Introduction :: RUSSIA
-
Founded in the 12th century, the Principality of Muscovy, was able to emerge from over 200 years of Mongol domination (13th-15th centuries) and to gradually conquer and absorb surrounding principalities. In the early 17th century, a new ROMANOV Dynasty continued this policy of expansion across Siberia to the Pacific. Under PETER I (ruled 1682-1725), hegemony was extended to the Baltic Sea and the country was renamed the Russian Empire. During the 19th century, more territorial acquisitions were made in Europe and Asia. Defeat in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-05 contributed to the Revolution of 1905, which resulted in the formation of a parliament and other reforms. Repeated devastating defeats of the Russian army in World War I led to widespread rioting in the major cities of the Russian Empire and to the overthrow in 1917 of the imperial household. The communists under Vladimir LENIN seized power soon after and formed the USSR. The brutal rule of Iosif STALIN (1928-53) strengthened communist rule and Russian dominance of the Soviet Union at a cost of tens of millions of lives. The Soviet economy and society stagnated in the following decades until General Secretary Mikhail GORBACHEV (1985-91) introduced glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) in an attempt to modernize communism, but his initiatives inadvertently released forces that by December 1991 splintered the USSR into Russia and 14 other independent republics. Following economic and political turmoil during President Boris YELTSIN’s term (1991-99), Russia shifted toward a centralized semi-authoritarian state in which the leadership seeks to legitimize its rule through managed elections, populist appeals by President PUTIN, foreign policy focused on enhancing the country’s geopolitical influence - particularly in the former Soviet Union - and continued economic growth. Russia has severely disabled a Chechen rebel movement, although violence still occurs throughout the North Caucasus.
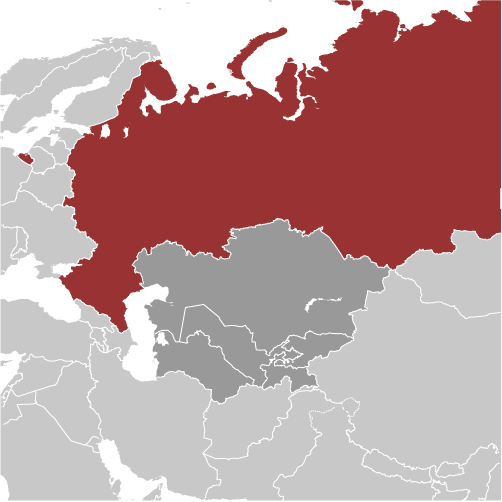
Geography :: RUSSIA
-
North Asia bordering the Arctic Ocean, extending from Europe (the portion west of the Urals) to the North Pacific Ocean
60 00 N, 100 00 E
Asia
total: 17,098,242 sq km
land: 16,377,742 sq km
water: 720,500 sq km
country comparison to the world: 1
approximately 1.8 times the size of the US
Area comparison map:

total: 22,408 km
border countries (14): Azerbaijan 338 km, Belarus 1,312 km, China (southeast) 4,133 km, China (south) 46 km, Estonia 324 km, Finland 1,309 km, Georgia 894 km, Kazakhstan 7,644 km, North Korea 18 km, Latvia 332 km, Lithuania (Kaliningrad Oblast) 261 km, Mongolia 3,452 km, Norway 191 km, Poland (Kaliningrad Oblast) 210 km, Ukraine 1,944 km
37,653 km
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
ranges from steppes in the south through humid continental in much of European Russia; subarctic in Siberia to tundra climate in the polar north; winters vary from cool along Black Sea coast to frigid in Siberia; summers vary from warm in the steppes to cool along Arctic coast
broad plain with low hills west of Urals; vast coniferous forest and tundra in Siberia; uplands and mountains along southern border regions
lowest point: Caspian Sea -28 m
highest point: Gora El'brus 5,633 m (highest point in Europe)
wide natural resource base including major deposits of oil, natural gas, coal, and many strategic minerals, reserves of rare earth elements, timber
note: formidable obstacles of climate, terrain, and distance hinder exploitation of natural resources
agricultural land: 13.1%
arable land 7.3%; permanent crops 0.1%; permanent pasture 5.7%
forest: 49.4%
other: 37.5% (2011 est.)
