Introduction :: PERU
-
Ancient Peru was the seat of several prominent Andean civilizations, most notably that of the Incas whose empire was captured by Spanish conquistadors in 1533. Peruvian independence was declared in 1821, and remaining Spanish forces were defeated in 1824. After a dozen years of military rule, Peru returned to democratic leadership in 1980, but experienced economic problems and the growth of a violent insurgency. President Alberto FUJIMORI's election in 1990 ushered in a decade that saw a dramatic turnaround in the economy and significant progress in curtailing guerrilla activity. Nevertheless, the president's increasing reliance on authoritarian measures and an economic slump in the late 1990s generated mounting dissatisfaction with his regime, which led to his resignation in 2000. A caretaker government oversaw a new election in the spring of 2001, which installed Alejandro TOLEDO Manrique as the new head of government - Peru's first democratically elected president of indigenous ethnicity. The presidential election of 2006 saw the return of Alan GARCIA Perez who, after a disappointing presidential term from 1985 to 1990, oversaw a robust economic rebound. In June 2011, former army officer Ollanta HUMALA Tasso was elected president; he has carried on the sound, market-oriented economic policies of the three preceding administrations.
Geography :: PERU
-
Western South America, bordering the South Pacific Ocean, between Chile and Ecuador
10 00 S, 76 00 W
South America
total: 1,285,216 sq km
land: 1,279,996 sq km
water: 5,220 sq km
country comparison to the world: 20
almost twice the size of Texas; slightly smaller than Alaska
Area comparison map:

total: 7,062 km
border countries (5): Bolivia 1,212 km, Brazil 2,659 km, Chile 168 km, Colombia 1,494 km, Ecuador 1,529 km
2,414 km
territorial sea: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm
varies from tropical in east to dry desert in west; temperate to frigid in Andes
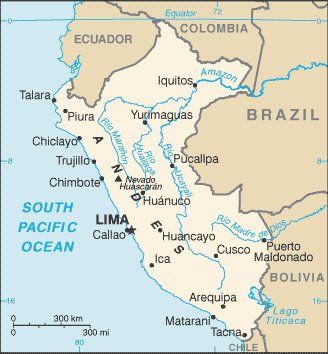
western coastal plain (costa), high and rugged Andes in center (sierra), eastern lowland jungle of Amazon Basin (selva)
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point: Nevado Huascaran 6,768 m
copper, silver, gold, petroleum, timber, fish, iron ore, coal, phosphate, potash, hydropower, natural gas
agricultural land: 18.8%
arable land 3.1%; permanent crops 1.1%; permanent pasture 14.6%
forest: 53%
other: 28.2% (2011 est.)
11,960 sq km (2003)
1,913 cu km (2011)
total: 19.34 cu km/yr (8%/10%/82%)
per capita: 727.6 cu m/yr (2005)
earthquakes, tsunamis, flooding, landslides, mild volcanic activity
volcanism: volcanic activity in the Andes Mountains; Ubinas (elev. 5,672 m), which last erupted in 2009, is the country's most active volcano; other historically active volcanoes include El Misti, Huaynaputina, Sabancaya, and Yucamane
deforestation (some the result of illegal logging); overgrazing of the slopes of the costa and sierra leading to soil erosion; desertification; air pollution in Lima; pollution of rivers and coastal waters from municipal and mining wastes
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
shares control of Lago Titicaca, world's highest navigable lake, with Bolivia; a remote slope of Nevado Mismi, a 5,316 m peak, is the ultimate source of the Amazon River
People and Society :: PERU
-
noun: Peruvian(s)
adjective: Peruvian
Amerindian 45%, mestizo (mixed Amerindian and white) 37%, white 15%, black, Japanese, Chinese, and other 3%
Spanish (official) 84.1%, Quechua (official) 13%, Aymara (official) 1.7%, Ashaninka 0.3%, other native languages (includes a large number of minor Amazonian languages) 0.7%, other (includes foreign languages and sign language) 0.2% (2007 est.)
Roman Catholic 81.3%, Evangelical 12.5%, other 3.3%, none 2.9% (2007 est.)
