Europe :: UKRAINE
Introduction :: UKRAINE
-
Ukraine was the center of the first eastern Slavic state, Kyivan Rus, which during the 10th and 11th centuries was the largest and most powerful state in Europe. Weakened by internecine quarrels and Mongol invasions, Kyivan Rus was incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and eventually into the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The cultural and religious legacy of Kyivan Rus laid the foundation for Ukrainian nationalism through subsequent centuries. A new Ukrainian state, the Cossack Hetmanate, was established during the mid-17th century after an uprising against the Poles. Despite continuous Muscovite pressure, the Hetmanate managed to remain autonomous for well over 100 years. During the latter part of the 18th century, most Ukrainian ethnographic territory was absorbed by the Russian Empire. Following the collapse of czarist Russia in 1917, Ukraine achieved a short-lived period of independence (1917-20), but was reconquered and endured a brutal Soviet rule that engineered two forced famines (1921-22 and 1932-33) in which over 8 million died. In World War II, German and Soviet armies were responsible for 7 to 8 million more deaths. Although Ukraine achieved final independence in 1991 with the dissolution of the USSR, democracy and prosperity remained elusive as the legacy of state control and endemic corruption stalled efforts at economic reform, privatization, and civil liberties.A peaceful mass protest referred to as the "Orange Revolution" in the closing months of 2004 forced the authorities to overturn a rigged presidential election and to allow a new internationally monitored vote that swept into power a reformist slate under Viktor YUSHCHENKO. Subsequent internal squabbles in the YUSHCHENKO camp allowed his rival Viktor YANUKOVYCH to stage a comeback in parliamentary (Rada) elections, become prime minister in August 2006, and be elected president in February 2010. In October 2012, Ukraine held Rada elections, widely criticized by Western observers as flawed due to use of government resources to favor ruling party candidates, interference with media access, and harassment of opposition candidates. President YANUKOVYCH's backtracking on a trade and cooperation agreement with the EU in November 2013 - in favor of closer economic ties with Russia - and subsequent use of force against civil society activists in favor of the agreement led to a three-month protest occupation of Kyiv's central square. The government's use of violence to break up the protest camp in February 2014 led to all out pitched battles, scores of deaths, international condemnation, and the president's abrupt departure to Russia. New elections in the spring allowed pro-West president Petro POROSHENKO to assume office on 7 June 2014.Shortly after YANUKOVYCH’s departure in March 2014, Russian President PUTIN ordered the invasion of Ukraine's Crimean Peninsula claiming the action was to protect ethnic Russians living there. Two weeks later, a "referendum" was held regarding the integration of Crimea into the Russian Federation. The "referendum" was condemned as illegitimate by the Ukrainian Government, the EU, the US, and the UN General Assembly. Although Russia illegally annexed Crimea after the "referendum," the Ukrainian Government asserts that Crimea remains part of Ukraine. Russia also continues to supply separatists in two of Ukraine's eastern provinces with manpower, funding, and materiel resulting in an armed conflict with the Ukrainian Government.
