Introduction :: SLOVAKIA
-
Slovakia's roots can be traced to the 9th century state of Great Moravia. Subsequently, the Slovaks became part of the Hungarian Kingdom, where they remained for the next 1,000 years. Following the formation of the dual Austro-Hungarian monarchy in 1867, language and education policies favoring the use of Hungarian (Magyarization) resulted in a strengthening of Slovak nationalism and a cultivation of cultural ties with the closely related Czechs, who were under Austrian rule. After the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire at the close of World War I, the Slovaks joined the Czechs to form Czechoslovakia. During the interwar period, Slovak nationalist leaders pushed for autonomy within Czechoslovakia, and in 1939 Slovakia became an independent state allied with Nazi Germany. Following World War II, Czechoslovakia was reconstituted and came under communist rule within Soviet-dominated Eastern Europe. In 1968, an invasion by Warsaw Pact troops ended the efforts of the country's leaders to liberalize communist rule and create "socialism with a human face," ushering in a period of repression known as "normalization." The peaceful "Velvet Revolution" swept the Communist Party from power at the end of 1989 and inaugurated a return to democratic rule and a market economy. On 1 January 1993, the country underwent a nonviolent "velvet divorce" into its two national components, Slovakia and the Czech Republic. Slovakia joined both NATO and the EU in the spring of 2004 and the euro zone on 1 January 2009.
Geography :: SLOVAKIA
-
Central Europe, south of Poland
48 40 N, 19 30 E
Europe
total: 49,035 sq km
land: 48,105 sq km
water: 930 sq km
country comparison to the world: 131
about twice the size of New Hampshire
total: 1,611 km
border countries (5): Austria 105 km, Czech Republic 241 km, Hungary 627 km, Poland 541 km, Ukraine 97 km
0 km (landlocked)
none (landlocked)
temperate; cool summers; cold, cloudy, humid winters
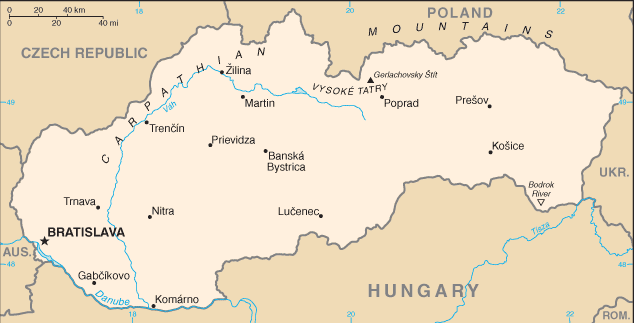
rugged mountains in the central and northern part and lowlands in the south
lowest point: Bodrok River 94 m
highest point: Gerlachovsky Stit 2,655 m
lignite, small amounts of iron ore, copper and manganese ore; salt; arable land
agricultural land: 40.1%
arable land 28.9%; permanent crops 0.4%; permanent pasture 10.8%
forest: 40.2%
other: 19.7% (2011 est.)
1,720 sq km (2007)
50.1 cu km (2011)
total: 0.69 cu km/yr (47%/51%/3%)
per capita: 126.7 cu m/yr (2010)
NA
air pollution from metallurgical plants presents human health risks; acid rain damaging forests
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
landlocked; most of the country is rugged and mountainous; the Tatra Mountains in the north are interspersed with many scenic lakes and valleys
People and Society :: SLOVAKIA
-
noun: Slovak(s)
adjective: Slovak
Slovak 80.7%, Hungarian 8.5%, Roma 2%, other and unspecified 8.8% (2011 est.)
Slovak (official) 78.6%, Hungarian 9.4%, Roma 2.3%, Ruthenian 1%, other or unspecified 8.8% (2011 est.)
Roman Catholic 62%, Protestant 8.2%, Greek Catholic 3.8%, other or unspecified 12.5%, none 13.4% (2011 est.)
5,445,027 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
0-14 years: 15.14% (male 422,297/female 402,154)
15-24 years: 11.78% (male 330,116/female 311,144)
25-54 years: 45.17% (male 1,241,594/female 1,217,885)
55-64 years: 13.56% (male 349,304/female 388,904)
65 years and over: 14.35% (male 299,097/female 482,532) (2015 est.)
population pyramid:

total dependency ratio: 40.8%
youth dependency ratio: 21.3%
elderly dependency ratio: 19.5%
potential support ratio: 5.1% (2015 est.)
total: 39.6 years
male: 37.9 years
female: 41.4 years (2015 est.)