43,460 sq km (2008)
4,508 cu km (2011)
total: 66.2 cu km/yr (20%/60%/20%)
per capita: 454.9 cu m/yr (2001)
permafrost over much of Siberia is a major impediment to development; volcanic activity in the Kuril Islands; volcanoes and earthquakes on the Kamchatka Peninsula; spring floods and summer/autumn forest fires throughout Siberia and parts of European Russia
volcanism: significant volcanic activity on the Kamchatka Peninsula and Kuril Islands; the peninsula alone is home to some 29 historically active volcanoes, with dozens more in the Kuril Islands; Kliuchevskoi (elev. 4,835 m), which erupted in 2007 and 2010, is Kamchatka's most active volcano; Avachinsky and Koryaksky volcanoes, which pose a threat to the city of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatskiy, have been deemed Decade Volcanoes by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to their explosive history and close proximity to human populations; other notable historically active volcanoes include Bezymianny, Chikurachki, Ebeko, Gorely, Grozny, Karymsky, Ketoi, Kronotsky, Ksudach, Medvezhia, Mutnovsky, Sarychev Peak, Shiveluch, Tiatia, Tolbachik, and Zheltovsky
air pollution from heavy industry, emissions of coal-fired electric plants, and transportation in major cities; industrial, municipal, and agricultural pollution of inland waterways and seacoasts; deforestation; soil erosion; soil contamination from improper application of agricultural chemicals; scattered areas of sometimes intense radioactive contamination; groundwater contamination from toxic waste; urban solid waste management; abandoned stocks of obsolete pesticides
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Sulfur 94
largest country in the world in terms of area but unfavorably located in relation to major sea lanes of the world; despite its size, much of the country lacks proper soils and climates (either too cold or too dry) for agriculture; Mount El'brus is Europe's tallest peak; Lake Baikal, the deepest lake in the world, is estimated to hold one fifth of the world's fresh water
People and Society :: RUSSIA
-
noun: Russian(s)
adjective: Russian
Russian 77.7%, Tatar 3.7%, Ukrainian 1.4%, Bashkir 1.1%, Chuvash 1%, Chechen 1%, other 10.2%, unspecified 3.9%
note: more than 190 ethnic groups are represented in Russia's 2010 census (2010 est.)
Russian (official) 96.3%, Dolgang 5.3%, German 1.5%, Chechen 1%, Tatar 3%, other 10.3%
note: shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census (2010 est.)
Russian Orthodox 15-20%, Muslim 10-15%, other Christian 2% (2006 est.)
note: estimates are of practicing worshipers; Russia has large populations of non-practicing believers and non-believers, a legacy of over seven decades of Soviet rule
142,423,773 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
0-14 years: 16.68% (male 12,204,992/female 11,556,764)
15-24 years: 10.15% (male 7,393,188/female 7,064,060)
25-54 years: 45.54% (male 31,779,688/female 33,086,346)
55-64 years: 14.01% (male 8,545,371/female 11,409,076)
65 years and over: 13.61% (male 5,978,578/female 13,405,710) (2015 est.)
population pyramid:

total dependency ratio: 43.1%
youth dependency ratio: 24%
elderly dependency ratio: 19.1%
potential support ratio: 5.2% (2015 est.)
total: 39.1 years
male: 36.2 years
female: 42.1 years (2015 est.)