Geography :: UKRAINE
-
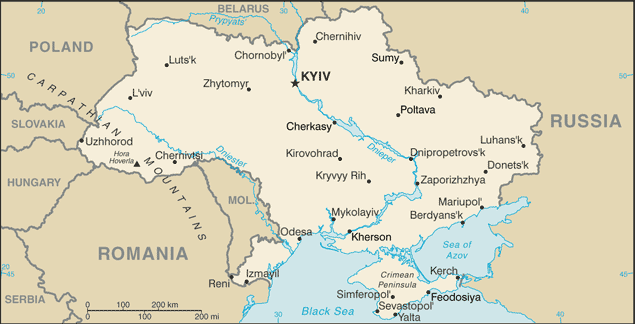
Eastern Europe, bordering the Black Sea, between Poland, Romania, and Moldova in the west and Russia in the east49 00 N, 32 00 EAsia, Europetotal: 603,550 sq kmland: 579,330 sq kmwater: 24,220 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 46almost four times the size of Georgia; slightly smaller than Texastotal: 5,618 kmborder countries (7): Belarus 1,111 km, Hungary 128 km, Moldova 1,202 km, Poland 535 km, Romania 601 km, Russia 1,944 km, Slovakia 97 km2,782 kmterritorial sea: 12 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: 200 m or to the depth of exploitationtemperate continental; Mediterranean only on the southern Crimean coast; precipitation disproportionately distributed, highest in west and north, lesser in east and southeast; winters vary from cool along the Black Sea to cold farther inland; warm summers across the greater part of the country, hot in the southmostly fertile plains (steppes) and plateaus, with mountains found only in the west (the Carpathians) or in the extreme south of the Crimean Peninsulalowest point: Black Sea 0 mhighest point: Hora Hoverla 2,061 miron ore, coal, manganese, natural gas, oil, salt, sulfur, graphite, titanium, magnesium, kaolin, nickel, mercury, timber, arable landagricultural land: 71.2%arable land 56.1%; permanent crops 1.5%; permanent pasture 13.6%forest: 16.8%other: 12% (2011 est.)21,750 sq km (2010)139.6 cu km (2011)total: 19.24 cu km/yr (24%/69%/7%)per capita: 415.7 cu m/yr (2010)NAinadequate supplies of potable water; air and water pollution; deforestation; radiation contamination in the northeast from 1986 accident at Chornobyl' Nuclear Power Plantparty to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compoundsstrategic position at the crossroads between Europe and Asia; second-largest country in Europe
People and Society :: UKRAINE
-
noun: Ukrainian(s)adjective: UkrainianUkrainian 77.8%, Russian 17.3%, Belarusian 0.6%, Moldovan 0.5%, Crimean Tatar 0.5%, Bulgarian 0.4%, Hungarian 0.3%, Romanian 0.3%, Polish 0.3%, Jewish 0.2%, other 1.8% (2001 est.)Ukrainian (official) 67.5%, Russian (regional language) 29.6%, other (includes small Crimean Tatar-, Moldavian-, and Hungarian-speaking minorities) 2.9% (2001 est.)note: 2012 legislation enables a language spoken by at least 10% of an oblast's population to be given the status of "regional language," allowing for its use in courts, schools, and other government institutions; Ukrainian remains the country's only official nationwide languageOrthodox (includes Ukrainian Autocephalous Orthodox (UAOC), Ukrainian Orthodox - Kyiv Patriarchate (UOC-KP), Ukrainian Orthodox - Moscow Patriarchate (UOC-MP), Ukrainian Greek Catholic, Roman Catholic, Protestant, Muslim, Jewishnote: Ukraine's population is overwhelmingly Christian; the vast majority - up to two-thirds - identify themselves as Orthodox, but many do not specify a particular branch; the UOC-KP and the UOC-MP each represent less than a quarter of the country's population, the Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church accounts for 8-10%, and the UAOC accounts for 1-2%; Muslim and Jewish adherents each compose less than 1% of the total population (2013 est.)44,429,471 (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 320-14 years: 15.22% (male 3,480,870/female 3,281,363)15-24 years: 10.85% (male 2,470,594/female 2,349,313)25-54 years: 44.63% (male 9,703,407/female 10,126,348)55-64 years: 13.5% (male 2,563,195/female 3,435,022)65 years and over: 15.8% (male 2,343,097/female 4,676,262) (2015 est.)total dependency ratio: 43.3%youth dependency ratio: 21.4%elderly dependency ratio: 21.9%potential support ratio: 4.6% (2015 est.)total: 40.1 yearsmale: 37 yearsfemale: 43.3 years (2015 est.)-0.6% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 22610.72 births/1,000 population (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 20314.46 deaths/1,000 population (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 2-2.25 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 113urban population: 69.7% of total population (2015)rate of urbanization: -0.33% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)KYIV (capital) 2.942 million; Kharkiv 1.441 million; Odesa 1.01 million; Dnipropetrovsk 957,000; Donetsk 934,000; Zaporizhzhya 753,000 (2015)at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.96 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.75 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.5 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.86 male(s)/female (2015 est.)total: 8.12 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 9.03 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 7.16 deaths/1,000 live births (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 154total population: 71.57 yearsmale: 66.81 yearsfemale: 76.63 years (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1571.53 children born/woman (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 21565.4% (2012)7.8% of GDP (2013)country comparison to the world: 663.54 physicians/1,000 population (2013)9 beds/1,000 population (2012)improved:urban: 95.5% of populationrural: 97.8% of populationtotal: 96.2% of populationunimproved:urban: 4.5% of populationrural: 2.2% of populationtotal: 3.8% of population (2015 est.)improved:urban: 97.4% of populationrural: 92.6% of populationtotal: 95.9% of populationunimproved:urban: 2.6% of populationrural: 7.4% of populationtotal: 4.1% of population (2015 est.)0.83% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 49210,700 (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 2513,400 (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 2021.7% (2014)country comparison to the world: 896.7% of GDP (2012)country comparison to the world: 35definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 99.8%male: 99.8%female: 99.7% (2015 est.)total: 15 yearsmale: 15 yearsfemale: 15 years (2013)total number: 356,213percentage: 7% (2005 est.)total: 17.3%male: 18.1%female: 16.1% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 67
Government :: UKRAINE
-
conventional long form: noneconventional short form: Ukrainelocal long form: nonelocal short form: Ukrayinaformer: Ukrainian National Republic, Ukrainian State, Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republicnote: name derives from the Old East Slavic word "ukraina" meaning borderland or march (militarized border region)republicname: Kyiv (Kiev)note: pronounced KAY-yivgeographic coordinates: 50 26 N, 30 31 Etime difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October24 provinces (oblasti, singular - oblast'), 1 autonomous republic* (avtonomna respublika), and 2 municipalities (mista, singular - misto) with oblast status**; Cherkasy, Chernihiv, Chernivtsi, Crimea or Avtonomna Respublika Krym* (Simferopol'), Dnipropetrovs'k, Donets'k, Ivano-Frankivs'k, Kharkiv, Kherson, Khmel'nyts'kyy, Kirovohrad, Kyiv**, Kyiv, Luhans'k, L'viv, Mykolayiv, Odesa, Poltava, Rivne, Sevastopol'**, Sumy, Ternopil', Vinnytsya, Volyn' (Luts'k), Zakarpattya (Uzhhorod), Zaporizhzhya, Zhytomyrnote 1: administrative divisions have the same names as their administrative centers (exceptions have the administrative center name following in parentheses)note 2: the United States does not recognize Russia's annexation of Ukraine's Autonomous Republic of Crimea and the municipality of Sevastopol, nor their redesignation as the Republic of Crimea and the Federal City of Sevastopol24 August 1991 (from the Soviet Union); notable earlier dates: ca. 982 (VOLODYMYR I consolidates Kyivan Rus), 1648 (establishment of Cossack Hetmanate)Independence Day, 24 August (1991); note - 22 January 1918, the day Ukraine first declared its independence (from Soviet Russia) and the day the short-lived Western and Greater (Eastern) Ukrainian republics united (1919), is now celebrated as Unity Dayseveral previous; latest adopted and ratified 28 June 1996; amended 2004, 2010; note - to revert to the 2004 version pending additional constitutional reforms (2014)civil law system; judicial review of legislative actshas not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt18 years of age; universalchief of state: President Petro POROSHENKO (since 7 June 2014)head of government: Prime Minister Arseniy YATSENYUK (since 27 February 2014)cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers nominated by the president, approved by the Verkhovna Radaelections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 25 May 2014 (next to be held in 2019); prime minister nominated by the president, confirmed by the Verkhovna Radaelection results: Petro POROSHENKO elected president; percent of vote - Petro POROSHENKO (independent) 54.5%, Yuliya TYMOSHENKO (Fatherland) 12.9%, Oleh LYASHKO (Radical Party) 8.4%, other 24.2%note: there is also a National Security and Defense Council or NSDC originally created in 1992 as the National Security Council; the NSDC staff is tasked with developing national security policy on domestic and international matters and advising the president; a presidential administration helps draft presidential edicts and provides policy support to the presidentdescription: unicameral Supreme Council or Verkhovna Rada (450 seats; 225 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 225 directly elected in a single nationwide constituency by proportional representation vote; members serve 5-year terms); note - because of the Russian annexation of Crimea and the partial occupation of two eastern provinces, 27 of the 450 seats remain unfilledelections: last held on 26 October 2014 (next to be held fall 2019)election results: percent of vote by party - NF 22.2%, BPP 21.8%, Samopomich 11%, OB 9.4%, Radical 7.4%, Batkivshchyna 5.7%, Svoboda 4.7%, CPU 3.9%, other 13.9%; seats won by party - BPP 132, NF 82, Samopomich 33, OB 29, Radical 22, Batkivshchyna 19, Svoboda 6, minor parties 4, independents 96, vacant 27; note - voting