0.02% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 191
9.91 births/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
9.74 deaths/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
0.04 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
urban population: 53.6% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: -0.31% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
BRATISLAVA (capital) 401,000 (2015)
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.9 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.62 male(s)/female
total population: 0.94 male(s)/female (2015 est.)
total: 5.27 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 5.91 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 4.58 deaths/1,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 175
total population: 76.88 years
male: 73.3 years
female: 80.71 years (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
1.39 children born/woman (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 212
8.2% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 62
3.32 physicians/1,000 population (2012)
6 beds/1,000 population (2011)
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 99.4% of population
rural: 98.2% of population
total: 98.8% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0.6% of population
rural: 1.8% of population
total: 1.2% of population (2015 est.)
0.02% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
NA
less than 100 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
27.4% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 54
4.1% of GDP (2011)
country comparison to the world: 103
total: 15 years
male: 14 years
female: 16 years (2012)
total: 34%
male: 35%
female: 32.5% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
Government :: SLOVAKIA
-
conventional long form: Slovak Republic
conventional short form: Slovakia
local long form: Slovenska republika
local short form: Slovensko
parliamentary democracy
name: Bratislava
geographic coordinates: 48 09 N, 17 07 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC,. during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
8 regions (kraje, singular - kraj); Banskobystricky, Bratislavsky, Kosicky, Nitriansky, Presovsky, Trenciansky, Trnavsky, Zilinsky
1 January 1993 (Czechoslovakia split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia)
Constitution Day, 1 September (1992)
several previous (preindependence); latest passed by National Council 1 September 1992, signed 3 September 1992, effective 1 October 1992; amended several times, last in 2009; note - amendments relating to same sex marriages were passed by the National Council in 2014 but failed to meet the required percentage of voters in a February 2015 referendum (2015)
civil law system based on Austro-Hungarian codes; note - legal code modified to comply with the obligations of Organization on Security and Cooperation in Europe
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
18 years of age; universal
chief of state: President Andrej KISKA (since 15 June 2014)
head of government: Prime Minister Robert FICO (since 4 April 2012); Deputy Prime Ministers Robert KALINAK, Peter KAZIMIR, Miroslav LAJCAK (since 4 April 2012), Lubomir VAZNY (since 26 November 2012)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president on the recommendation of the prime minister
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held in 2 rounds on 15 and 29 March 2014 (next to be held in March 2019); following National Council elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the president
election results: Andrej KISKA elected president; percent of vote in second round - Andrej KISKA (independent) 59.4%, Robert FICO (Smer-SD) 40.6%
description: unicameral National Council or Narodna Rada (150 seats; members directly elected in a single national constituency by proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)
elections: last held on 10 March 2012 (next to be held in 2016)
election results: percent of vote by party - Smer-SD 44.4%, KDH 8.8%, OLaNO 8.6%, Most-Hid 6.9%, SDKU-DS 6.1%, SaS 5.9%, other 19.3%; seats by party - Smer-SD 83, KDH 16, OLaNO 16, Most-Hid 13, SDKU-DS 11, SaS 11
highest court(s): Supreme Court of the Slovak Republic (consists of 84 judges - as of 2015 - organized into criminal, civil, commercial, and administrative divisions with 3- and 5-judge panels; Constitutional Court (consists of 13 judges)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judge candidates proposed by the Judicial Council of the Slovak Republic, a 17-member independent body to include the Supreme Court chief justice and presidential and governmental appointees; judges appointed by the president for life with mandatory retirement at age 65; Constitutional Court judges nominated by the National Council of the Republic and appointed by the president; judges appointed for 12-year terms
subordinate courts: regional and district civil courts; Higher Military Court; military district courts; Court of Audit
parties in the Parliament:
Christian Democratic Movement or KDH [Jan FIGEL]
Direction-Social Democracy or Smer-SD [Robert FICO]
Freedom and Solidarity or SaS [Richard SULIK]
Most-Hid or Bridge [Bela BUGAR]
Ordinary People and Independent Personalities or OLaNO [Igor MATOVIC]
Slovak Democratic and Christian Union-Democratic Party or SDKU-DS [Pavol FRESO]
selected parties outside the Parliament:
Civic Conservative Party or OKS [Ondrej DOSTAL]
Nation and Justice - Our Party or NAS [Anna BELOUSOVOVA]
Network or Siet [Radoslav PROCHAZKA]
New Majority or NOVA [Daniel LIPSIC]
Party of the Hungarian Coalition or SMK [Jozsef BERENYI]
People's Party - Our Slovakia or LSNS [Marian KOTLEBA]
Slovak National Party or SNS [Andrej DANKO]
Association of Towns and Villages or ZMOS
Confederation of Trade Unions or KOZ
Entrepreneurs Association of Slovakia or ZPS
Federation of Employers' Associations of the Slovak Republic or AZZZ
Medical Trade Association or LOZ
National Union of Employers or RUZ
Slovak Chamber of Commerce and Industry or SOPK