-0.04% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200
11.6 births/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 168
13.69 deaths/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
1.69 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
urban population: 74% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: -0.13% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
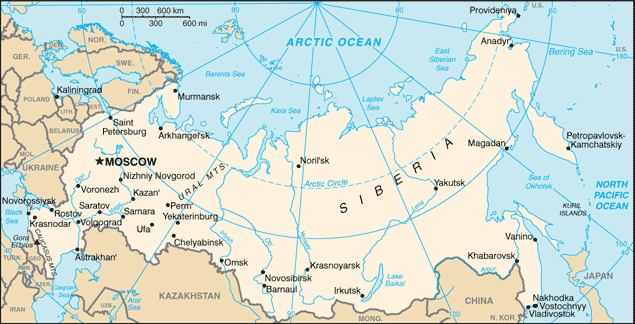
MOSCOW (capital) 12.166 million; Saint Petersburg 4.993 million; Novosibirsk 1.497 million; Yekaterinburg 1.379 million; Nizhniy Novgorod 1.212 million; Samara 1.164 million (2015)
at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.75 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.45 male(s)/female
total population: 0.86 male(s)/female (2015 est.)
total: 6.97 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 7.81 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 6.07 deaths/1,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
total population: 70.47 years
male: 64.7 years
female: 76.57 years (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
1.61 children born/woman (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 179
68%
note: percent of women aged 15-44 (2011)
6.5% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 106
4.31 physicians/1,000 population (2006)
9.7 beds/1,000 population (2006)
improved:
urban: 98.9% of population
rural: 91.2% of population
total: 96.9% of population
unimproved:
urban: 1.1% of population
rural: 8.8% of population
total: 3.1% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 77% of population
rural: 58.7% of population
total: 72.2% of population
unimproved:
urban: 23% of population
rural: 41.3% of population
total: 27.8% of population (2015 est.)
NA
NA
NA
degree of risk: intermediate
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea
vectorborne disease: tickborne encephalitis
note: highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza has been identified in this country; it poses a negligible risk with extremely rare cases possible among US citizens who have close contact with birds (2013)
26.2% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 46
4.1% of GDP (2008)
country comparison to the world: 110
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99.7%
male: 99.7%
female: 99.6% (2015 est.)
total: 15 years
male: 14 years
female: 15 years (2012)
total: 14.8%
male: 14.5%
female: 15.1% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
Government :: RUSSIA
-
conventional long form: Russian Federation
conventional short form: Russia
local long form: Rossiyskaya Federatsiya
local short form: Rossiya
former: Russian Empire, Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
federation
name: Moscow
geographic coordinates: 55 45 N, 37 36 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
note: Russia has 11 time zones, which includes two that were added in 2014
46 provinces (oblastey, singular - oblast), 21 republics (respublik, singular - respublika), 4 autonomous okrugs (avtonomnykh okrugov, singular - avtonomnyy okrug), 9 krays (krayev, singular - kray), 2 federal cities (goroda, singular - gorod), and 1 autonomous oblast (avtonomnaya oblast')
oblasts: Amur (Blagoveshchensk), Arkhangel'sk, Astrakhan', Belgorod, Bryansk, Chelyabinsk, Irkutsk, Ivanovo, Kaliningrad, Kaluga, Kemerovo, Kirov, Kostroma, Kurgan, Kursk, Leningrad, Lipetsk, Magadan, Moscow, Murmansk, Nizhniy Novgorod, Novgorod, Novosibirsk, Omsk, Orenburg, Orel, Penza, Pskov, Rostov, Ryazan', Sakhalin (Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk), Samara, Saratov, Smolensk, Sverdlovsk (Yekaterinburg), Tambov, Tomsk, Tula, Tver', Tyumen', Ul'yanovsk, Vladimir, Volgograd, Vologda, Voronezh, Yaroslavl'
republics: Adygeya (Maykop), Altay (Gorno-Altaysk), Bashkortostan (Ufa), Buryatiya (Ulan-Ude), Chechnya (Groznyy), Chuvashiya (Cheboksary), Dagestan (Makhachkala), Ingushetiya (Magas), Kabardino-Balkariya (Nal'chik), Kalmykiya (Elista), Karachayevo-Cherkesiya (Cherkessk), Kareliya (Petrozavodsk), Khakasiya (Abakan), Komi (Syktyvkar), Mariy-El (Yoshkar-Ola), Mordoviya (Saransk), North Ossetia (Vladikavkaz), Sakha [Yakutiya] (Yakutsk), Tatarstan (Kazan'), Tyva (Kyzyl), Udmurtiya (Izhevsk)