not held in Crimea and parts of two Russian-occupied eastern oblasts leaving 27 seats vacant; seats of first parliamentary session (27 November 2014) following weeks of negotiations - BPP 145, NF 83, Samopomich 32, OB 40, Radical 22, VN 20, Batkivshchyna 19, ER 19, independents 38, vacant 32highest court(s): Supreme Court of Ukraine or SCU (consists of 95 judges organized into civil, criminal, commercial, and administrative chambers, and a military panel); Constitutional Court (consists of 18 justices)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges proposed by the Supreme Council of Justice or SCJ (a 20-member independent body of judicial officials and other appointees) and appointed by presidential decree; judges initially appointed for 5 years and, if approved by the SCJ, serve until mandatory retirement at age 65; Constitutional Court justices appointed - 6 each by the president, by the SCU, and by the Verkhovna Rada; justices appointed for 9-year non-renewable termssubordinate courts: specialized high courts; Courts of Cassation; Courts of Appeal; regional, district, city, and town courtsBatkivshchyna ("Fatherland") [Yuliya TYMOSHENKO]Communist Party of Ukraine or CPU [Petro SYMONENKO]Opposition Bloc or OB [Yuriy BOIKO]People's Front or NF [Arseniy YATSENIUK]People's Will or VN [Ihor YEREMEYEV]Radical Party [Oleh LYASHKO]Samopomich ("Selfreliance") [Andriy SADOVYI]Svoboda ("Freedom") [Oleh TYAHNYBOK]UDAR-Solidarity [Vitali KLITSCHKO] (formed from the merger of the Petro Poroshenko Bloc (BPP) and UDAR)Committee of Voters of Ukraine [Oleksandr CHERNENKO]OPORA [Olha AIVAZOVSKA]Australia Group, BSEC, CBSS (observer), CD, CE, CEI, CICA (observer), CIS (participating member, has not signed the 1993 CIS charter), EAEC (observer), EAPC, EBRD, FAO, GCTU, GUAM, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAIA (observer), MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM (observer), NSG, OAS (observer), OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, PFP, SELEC (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZCchief of mission: Ambassador Valerii CHALYI (since 3 August 2015)chancery: 3350 M Street NW, Washington, DC 20007telephone: [1] (202) 349-2920FAX: [1] (202) 333-0817consulate(s) general: Chicago, New York, San Franciscochief of mission: Ambassador Geoffrey R. PYATT (since 7 August 2013)embassy: 4 Igor Sikorsky Street, 04112 Kyivmailing address: 5850 Kyiv Place, Washington, DC 20521-5850telephone: [380] (44) 521-5000FAX: [380] (44) 521-5155two equal horizontal bands of azure (top) and golden yellow represent grain fields under a blue skytryzub (trident); national colors: blue, yellowname: "Shche ne vmerla Ukraina" (Ukraine Has Not Yet Perished)lyrics/music: Paul CHUBYNSKYI/Mikhail VERBYTSKYInote: music adopted 1991, lyrics adopted 2003; song first performed in 1864 at the Ukraine Theatre in Lviv; the lyrics, originally written in 1862, were revised in 2003
Economy :: UKRAINE
-
After Russia, the Ukrainian republic was the most important economic component of the former Soviet Union, producing about four times the output of the next-ranking republic. Its fertile black soil generated more than one-fourth of Soviet agricultural output, and its farms provided substantial quantities of meat, milk, grain, and vegetables to other republics. Likewise, its diversified heavy industry supplied the unique equipment (for example, large diameter pipes) and raw materials to industrial and mining sites (vertical drilling apparatus) in other regions of the former USSR.Shortly after independence in August 1991, the Ukrainian Government liberalized most prices and erected a legal framework for privatization, but widespread resistance to reform within the government and the legislature soon stalled reform efforts and led to some backtracking. Output by 1999 had fallen to less than 40% of the 1991 level. Outside institutions - particularly the IMF –encouraged Ukraine to quicken the pace and scope of reforms to foster economic growth. Ukrainian Government officials eliminated most tax and customs privileges in a March 2005 budget law, bringing more economic activity out of Ukraine's large shadow economy, but more improvements are needed, including fighting corruption, developing capital markets, and improving the legislative framework. From 2000 until mid-2008, Ukraine's economy was buoyant despite political turmoil between the prime minister and president.Ukraine's dependence on Russia for energy supplies and the lack of significant structural reform have made the Ukrainian economy vulnerable to external shocks. Ukraine depends on imports to meet about three-fourths of its annual oil and natural gas requirements and 100% of its nuclear fuel needs. In January 2009, after a two-week dispute that saw gas supplies cutoff to Europe, Ukraine agreed to 10-year gas supply and transit contracts with Russia that brought gas prices to "world" levels. The strict terms of the contracts further hobbled Ukraine's