Lithuania, primarily due to concerns over oil exploration rights; as a member state that forms part of the EU's external border, Latvia has implemented the strict Schengen border rules with Russia
stateless persons: 262,802 (2014); note - individuals who were Latvian citizens prior to the 1940 Soviet occupation and their descendants were recognized as Latvian citizens when the country's independence was restored in 1991; citizens of the former Soviet Union residing in Latvia who have neither Latvian nor other citizenship are considered non-citizens (officially there is no statelessness in Latvia) and are entitled to non-citizen passports; children born after Latvian independence to stateless parents are entitled to Latvian citizenship upon their parents' request; non-citizens cannot vote or hold certain government jobs and are exempt from military service but can travel visa-free in the EU under the Schengen accord like Latvian citizens; non-citizens can obtain naturalization if they have been permanent residents of Latvia for at least five years, pass tests in Latvian language and history, and know the words of the Latvian national anthem
transshipment and destination point for cocaine, synthetic drugs, opiates, and cannabis from Southwest Asia, Western Europe, Latin America, and neighboring Balkan countries; despite improved legislation, vulnerable to money laundering due to nascent enforcement capabilities and comparatively weak regulation of offshore companies and the gaming industry; CIS organized crime (including counterfeiting, corruption, extortion, stolen cars, and prostitution) accounts for most laundered proceeds
 Central Intelligence Agency
Central Intelligence Agency