autonomous okrugs: Chukotka (Anadyr'), Khanty-Mansi-Yugra (Khanty-Mansiysk), Nenets (Nar'yan-Mar), Yamalo-Nenets (Salekhard)
krays: Altay (Barnaul), Kamchatka (Petropavlovsk-Kamchatskiy), Khabarovsk, Krasnodar, Krasnoyarsk, Perm', Primorskiy [Maritime] (Vladivostok), Stavropol', Zabaykal'sk (Chita)
federal cities: Moscow [Moskva], Saint Petersburg [Sankt-Peterburg]
autonomous oblast: Yevreyskaya [Jewish] (Birobidzhan)
note 1: administrative divisions have the same names as their administrative centers (exceptions have the administrative center name following in parentheses)
note 2: the United States does not recognize Russia's annexation of Ukraine's Autonomous Republic of Crimea and the municipality of Sevastopol, nor their redesignation as the Republic of Crimea and the Federal City of Sevastopol
24 August 1991 (from the Soviet Union); notable earlier dates: 1157 (Principality of Vladimir-Suzdal created); 16 January 1547 (Tsardom of Muscovy established); 22 October 1721 (Russian Empire proclaimed); 30 December 1922 (Soviet Union established)
Russia Day, 12 June (1990)
several previous (during Russian Empire and Soviet eras); latest drafted 12 July 1993, adopted by referendum 12 December 1993, effective 25 December 1993; amended 2008 (2013)
civil law system; judicial review of legislative acts
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
18 years of age; universal
chief of state: President Vladimir Vladimirovich PUTIN (since 7 May 2012)
head of government: Premier Dmitriy Anatolyevich MEDVEDEV (since 8 May 2012); First Deputy Premier Igor Ivanovich SHUVALOV (since 12 May 2008); Deputy Premiers Arkadiy Vladimirovich DVORKOVICH (since 21 May 2012), Olga Yuryevna GOLODETS (since 21 May 2012), Aleksandr Gennadiyevich KHLOPONIN (since 19 January 2010), Dmitriy Nikolayevich KOZAK (since 14 October 2008), Dmitriy Olegovich ROGOZIN (since 23 December 2011), Sergey Eduardovich PRIKHODKO (since 22 May 2013), Yuriy Petrovich TRUTNEV (since 31 August 2013)
cabinet: the "Government" is composed of the premier, his deputies, and ministers, all appointed by the president; the premier is also confirmed by the Duma
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 6-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 4 March 2012 (next to be held in March 2018); note - term length extended to 6 years from 4 years in late 2008, effective after the 2012 election; there is no vice president; premier appointed by the president with the approval of the Duma
election results: Vladimir PUTIN elected president; percent of vote - Vladimir PUTIN (United Russia) 63.6%, Gennadiy ZYUGANOV (CPRF) 17.2%, Mikhail PROKHOROV(Civic Platform) 8%, Vladimir ZHIRINOVSKIY (LDPR) 6.2%, Sergey MIRONOV (A Just Russia) 3.9%, other 1.1%; Dmitriy MEDVEDEV (United Russia) approved as premier by Duma; vote - 299 to 144
note: there is also a Presidential Administration that provides staff and policy support to the president, drafts presidential decrees, and coordinates policy among government agencies; a Security Council also reports directly to the president
description: bicameral Federal Assembly or Federalnoye Sobraniye consists of the Federation Council or Sovet Federatsii (166 seats; 2 members in each of the 83 federal administrative units - oblasts, krays, republics, autonomous okrugs and oblasts, and the federal cities of Moscow and Saint Petersburg - appointed by the top executive and legislative officials; members serve 4-year terms) and the State Duma or Gosudarstvennaya Duma (450 seats; as of February 2014, the electoral system reverted to a mixed electoral system for the 2016 election in which one-half of the members are directly elected by simple majority vote and one-half directly elected by proportional representation vote; members serve 5-year terms)
elections: State Duma - last held on 4 December 2011 (next to be held in December 2016)