cash-strapped state gas company, Naftohaz. The economy contracted nearly 15% in 2009, among the worst economic performances in the world. In April 2010, Ukraine negotiated a price discount on Russian gas imports in exchange for extending Russia's lease on its naval base in Crimea.Movement toward an Association Agreement with the European Union, which would commit Ukraine to economic and financial reforms in exchange for preferential access to EU markets, was curtailed by a November 2013 decision of President YANUKOVYCH. In response, on 17 December 2013 then President YANUKOVYCH and President PUTIN concluded a financial assistance package containing $15 billion in loans and lower gas prices. However, the end of the YANUKOVYCH government in February 2014 caused Russia to halt further funding. With the formation of an interim government in late February 2014, the international community began efforts to stabilize the Ukrainian economy, including a 27 March 2014 IMF assistance package of $14-18 billion. Russia’s seizure of the Crimean Peninsula created uncertainty as to the annual rate of growth of the Ukrainian economy in 2014.$370.8 billion (2014 est.)$398 billion (2013 est.)$398.1 billion (2012 est.)note: data are in 2014 US dollarscountry comparison to the world: 49$130.7 billion (2014 est.)-6.8% (2014 est.)0% (2013 est.)0.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 218$8,700 (2014 est.)$9,300 (2013 est.)$9,300 (2012 est.)note: data are in 2014 US dollarscountry comparison to the world: 13910.8% of GDP (2014 est.)10% of GDP (2013 est.)13.6% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 164household consumption: 81.8%government consumption: 21.1%investment in fixed capital: 15.6%investment in inventories: -0.3%exports of goods and services: 51.4%imports of goods and services: -69.6%(2014 est.)agriculture: 12.1%industry: 29%services: 58.8%(2014 est.)grain, sugar beets, sunflower seeds, vegetables; beef, milkcoal, electric power, ferrous and nonferrous metals, machinery and transport equipment, chemicals, food processing-9% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 19722.11 million (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 30agriculture: 5.6%industry: 26%services: 68.4%(2012)10.5% (2014 est.)7.2% (2013 est.)note: officially registered; large number of unregistered or underemployed workerscountry comparison to the world: 10324.1% (2010 est.)lowest 10%: 3.8%highest 10%: 22.5% (2011 est.)28.2 (2009)29 (1999)country comparison to the world: 124revenues: $39.14 billionexpenditures: $45.85 billionnote: this is the planned, consolidated budget (2014 est.)29% of GDP (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 94-5% of GDP (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 16866.2% of GDP (2014 est.)40.3% of GDP (2013 est.)note: the total public debt of $64.5 billion consists of: domestic public debt ($23.8 billion); external public debt ($26.1 billion); and sovereign guarantees ($14.6 billion)country comparison to the world: 46calendar year12.1% (2014 est.)-0.3% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 2147.5% (31 January 2012)11.97% (31 December 2010)country comparison to the world: 4118% (31 December 2014 est.)16.65% (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 19$33.97 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$48.02 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 58$78.02 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$113.4 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 59$111.7 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$150.9 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 51$20.71 billion (31 December 2012 est.)$25.56 billion (31 December 2011)$39.46 billion (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 65-$5.228 billion (2014 est.)-$16.4 billion (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 173$52.46 billion (2014 est.)$59.1 billion (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 59ferrous and nonferrous metals, fuel and petroleum products, chemicals, machinery and transport equipment, foodstuffsRussia 18.2%, Turkey 6.6%, Egypt 5.3%, China 5%, Poland 4.9%, Italy 4.6% (2014)$60.4 billion (2014 est.)$80.85 billion (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 50energy, machinery and equipment, chemicalsRussia 23.3%, China 10%, Germany 9.9%, Belarus 7.3%, Poland 5.6% (2014)$18.37 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$20.42 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 61$153.6 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$136 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 39$61.97 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$58.97 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 53$8.908 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$8.308 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 59hryvnia (UAH) per US dollar -11.58 (2014 est.)7.993 (2013 est.)7.99 (2012 est.)7.9676 (2011 est.)7.9356 (2010 est.)