Peru's urban and coastal communities have benefited much more from recent economic growth than rural, Afro-Peruvian, indigenous, and poor populations of the Amazon and mountain regions. The poverty rate has dropped substantially during the last decade but remains stubbornly high at about 30% (more than 55% in rural areas). After remaining almost static for about a decade, Peru's malnutrition rate began falling in 2005, when the government introduced a coordinated strategy focusing on hygiene, sanitation, and clean water. School enrollment has improved, but achievement scores reflect ongoing problems with educational quality. Many poor children temporarily or permanently drop out of school to help support their families. About a quarter to a third of Peruvian children aged 6 to 14 work, often putting in long hours at hazardous mining or construction sites.
Peru was a country of immigration in the 19th and early 20th centuries, but has become a country of emigration in the last few decades. Beginning in the 19th century, Peru brought in Asian contract laborers mainly to work on coastal plantations. Populations of Chinese and Japanese descent - among the largest in Latin America - are economically and culturally influential in Peru today. Peruvian emigration began rising in the 1980s due to an economic crisis and a violent internal conflict, but outflows have stabilized in the last few years as economic conditions have improved. Nonetheless, more than 2 million Peruvians have emigrated in the last decade, principally to the US, Spain, and Argentina.
30,444,999 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
0-14 years: 26.95% (male 4,174,434/female 4,029,691)
15-24 years: 18.93% (male 2,884,314/female 2,877,403)
25-54 years: 39.65% (male 5,801,997/female 6,268,941)
55-64 years: 7.45% (male 1,103,641/female 1,164,821)
65 years and over: 7.03% (male 1,013,806/female 1,125,951) (2015 est.)
population pyramid:

total dependency ratio: 53.2%
youth dependency ratio: 42.7%
elderly dependency ratio: 10.5%
potential support ratio: 9.6% (2015 est.)
total: 27.3 years
male: 26.6 years
female: 28.1 years (2015 est.)
0.97% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
18.28 births/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
6.01 deaths/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 164
-2.53 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
urban population: 78.6% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: 1.69% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
LIMA (capital) 9.897 million; Arequipa 850,000; Trujillo 798,000 (2015)
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.93 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.95 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.9 male(s)/female
total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2015 est.)
total: 19.59 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 21.79 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 17.29 deaths/1,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
total population: 73.48 years
male: 71.45 years
female: 75.6 years (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 130
2.18 children born/woman (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
75.5% (2012)
5.3% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 140
1.13 physicians/1,000 population (2012)
1.5 beds/1,000 population (2012)
improved:
urban: 91.4% of population
rural: 69.2% of population
total: 86.7% of population
unimproved:
urban: 8.6% of population
rural: 30.8% of population
total: 13.3% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 82.5% of population
rural: 53.2% of population
total: 76.2% of population
unimproved:
urban: 17.5% of population
rural: 46.8% of population
total: 23.8% of population (2015 est.)
0.36% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
71,900 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
2,500 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne disease: dengue fever, malaria, and Bartonellosis (Oroya fever) (2013)
20.4% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 117
3.5% (2012)
country comparison to the world: 103
3.3% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 145
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 94.5%
male: 97.3%
female: 91.7% (2015 est.)
total: 13 years
male: 13 years
female: 13 years (2010)
total number: 2,545,855
percentage: 34%
note: data represents children ages 5-17 (2007 est.)