The Business Alliance of Slovakia or PAS
Australia Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CBSS (observer), CD, CE, CEI, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, EU, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, SELEC (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNIDO, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
chief of mission: Ambassador Peter KMEC (since 17 September 2012)
chancery: 3523 International Court NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 237-1054
FAX: [1] (202) 237-6438
consulate(s) general: New York
chief of mission: Ambassador Theodore SEDGWICK (since 4 July 2010)
embassy: Hviezdoslavovo Namestie 4, 81102 Bratislava
mailing address: P.O. Box 309, 814 99 Bratislava
telephone: [421] (2) 5443-3338
FAX: [421] (2) 5441-8861
three equal horizontal bands of white (top), blue, and red derive from the Pan-Slav colors; the Slovakian coat of arms (consisting of a red shield bordered in white and bearing a white double-barred cross of St. Cyril and St. Methodius surmounting three blue hills) is centered over the bands but offset slightly to the hoist side
note: the Pan-Slav colors were inspired by the 19th-century flag of Russia
double-barred cross (Cross of St. Cyril and St. Methodius) surmounting three peaks; national colors: white, blue, red
name: "Nad Tatrou sa blyska" (Lightning Over the Tatras)
lyrics/music: Janko MATUSKA/traditional
note: adopted 1993, in use since 1844; music based on the Slovak folk song "Kopala studienku"
Economy :: SLOVAKIA
-
Slovakia has made significant economic reforms since its separation from the Czech Republic in 1993. With a population of 5.4 million, the Slovak Republic has a small, open economy, with exports, at about 92% of GDP, serving as the main driver of GDP growth. Slovakia joined the European Union (EU) in 2004 and the Eurozone in 2009. The country’s banking sector is sound. Slovakia has led the region garnering FDI, because of its relatively low-cost, highly-skilled labor force, reasonable tax rates, and favorable geographic location in the heart of Central Europe. However, recent increases in corporate taxes, as well as changes to the Labor Code, slow dispute resolution, and ongoing corruption potentially threaten the attractiveness of the Slovak market. Moreover, the energy sector is characterized by high costs, unpredictable regulatory oversight, and growing government interference.
$152.6 billion (2014 est.)
$149 billion (2013 est.)
$146.9 billion (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 72
$99.97 billion (2014 est.)
2.4% (2014 est.)
1.4% (2013 est.)
1.6% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
$28,200 (2014 est.)
$27,500 (2013 est.)
$27,100 (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 61
21.2% of GDP (2014 est.)
22.2% of GDP (2013 est.)
22% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
household consumption: 56.7%
government consumption: 18.5%
investment in fixed capital: 21.1%
investment in inventories: -0.4%
exports of goods and services: 91.9%
imports of goods and services: -87.8%
(2014 est.)
agriculture: 3.4%
industry: 22.5%
services: 74.1% (2014 est.)
grains, potatoes, sugar beets, hops, fruit; pigs, cattle, poultry; forest products
automobiles; metal and metal products; electricity, gas, coke, oil, nuclear fuel; chemicals, synthetic fibers, wood and paper products; machinery; earthenware and ceramics; textiles; electrical and optical apparatus; rubber products; food and beverages; pharmaceutical
3.2% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 30
2.363 million (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
agriculture: 3.5%
industry: 25.9%
services: 70.6% (2014)
13.2% (2014 est.)
14.2% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
20.5% (2012 est.)
lowest 10%: 4.4%
highest 10%: 26% (2013 est.)
25.3 (2012)
25.7 (2011)
country comparison to the world: 132
revenues: $36.45 billion
expenditures: $39.36 billion (2014 est.)
36.5% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
-2.9% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
54.1% of GDP (2014 est.)
54.6% of GDP (2013 est.)
note: data cover general Government Gross Debt, and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by Government entities, including sub-sectors of central government, state government, local government, and social security funds.
country comparison to the world: 58
calendar year
-0.1% (2014 est.)
1.5% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
0.3% (10 September 2014)
0.75% (13 November 2013)
note: this is the European Central Bank's rate on the marginal lending facility, which offers overnight credit to banks from the euro area; Slovakia became a member of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) on 1 January 2009
country comparison to the world: 122
3.2% (31 December 2014 est.)
3.34% (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 172
$45.57 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$42.37 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
note: see entry for the European Union for money supply for the entire euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 18 members of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own borders
country comparison to the world: 56
$64.13 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$62.69 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
$53.6 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$72.07 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
$5.172 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$4.04 billion (31 December 2013)
$4.611 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
$58.62 million (2014 est.)
$1.402 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
$85.94 billion (2014 est.)
$85.22 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
vehicles and related parts 25%, machinery and electrical equipment 21%, nuclear reactors and furnaces 12%, iron and steel 5%, mineral oils and fuels 5% (2014 est.)