election results: State Duma - United Russia 49.6%, CPRF 19.2%, A Just Russia 13.2%, LDPR 11.7%, other 6.3%; seats by party - United Russia 238, CPRF 92, A Just Russia 64, LDPR 56
note: the State Duma now includes 2 representatives each from the Republic of Crimea and Federal City of Sevastopol, two annexed Ukrainian regions that the United States does not recognize as part of Russia
highest court(s): Supreme Court of the Russian Federation (consists of 170 members organized into the Judicial Panel for Civil Affairs, the Judicial Panel for Criminal Affairs, and the Military Panel); Constitutional Court (consists of 19 members); note - in February 2014, Russia’s Superior Court of Arbitration was abolished and its former authorities transferred to the Supreme Court, which in addition to being the country’s highest judicial authority for appeals, civil, criminal, administrative cases, and military cases, and the disciplinary judicial board, now has jurisdiction over economic disputes
judge selection and term of office: all members of Russia's 3 highest courts nominated by the president and appointed by the Federation Council (the upper house of the legislature); members of all 3 courts appointed for life
subordinate courts: Higher Arbitration Court; regional (kray) and provincial (oblast) courts; Moscow and St. Petersburg city courts; autonomous province and district courts; note - the 14 Russian Republics have court systems specified by their own constitutions
A Just Russia [Sergey MIRONOV]
Communist Party of the Russian Federation or CPRF [Gennadiy ZYUGANOV]
Liberal Democratic Party of Russia or LDPR [Vladimir ZHIRINOVSKIY]
United Russia [Dmitriy MEDVEDEV]
note: 78 political parties are registered with Russia's Ministry of Justice (as of January 2014), but only four parties maintain representation in Russia's national legislature
Confederation of Labor of Russia or KTR
Federation of Independent Trade Unions of Russia
Golos Association in Defense of Voters' Rights
Memorial
Movement Against Illegal Migration
Russkiye
Solidarnost
The World Russian People's Congress
Union of the Committees of Soldiers' Mothers
Union of Russian Writers
other: business associations; environmental organizations; religious groups (especially those with Orthodox or Muslim affiliation); veterans groups
APEC, Arctic Council, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), BIS, BRICS, BSEC, CBSS, CD, CE, CERN (observer), CICA, CIS, CSTO, EAEC, EAPC, EAS, EBRD, FAO, FATF, G-20, GCTU, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAIA (observer), MIGA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OIC (observer), OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PFP, SCO, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNSC (permanent), UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
chief of mission: Ambassador Sergey Ivanovich KISLYAK (since 16 September 2008)
chancery: 2650 Wisconsin Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20007
telephone: [1] (202) 298-5700, 5701, 5704, 5708
FAX: [1] (202) 298-5735
consulate(s) general: Houston, San Francisco
consulate(s): New York, Seattle
chief of mission: Ambassador John Francis TEFFT (since 19 November 2014)
embassy: Bolshoy Deviatinskiy Pereulok No. 8, 121099 Moscow
mailing address: PSC-77, APO AE 09721
telephone: [7] (495) 728-5000
FAX: [7] (495) 728-5090
consulate(s) general: Saint Petersburg, Vladivostok, Yekaterinburg
three equal horizontal bands of white (top), blue, and red
note: the colors may have been based on those of the Dutch flag; despite many popular interpretations, there is no official meaning assigned to the colors of the Russian flag; this flag inspired several other Slav countries to adopt horizontal tricolors of the same colors but in different arrangements, and so red, blue, and white became the Pan-Slav colors
bear, double-headed eagle; national colors: white, blue, red
name: "Gimn Rossiyskoy Federatsii" (National Anthem of the Russian Federation)
lyrics/music: Sergey Vladimirovich MIKHALKOV/Aleksandr Vasilyevich ALEKSANDROV