total: 9.5%
male: 9.4%
female: 9.7% (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
Government :: PERU
-
conventional long form: Republic of Peru
conventional short form: Peru
local long form: Republica del Peru
local short form: Peru
constitutional republic
name: Lima
geographic coordinates: 12 03 S, 77 03 W
time difference: UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
25 regions (regiones, singular - region) and 1 province* (provincia); Amazonas, Ancash, Apurimac, Arequipa, Ayacucho, Cajamarca, Callao, Cusco, Huancavelica, Huanuco, Ica, Junin, La Libertad, Lambayeque, Lima, Lima*, Loreto, Madre de Dios, Moquegua, Pasco, Piura, Puno, San Martin, Tacna, Tumbes, Ucayali
note: Callao, the largest port in Peru, is also referred to as a constitutional province, the only province of the the Callao region
28 July 1821 (from Spain)
Independence Day, 28 July (1821)
several previous; latest promulgated 29 December 1993, enacted 31 December 1993; amended several times, last in 2009 (2009)
civil law system
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
18 years of age; universal and compulsory until the age of 70
chief of state: President Ollanta HUMALA Tasso (since 28 July 2011); First Vice President Marisol ESPINOZA Cruz (since 28 July 2011); Second Vice President (vacant); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Ollanta HUMALA Tasso (since 28 July 2011); First Vice President Marisol ESPINOZA Cruz (since 28 July 2011); Second Vice President (vacant)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for nonconsecutive terms); election last held on 10 April 2011 with runoff on 6 June 2011 (next to be held in April 2016)
election results: Ollanta HUMALA Tasso elected president; percent of vote - Ollanta HUMALA Tasso (Peruvian Nationalist Party) 51.5%, Keiko FUJIMORI Higuchi (Fuerza Popular) 48.5%
note: Prime Minister Pedro CATERIANO Bellido (since 2 April 2015) does not exercise executive power; this power rests with the president; note - Prime Minister Ana JARA was removed from office by Congress in a vote of no confidence on 30 March 2015
description: unicameral Congress of the Republic of Peru or Congreso de la Republica del Peru (130 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote to serve 5-year terms)
elections: last held on 10 April 2011 with run-off election on 6 June 2011 (next to be held in April 2016)
election results: percent of vote by party - Gana Peru 25.3%, Fuerza 2011 23%, PP 14.8%, Alliance for Great Change 14.4%, National Solidarity 10.2%, Peruvian Aprista Party 6.4%, other 5.9%; seats by party - Gana Peru 47, Fuerza 2011 37, PP 21, Alliance for Great Change 12, National Solidarity 9, Peruvian Aprista Party 4; seats by bloc party as of 10 March 2014 - Gana Peru 43, Fuerza Popular (formerly Fuerza 2011) 36, PP 10, Accion Popular-Frente Amplio 10, National Solidarity 9, Union Regional 8, Partido Popular Cristiano-Alianza Para el Progreso 7, Concertacion Parlamentaria 6, Independent 1; note - defections by members of the National Assembly are commonplace, resulting in the formation of new blocs and frequent changes in the numbers of seats held by the various blocs
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of 16 judges and divided into civil, criminal, and constitutional-social sectors)
judge selection and term of office: justices proposed by the National Council of the Judiciary or National Judicial Council (a 7-member independent body), nominated by the president, and confirmed by the Congress (all appointments reviewed by the Council every 7 years); justices appointed for life or until age 70
subordinate courts: Court of Constitutional Guarantees; Superior Courts or Cortes Superiores; specialized civil, criminal, and mixed courts; 2 types of peace courts in which professional judges and selected members of the local communities preside
Alliance for Progress (Alianza para el Progreso) or APP [Cesar ACUNA Peralta]
Fuerza Popular (formerly Fuerza 2011) [Keiko FUJIMORI Higuchi]
National Solidarity (Solidaridad Nacional) or SN [Luis CASTANEDA Lossio]
Peru Posible or PP (a coalition of Accion Popular and Somos Peru) [Alejandro TOLEDO Manrique]
Peruvian Aprista Party (Partido Aprista Peruano) or PAP [Alan GARCIA Perez] (also referred to by its original name Alianza Popular Revolucionaria Americana or APRA)
Peruvian Nationalist Party [Ollanta HUMALA]
Popular Christian Party (Partido Popular Cristiano) or PPC [Lourdes FLORES Nano]
Wide Front (Frente Amplio), a coalition of left-of-center parties including Tierra y Libertad [Marco ARANA Zegarra], Ciudadanos por el Gran Cambio [Salomon LERNER Ghitis], and Fuerza Social [Susana VILLARAN de la Puente]