Energy :: UKRAINE
-
198.1 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 22175.3 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 226 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 281.5 billion kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 6254.89 million kW (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 1764.9% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 12424.3% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 510.1% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 1160.6% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 8968,520 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 530 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 197155,300 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 38395 million bbl (1 January 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 53262,300 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 48317,700 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 4080,980 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 50126,500 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 4119.65 billion cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 3352.55 billion cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 180 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 19832.9 billion cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 111.104 trillion cu m (1 January 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 26290.4 million Mt (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 24
Communications :: UKRAINE
-
total subscriptions: 10.46 millionsubscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 23 (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 20total: 61.2 millionsubscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 136 (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 25general assessment: Ukraine's telecommunication development plan emphasizes improving domestic trunk lines, international connections, and the mobile-cellular systemdomestic: at independence in December 1991, Ukraine inherited a telephone system that was antiquated, inefficient, and in disrepair; more than 3.5 million applications for telephones could not be satisfied; telephone density is rising and the domestic trunk system is being improved; about one-third of Ukraine's networks are digital, and a majority of regional centers now have digital switching stations; improvements in local networks and local exchanges continue to lag; the mobile-cellular telephone system's expansion has slowed, largely due to saturation of the market which has reached 125 mobile phones per 100 peopleinternational: country code - 380; 2 new domestic trunk lines are a part of the fiber-optic Trans-Asia-Europe (TAE) system and 3 Ukrainian links have been installed in the fiber-optic Trans-European Lines (TEL) project that connects 18 countries; additional international service is provided by the Italy-Turkey-Ukraine-Russia (ITUR) fiber-optic submarine cable and by an unknown number of earth stations in the Intelsat, Inmarsat, and Intersputnik satellite systems (2010)state-controlled nationwide TV broadcast channel (UT1) and a number of privately owned TV networks provide basic TV coverage; multi-channel cable and satellite TV services are available; Russian television broadcasts have a small audience nationwide, but larger audiences in the eastern and southern regions; the radio broadcast market, a mix of independent and state-owned networks, is comprised of some 300 stations (2007)524 (station frequency types NA) (2006)647 (2006).uatotal: 16.8 millionpercent of population: 37.5% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 32
Transportation :: UKRAINE
-
187 (2013)country comparison to the world: 31total: 108over 3,047 m: 132,438 to 3,047 m: 421,524 to 2,437 m: 22914 to 1,523 m: 3under 914 m: 28 (2013)total: 791,524 to 2,437 m: 5914 to 1,523 m: 5under 914 m:69 (2013)9 (2013)gas 36,720 km; oil 4,514 km; refined products 4,363 km (2013)total: 21,733 kmbroad gauge: 21,684 km 1.524-m gauge (9,250 km electrified)standard gauge: 49 km 1.435-m gauge (49 km electrified) (2014)country comparison to the world: 12total: 169,694 kmpaved: 166,095 km (includes 17 km of expressways)unpaved: 3,599 km (2012)country comparison to the world: 291,672 km (most on Dnieper River) (2012)country comparison to the world: 46total: 134by type: bulk carrier 3, cargo 98, chemical tanker 1, passenger 6, passenger/cargo 5, petroleum tanker 8, refrigerated cargo 11, specialized tanker 2registered in other countries: 172 (Belize 6, Cambodia 35, Comoros 10, Cyprus 3, Dominica 1, Georgia 10, Liberia 10, Malta 29, Marshall Islands 1, Moldova 14, Mongolia 1, Panama 8, Russia 12, Saint Kitts and Nevis 8, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 12, Sierra Leone 5, Slovakia 2, unknown 5) (2010)country comparison to the world: 43major seaport(s): Feodosiya (Theodosia), Illichivsk, Mariupol', Mykolayiv, Odesa, Yuzhnyy