note: in 2000, Russia adopted the tune of the anthem of the former Soviet Union (composed in 1939); the lyrics, also adopted in 2000, were written by the same person who authored the Soviet lyrics in 1943
Economy :: RUSSIA
-
Russia has undergone significant changes since the collapse of the Soviet Union, moving from a globally-isolated, centrally-planned economy towards a more market-based and globally-integrated economy, but stalling as a partially reformed, statist economy with a high concentration of wealth in officials' hands. Economic reforms in the 1990s privatized most industry, with notable exceptions in the energy and defense-related sectors. The protection of property rights is still weak and the private sector remains subject to heavy state interference. Russia is one of the world's leading producers of oil and natural gas, and is also a top exporter of metals such as steel and primary aluminum. Russia's manufacturing sector is generally uncompetitive on world markets and is geared toward domestic consumption. Russia's reliance on commodity exports makes it vulnerable to boom and bust cycles that follow the volatile swings in global prices. The economy, which had averaged 7% growth during 1998-2008 as oil prices rose rapidly, was one of the hardest hit by the 2008-09 global economic crisis as oil prices plummeted and the foreign credits that Russian banks and firms relied on dried up. In 2014, economic growth declined further when Russia forcibly violated Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity, and interfered in Ukraine’s internal affairs. In the second half of 2014, the Russian ruble lost about half of its value, contributing to increased capital outflows that reached $151.5 billion for the year; the ruble remains volatile. Declining oil prices, lack of economic reforms, and the imposition of foreign sanctions have contributed to the downturn and created wide expectations the economy will continue to slump. In April 2015, the Russian Ministry of Economic Development predicted that the Russia’s economy will contract by 3% in 2015, and average only 2.5% growth through 2030.
$3.565 trillion (2014 est.)
$3.543 trillion (2013 est.)
$3.497 trillion (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 7
$1.857 trillion (2014 est.)
0.6% (2014 est.)
1.3% (2013 est.)
3.4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 196
$24,800 (2014 est.)
$24,700 (2013 est.)
$24,300 (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 69
23% of GDP (2014 est.)
23.3% of GDP (2013 est.)
27.2% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
household consumption: 51.4%
government consumption: 19.7%
investment in fixed capital: 19.6%
investment in inventories: 2.2%
exports of goods and services: 29.7%
imports of goods and services: -22.6%
(2014 est.)
agriculture: 4%
industry: 36.3%
services: 59.7% (2014 est.)
grain, sugar beets, sunflower seeds, vegetables, fruits; beef, milk
complete range of mining and extractive industries producing coal, oil, gas, chemicals, and metals; all forms of machine building from rolling mills to high-performance aircraft and space vehicles; defense industries (including radar, missile production, advanced electronic components), shipbuilding; road and rail transportation equipment; communications equipment; agricultural machinery, tractors, and construction equipment; electric power generating and transmitting equipment; medical and scientific instruments; consumer durables, textiles, foodstuffs, handicrafts
0.6% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
75.25 million (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
agriculture: 9.7%
industry: 27.8%
services: 62.5% (2012)
5.1% (2014 est.)
5.5% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
11% (2013 est.)
lowest 10%: 5.7%
highest 10%: 42.4% (2011 est.)
42 (2012)
41.7 (2011)
country comparison to the world: 50
revenues: $416.5 billion
expenditures: $408.3 billion (2014 est.)
20.2% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
0.4% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
13.4% of GDP (2014 est.)