General Workers Confederation of Peru (Confederacion General de Trabajadores del Peru) or CGTP [Mario HUAMAN]
Shining Path (Sendero Luminoso) or SL [Abimael GUZMAN Reynoso (imprisoned), Victor QUISPE Palomino (top leader at-large)] (leftist guerrilla group)
APEC, BIS, CAN, CD, CELAC, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-24, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA, Mercosur (associate), MIGA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, Pacific Alliance, PCA, SICA (observer), UN, UNAMID, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
chief of mission: Ambassador Luis Miguel CASTILLA Rubio (since 4 February 2015)
chancery: 1700 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036
telephone: [1] (202) 833-9860 through 9869
FAX: [1] (202) 659-8124
consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Dallas, Denver, Hartford (CT), Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, Paterson (NJ), San Francisco, Washington DC
chief of mission: Ambassador Brian A. NICHOLS (since 30 June 2014)
embassy: Avenida La Encalada, Cuadra 17 s/n, Surco, Lima 33
mailing address: P. O. Box 1995, Lima 1; American Embassy (Lima), APO AA 34031-5000
telephone: [51] (1) 618-2000
FAX: [51] (1) 618-2397
three equal, vertical bands of red (hoist side), white, and red with the coat of arms centered in the white band; the coat of arms features a shield bearing a vicuna (representing fauna), a cinchona tree (the source of quinine, signifying flora), and a yellow cornucopia spilling out coins (denoting mineral wealth); red recalls blood shed for independence, white symbolizes peace
vicuna (a camelid related to the llama); national colors: red, white
name: "Himno Nacional del Peru" (National Anthem of Peru)
lyrics/music: Jose DE LA TORRE Ugarte/Jose Bernardo ALZEDO
note: adopted 1822; the song won a national anthem contest
Economy :: PERU
-
Peru's economy reflects its varied topography - an arid lowland coastal region, the central high sierra of the Andes, the dense forest of the Amazon, with tropical lands bordering Colombia and Brazil. A wide range of important mineral resources are found in the mountainous and coastal areas, and Peru's coastal waters provide excellent fishing grounds. Peru is the world's second largest producer of silver and third largest producer of copper. The Peruvian economy grew by an average of 5.6% from 2009-13 with a stable exchange rate and low inflation, which in 2013 was just below the upper limit of the Central Bank target range of 1 to 3%. This growth was due partly to high international prices for Peru's metals and minerals exports, which account for almost 60% of the country's total exports. Growth slipped in 2014, due to weaker world prices for these resources. Despite Peru's strong macroeconomic performance, dependence on minerals and metals exports and imported foodstuffs makes the economy vulnerable to fluctuations in world prices. Peru's rapid expansion coupled with cash transfers and other programs have helped to reduce the national poverty rate by 28 percentage points since 2002, but inequality persists and continues to pose a challenge for the Ollanta HUMALA administration, which has championed a policy of social inclusion and a more equitable distribution of income. Poor infrastructure hinders the spread of growth to Peru's non-coastal areas. The HUMALA administration passed several economic stimulus packages in 2014 to bolster growth, including reforms to environmental regulations in order to spur investment in Peru’s lucrative mining sector, a move that was opposed by some environmental groups. Peru's free trade policy has continued under the HUMALA administration; since 2006, Peru has signed trade deals with the US, Canada, Singapore, China, Korea, Mexico, Japan, the EU, the European Free Trade Association, Chile, Thailand, Costa Rica, Panama, Venezuela, concluded negotiations with Guatemala, and begun trade talks with Honduras, El Salvador, India, Indonesia, Turkey and the Trans-Pacific Partnership. Peru also has signed a trade pact with Chile, Colombia, and Mexico, called the Pacific Alliance, that seeks integration of services, capital, investment and movement of people. Since the US-Peru Trade Promotion Agreement entered into force in February 2009, total trade between Peru and the United States has doubled.
$371.3 billion (2014 est.)
$362.8 billion (2013 est.)
$343 billion (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 48
$202.9 billion (2014 est.)
2.4% (2014 est.)
5.8% (2013 est.)
6% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
$11,800 (2014 est.)
$11,500 (2013 est.)
$10,900 (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 119
22.7% of GDP (2014 est.)
23.8% of GDP (2013 est.)