Military :: UKRAINE
-
Ground Forces, Naval Forces, Air Forces (2013)18-25 years of age for compulsory and voluntary military service; conscript service obligation is 12 months for Army and Air Force, 18 months for Navy (2012)males age 16-49: 10,984,394females age 16-49: 11.26 million (2010 est.)males age 16-49: 6,893,551females age 16-49: 8,792,504 (2010 est.)male: 246,397female: 234,916 (2010 est.)2.77% of GDP (2012)2.4% of GDP (2011)2.77% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 26
Transnational Issues :: UKRAINE
-
1997 boundary delimitation treaty with Belarus remains unratified due to unresolved financial claims, stalling demarcation and reducing border security; delimitation of land boundary with Russia is complete and demarcation began in 2012; the dispute over the boundary between Russia and Ukraine through the Kerch Strait and Sea of Azov is suspended due to the occupation of Crimea by Russia; Ukraine and Moldova signed an agreement officially delimiting their border in 1999, but the border has not been demarcated due to Moldova's difficulties with the break-away region of Transnistria; Moldova and Ukraine operate joint customs posts to monitor transit of people and commodities through Moldova's Transnistria Region, which remains under the auspices of an Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe-mandated peacekeeping mission comprised of Moldovan, Transnistrian, Russian, and Ukrainian troops; the ICJ ruled largely in favor of Romania in its dispute submitted in 2004 over Ukrainian-administered Zmiyinyy/Serpilor (Snake) Island and Black Sea maritime boundary delimitation; Romania opposes Ukraine's reopening of a navigation canal from the Danube border through Ukraine to the Black SeaIDPs: 1,449,245 (Russian-sponsored separatist violence in Crimea and eastern Ukraine) (2015)stateless persons: 35,335 (2014); note - citizens of the former USSR who were permanently resident in Ukraine were granted citizenship upon Ukraine's independence in 1991, but some missed this window of opportunity; people arriving after 1991, Crimean Tatars, ethnic Koreans, people with expired Soviet passports, and people with no documents have difficulty acquiring Ukrainian citizenship; following the fall of the Soviet Union in 1989, thousands of Crimean Tatars and their descendants deported from Ukraine under the STALIN regime returned to their homeland, some being stateless and others holding the citizenship of Uzbekistan or other former Soviet republics; a 1998 bilateral agreement between Ukraine and Uzbekistan simplified the process of renouncing Uzbek citizenship and obtaining Ukrainian citizenshipcurrent situation: Ukraine is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; Ukrainian victims are sex trafficked within Ukraine as well as in Russia, Poland, Iraq, Spain, Turkey, Cyprus, Greece, Seychelles, Portugal, the Czech Republic, Israel, Italy, South Korea, Moldova, China, the United Arab Emirates, Montenegro, UK, Kazakhstan, Tunisia, and other countries; small numbers of foreigners from Moldova, Russia, Vietnam, Uzbekistan, Pakistan, Cameroon, and Azerbaijan were victims of labor trafficking in Ukraine; Ukrainian recruiters most often target Ukrainians from rural areas with limited job prospects using fraud, coercion, and debt bondagetier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – Ukraine does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; the former Yanukovych government adopted standards of social services for victims, re-established its anti-trafficking unit, and increased the unit’s number of officers; the number of human trafficking cases investigated and prosecuted continued to decline in 2013, but significantly fewer victims were identified and referred to care; the government continued to rely on international donors to fund protective services and to provide inadequate funding to NGOs for assisting trafficking victims (2014)limited cultivation of cannabis and opium poppy, mostly for CIS consumption; some synthetic drug production for export to the West; limited government eradication program; used as transshipment point for opiates and other illicit drugs from Africa, Latin America, and Turkey to Europe and Russia; Ukraine has improved anti-money-laundering controls, resulting in its removal from the Financial Action Task Force's (FATF's) Noncooperative Countries and Territories List in February 2004; Ukraine's anti-money-laundering regime continues to be monitored by FATF