8.1% of GDP (2013 est.)
note: data cover general government debt, and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment, debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions
country comparison to the world: 147
calendar year
11.4% (2014 est.)
6.8% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 213
17% (2014 est.)
8% (31 December 2011)
note: this is the so-called refinancing rate, but in Russia banks do not get refinancing at this rate; this is a reference rate used primarily for fiscal purposes
country comparison to the world: 6
11.3% (2014 est.)
9.47% (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
$158.6 billion (1 December 2014 est.)
$320.9 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
$926.8 billion (31 October 2014 est.)
$1.087 trillion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
$882.2 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$984.9 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
$874.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
$796.4 billion (31 December 2011)
$1.005 trillion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
$57.41 billion (2014 est.)
$32.76 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
$520.3 billion (2014 est.)
$527.3 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
petroleum and petroleum products, natural gas, metals, wood and wood products, chemicals, and a wide variety of civilian and military manufactures
Netherlands 13.7%, China 7.5%, Germany 7.5%, Italy 7.2%, Turkey 5% (2014)
$323.9 billion (2014 est.)
$315 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
machinery, vehicles, pharmaceutical products, plastic, semi-finished metal products, meat, fruits and nuts, optical and medical instruments, iron, steel
China 17.8%, Germany 11.5%, US 6.6%, Italy 4.5%, Belarus 4.1% (2014)
$385.5 billion (31 December, 2014 est.)
$509.6 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
$683.6 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$728.9 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
$606 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$566.5 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
$533.5 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$479.5 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
Russian rubles (RUB) per US dollar -
67.7 (19 December 2014 est.)
32.73 (2013 est.)
30.84 (2012 est.)
29.382 (2011 est.)
30.368 (2010 est.)
Energy :: RUSSIA
-
1.054 trillion kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
1.037 trillion kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
15.7 billion kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
2.7 billion kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
239.7 million kW (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
69.2% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
10.6% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
20.2% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
10.05 million bbl/day (31 September 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
4.625 million bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
17,610 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
80 billion bbl (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
4.812 million bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
3.32 million bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
2.968 million bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
28,040 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
668 billion cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
413.5 billion cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 3
196 billion cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
8.2 billion cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
47.8 trillion cu m (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
1.782 billion Mt (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
Communications :: RUSSIA
-
total subscriptions: 39.43 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 28 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
total: 221 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 155 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
general assessment: the telephone system is experiencing significant changes; more than 1,000 companies licensed to offer communication services; access to digital lines has improved, particularly in urban centers; progress made toward building the telecommunications infrastructure necessary for a market economy; the estimated number of mobile subscribers jumped from fewer than 1 million in 1998 to more than 235 million in 2011; fixed-line service has improved but a large demand remains