23.5% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
household consumption: 64%
government consumption: 11.2%
investment in fixed capital: 26.2%
investment in inventories: 0.2%
exports of goods and services: 21.8%
imports of goods and services: -23.5%
(2014 est.)
agriculture: 7.1%
industry: 36.7%
services: 56.2% (2014 est.)
artichokes, asparagus, avocados, blueberries, coffee, cocoa, cotton, sugarcane, rice, potatoes, corn, plantains, grapes, oranges, pineapples, guavas, bananas, apples, lemons, pears, coca, tomatoes, mangoes, barley, medicinal plants, quinoa, palm oil, marigold, onion, wheat, dry beans; poultry, beef, pork, dairy products; guinea pigs; fish
mining and refining of minerals; steel, metal fabrication; petroleum extraction and refining, natural gas and natural gas liquefaction; fishing and fish processing, cement, glass, textiles, clothing, food processing, beer, soft drinks, rubber, machinery, electrical machinery, chemicals, furniture
4.2% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
16.55 million
note: individuals older than 14 years of age (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
agriculture: 25.8%
industry: 17.4%
services: 56.8% (2011)
6% (2014 est.)
6.5% (2013 est.)
note: data are for metropolitan Lima; widespread underemployment
country comparison to the world: 84
25.8% (2012 est.)
lowest 10%: 1.4%
highest 10%: 36.1% (2010 est.)
45.3 (2012)
51 (2005)
country comparison to the world: 39
revenues: $64.25 billion
expenditures: $64.49 billion (2014 est.)
30.9% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
-0.1% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
15.9% of GDP (2014 est.)
16.3% of GDP (2013 est.)
note: data cover general government debt, and includes debt instruments issued by government entities other than the treasury; the data exclude treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities
country comparison to the world: 145
calendar year
3.2% (2014 est.)
2.8% (2013 est.)
note: data are for metropolitan Lima, annual average
country comparison to the world: 140
5.05% (31 December 2012)
5.05% (31 December 2011)
country comparison to the world: 73
15.7% (31 December 2014 est.)
18.16% (31 December 2013 est.)
note: domestic currency lending rate, 90 day maturity
country comparison to the world: 32
$33.71 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$32.59 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
$91.26 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$84.1 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
$47.4 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$43.06 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
$153.4 billion (31 December 2012)
$121.6 billion (31 December 2011)
$160.9 billion (31 December 2010)
country comparison to the world: 38
-$8.234 billion (2014 est.)
-$9.126 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 180
$36.43 billion (2014 est.)
$42.18 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
copper, gold, lead, zinc, tin, iron ore, molybdenum, silver; crude petroleum and petroleum products, natural gas; coffee, asparagus and other vegetables, fruit, apparel and textiles, fishmeal, fish, chemicals, fabricated metal products and machinery, alloys
China 18.3%, US 16.1%, Switzerland 6.9%, Canada 6.6%, Brazil 4.2%, Japan 4.1% (2014)
$40.25 billion (2014 est.)
$42.22 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
petroleum and petroleum products, chemicals, plastics, machinery, vehicles, TV sets, power shovels, front-end loaders, telephones and telecommunication equipment, iron and steel, wheat, corn, soybean products, paper, cotton, vaccines and medicines
China 21%, US 21%, Brazil 4.7%, Mexico 4.6%, Ecuador 4.2% (2014)
$63.35 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$65.71 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
$56.47 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$55.62 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
$81.63 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$72.61 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
$3.883 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$3.849 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
nuevo sol (PEN) per US dollar -
2.836 (2014 est.)
2.7019 (2013 est.)
2.64 (2012 est.)
2.7541 (2011 est.)
2.8251 (2010 est.)