Germany 23.3%, Czech Republic 13.6%, Poland 8.8%, Hungary 6.6%, Austria 6.5%, UK 5.4%, France 5.2%, Italy 4.8% (2014)
$79.78 billion (2014 est.)
$79.78 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
machinery and electrical equipment 19%, vehicles and related parts 13%, nuclear reactors and furnaces 12%, fuel and mineral oils 11% (2014 est.)
Germany 19%, Czech Republic 16.9%, Austria 9.3%, Russia 7.9%, Poland 6.2%, Hungary 6.2%, South Korea 4.2%, China 4% (2014)
$2.878 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$1.176 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
$106.6 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
$114 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
$69.76 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$67.46 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
$13.09 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$12.92 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
euros (EUR) per US dollar -
0.7489 (2014 est.)
0.7634 (2013 est.)
0.78 (2012 est.)
0.7185 (2011 est.)
0.755 (2010 est.)
Energy :: SLOVAKIA
-
28.59 billion kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
28.68 billion kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
11.86 billion kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
12.93 billion kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
8.074 million kW (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
43.6% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 162
24.9% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
22% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
9.4% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
5,200 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
201.4 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
106,800 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
9 million bbl (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
9,522 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 69
136,000 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
175,200 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
303,600 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
95 million cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
5.1 billion cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
15 million cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
5.579 billion cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
14.16 billion cu m (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
29.27 million Mt (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
Communications :: SLOVAKIA
-
total subscriptions: 920,000
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 17 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
total: 6.4 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 117 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
general assessment: a modern telecommunications system that has expanded dramatically in recent years with the growth of cellular services
domestic: analog system is now receiving digital equipment and is being enlarged with fiber-optic cable, especially in the larger cities; 3 companies provide nationwide cellular services
international: country code - 421; 3 international exchanges (1 in Bratislava and 2 in Banska Bystrica) are available; Slovakia is participating in several international telecommunications projects that will increase the availability of external services (2011)
state-owned public broadcaster, Radio and Television of Slovakia (RTVS), operates 3 national TV stations and multiple national and regional radio networks; roughly 35 privately owned TV stations operating nationally, regionally, and locally; about 40% of households are connected to multi-channel cable or satellite TV; more than 20 privately owned radio stations (2008)
AM 1, FM 22, shortwave 1 (2008)
37 (2008)
.sk
total: 4.5 million
percent of population: 82.7% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
Transportation :: SLOVAKIA
-
35 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 111
total: 21
over 3,047 m: 2
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2
1,524 to 2,437 m: 3
914 to 1,523 m: 3
under 914 m: 11 (2013)
total: 14
914 to 1,523 m: 9
under 914 m:
5 (2013)
1 (2013)
gas 6,774 km; oil 419 km (2013)
total: 3,624 km
broad gauge: 99 km 1.520-m gauge
standard gauge: 3,475 km 1.435-m gauge (1,616 km electrified)
narrow gauge: 50 km 1.000-m or 0.750-m gauge (2014)
country comparison to the world: 49
total: 54,869 km (includes local roads, national roads, and 420 km of highways) (2012)
country comparison to the world: 82
172 km (on Danube River) (2012)
country comparison to the world: 99
total: 11
by type: cargo 9, refrigerated cargo 2
foreign-owned: 11 (Germany 3, Ireland 1, Italy 2, Montenegro 1, Slovenia 1, Turkey 1, Ukraine 2) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 112
river port(s): Bratislava, Komarno (Danube)
Military :: SLOVAKIA
-
Armed Forces of the Slovak Republic (Ozbrojene Sily Slovenskej Republiky): Land Forces (Pozemne Sily), Air Forces (Vzdusne Sily) (2010)
18-30 years of age for voluntary military service; conscription in peacetime suspended in 2006; women are eligible to serve (2012)
males age 16-49: 1,405,310
females age 16-49: 1,369,897 (2010 est.)
males age 16-49: 1,156,113
females age 16-49: 1,139,380 (2010 est.)
male: 31,646
female: 30,219 (2010 est.)
1.02% of GDP (2014)
1% of GDP (2013)
1.12% of GDP (2012)
1.1% of GDP (2011)
1.12% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 89
Transnational Issues :: SLOVAKIA
-
bilateral government, legal, technical and economic working group negotiations continued in 2006 between Slovakia and Hungary over Hungary's completion of its portion of the Gabcikovo-Nagymaros hydroelectric dam project along the Danube; as a member state that forms part of the EU's external border, Slovakia has implemented the strict Schengen border rules
stateless persons: 1,523 (2014)
transshipment point for Southwest Asian heroin bound for Western Europe; producer of synthetic drugs for regional market; consumer of ecstasy
 Central Intelligence Agency
Central Intelligence Agency