Energy :: PERU
-
38.4 billion kWh (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
35.71 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
2 million kWh (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
0 kWh (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 187
8.557 million kW (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
59.6% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
0% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
40.4% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
0% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
170,500 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
15,610 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
99,590 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
632.9 million bbl (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
159,500 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
171,400 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
82,080 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
43,480 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 76
32.4 billion cu m (2012)
country comparison to the world: 28
11.85 billion cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
8.73 billion cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
0 cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
435.4 billion cu m (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
53.58 million Mt (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
Communications :: PERU
-
total subscriptions: 3.03 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 10 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
total: 31.7 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 105 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
general assessment: adequate for most requirements; nationwide microwave radio relay system and a domestic satellite system with 12 earth stations
domestic: fixed-line teledensity is only about 12 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular teledensity, spurred by competition among multiple providers, exceeds 100 telephones per 100 persons
international: country code - 51; the South America-1 (SAM-1) and Pan American (PAN-AM) submarine cable systems provide links to parts of Central and South America, the Caribbean, and US; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2010)
10 major TV networks of which only one, Television Nacional de Peru, is state owned; multi-channel cable TV services are available; in excess of 2,000 radio stations including a substantial number of indigenous language stations (2010)
AM 472, FM 198, shortwave 189 (1999)
13 (plus 112 repeaters) (1997)
.pe
total: 12.3 million
percent of population: 40.9% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
Transportation :: PERU
-
191 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 30
total: 59
over 3,047 m: 5
2,438 to 3,047 m: 21
1,524 to 2,437 m: 16
914 to 1,523 m: 12
under 914 m: 5 (2013)
total: 132
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 19
914 to 1,523 m: 30
under 914 m:
82 (2013)
5 (2013)
extra heavy crude 786 km; gas 1,526 km; liquid petroleum gas 679 km; oil 1,033 km; refined products 15 km (2013)
total: 1,854.4 km
standard gauge: 1,730.4 km 1.435-m gauge (34 km electrified)
narrow gauge: 124 km 0.914-m gauge (2014)
country comparison to the world: 74
total: 140,672 km (18,699 km paved)
note: includes 24,593 km of national roads (14,748 km paved), 24,235 km of departmental roads (2,340 km paved), and 91,844 km of local roads (1,611 km paved) (2012)
country comparison to the world: 35
8,808 km (8,600 km of navigable tributaries on the Amazon system and 208 km on Lago Titicaca) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 14
total: 22
by type: cargo 2, chemical tanker 5, liquefied gas 2, petroleum tanker 13
foreign-owned: 8 (Chile 6, Ecuador 1, Spain 1)
registered in other countries: 9 (Panama 9) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 92
major seaport(s): Callao, Matarani, Paita
river port(s): Iquitos, Pucallpa, Yurimaguas (Amazon)
oil terminals: Conchan oil terminal, La Pampilla oil terminal
container port(s) (TEUs): Callao (1,616,365)
Military :: PERU
-
Peruvian Army (Ejercito Peruano), Peruvian Navy (Marina de Guerra del Peru, MGP; includes naval air, naval infantry, and Coast Guard), Air Force of Peru (Fuerza Aerea del Peru, FAP) (2013)
18-50 years of age for male and 18-45 years of age for female voluntary military service; no conscription (2012)
males age 16-49: 7,385,588
females age 16-49: 7,727,623 (2010 est.)
males age 16-49: 5,788,629
females age 16-49: 6,565,097 (2010 est.)
male: 304,094
female: 298,447 (2010 est.)
1.28% of GDP (2012)
1.15% of GDP (2011)
1.28% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 78
Transnational Issues :: PERU
-
Chile and Ecuador rejected Peru's November 2005 unilateral legislation to shift the axis of their joint treaty-defined maritime boundaries along the parallels of latitude to equidistance lines which favor Peru; organized illegal narcotics operations in Colombia have penetrated Peru's shared border; Peru rejects Bolivia's claim to restore maritime access through a sovereign corridor through Chile along the Peruvian border
IDPs: at least 150,000 (civil war from 1980-2000; most IDPs are indigenous peasants in Andean and Amazonian regions; as of 2011, no new information on the situation of these IDPs) (2014)
until 1996 the world's largest coca leaf producer, Peru is now the world's second largest producer of coca leaf, though it lags far behind Colombia; cultivation of coca in Peru was estimated at 40,000 hectares in 2009, a slight decrease over 2008; second largest producer of cocaine, estimated at 225 metric tons of potential pure cocaine in 2009; finished cocaine is shipped out from Pacific ports to the international drug market; increasing amounts of base and finished cocaine, however, are being moved to Brazil, Chile, Argentina, and Bolivia for use in the Southern Cone or transshipment to Europe and Africa; increasing domestic drug consumption
 Central Intelligence Agency
Central Intelligence Agency