domestic: cross-country digital trunk lines run from Saint Petersburg to Khabarovsk, and from Moscow to Novorossiysk; the telephone systems in 60 regional capitals have modern digital infrastructures; cellular services, both analog and digital, are available in many areas; in rural areas, telephone services are still outdated, inadequate, and low-density
international: country code - 7; connected internationally by undersea fiber optic cables; satellite earth stations provide access to Intelsat, Intersputnik, Eutelsat, Inmarsat, and Orbita systems (2011)
6 national TV stations with the federal government owning 1 and holding a controlling interest in a second; state-owned Gazprom maintains a controlling interest in a third national channel; government-affiliated Bank Rossiya owns controlling interest in a fourth and fifth, while the sixth national channel is owned by the Moscow city administration; roughly 3,300 national, regional, and local TV stations with over two-thirds completely or partially controlled by the federal or local governments; satellite TV services are available; 2 state-run national radio networks with a third majority-owned by Gazprom; roughly 2,400 public and commercial radio stations (2007)
AM 323, FM about 1,500, shortwave 62 (2004)
7,306 (1998)
.ru; note - Russia also has responsibility for a legacy domain ".su" that was allocated to the Soviet Union and is being phased out
total: 84.4 million
percent of population: 59.3% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
Transportation :: RUSSIA
-
1,218 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 5
total: 594
over 3,047 m: 54
2,438 to 3,047 m: 197
1,524 to 2,437 m: 123
914 to 1,523 m: 95
under 914 m: 125 (2013)
total: 624
over 3,047 m: 4
2,438 to 3,047 m: 13
1,524 to 2,437 m: 69
914 to 1,523 m: 81
under 914 m:
457 (2013)
49 (2013)
condensate 122 km; gas 163,872 km; liquid petroleum gas 1,378 km; oil 80,820 km; oil/gas/water 40 km; refined products 13,658 km; water 23 km (2013)
total: 87,157 km
broad gauge: 86,200 km 1.520-m gauge (40,300 km electrified)
narrow gauge: 957 km 1.067-m gauge (on Sakhalin Island)
note: an additional 30,000 km of non-common carrier lines serve industries (2014)
country comparison to the world: 2
total: 1,283,387 km
paved: 927,721 km (includes 39,143 km of expressways)
unpaved: 355,666 km (2012)
country comparison to the world: 5
102,000 km (including 48,000 km with guaranteed depth; the 72,000-km system in European Russia links Baltic Sea, White Sea, Caspian Sea, Sea of Azov, and Black Sea) (2009)
country comparison to the world: 2
total: 1,143
by type: bulk carrier 20, cargo 642, carrier 3, chemical tanker 57, combination ore/oil 42, container 13, passenger 15, passenger/cargo 7, petroleum tanker 244, refrigerated cargo 84, roll on/roll off 13, specialized tanker 3
foreign-owned: 155 (Belgium 4, Cyprus 13, Estonia 1, Ireland 1, Italy 14, Latvia 2, Netherlands 2, Romania 1, South Korea 1, Switzerland 3, Turkey 101, Ukraine 12)
registered in other countries: 439 (Antigua and Barbuda 3, Belgium 1, Belize 30, Bulgaria 2, Cambodia 50, Comoros 12, Cook Islands 1, Cyprus 46, Dominica 3, Georgia 6, Hong Kong 1, Kiribati 1, Liberia 109, Malaysia 2, Malta 45, Marshall Islands 5, Moldova 5, Mongolia 2, Panama 49, Romania 1, Saint Kitts and Nevis 13, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 11, Sierra Leone 7, Singapore 2, Spain 6, Vanuatu 7, unknown 19) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 11
major seaport(s): Kaliningrad, Nakhodka, Novorossiysk, Primorsk, Vostochnyy
river port(s): Saint Petersburg (Neva River)
oil terminal(s): Kavkaz oil terminal
container port(s) (TEUs): Saint Petersburg (2,365,174)
LNG terminal(s) (export): Sakhalin Island
Military :: RUSSIA
-
Ground Troops (Sukhoputnyye Voyskia, SV), Navy (Voyenno-Morskoy Flot, VMF), Air Forces (Voyenno-Vozdushniye Sily, VVS); Airborne Troops (Vozdushno-Desantnyye Voyska, VDV), Missile Troops of Strategic Purpose (Raketnyye Voyska Strategicheskogo Naznacheniya, RVSN) referred to commonly as Strategic Rocket Forces, and Aerospace Defense Troops (Voyska Vozdushno-Kosmicheskoy Oborony or Voyska VKO) are independent "combat arms," not subordinate to any of the three branches; Russian Ground Troops include the following combat arms: motorized-rifle troops, tank troops, missile and artillery troops, air defense of the Ground Troops (2014)
18-27 years of age for compulsory or voluntary military service; males are registered for the draft at 17 years of age; 1-year service obligation (conscripts can only be sent to combat zones after 6 months of training); reserve obligation for non-officers to age 50; enrollment in military schools from the age of 16, cadets classified as members of the armed forces
note: the chief of the General Staff Mobilization Directorate announced in May 2013 that for health reasons, only 65% of draftees called up during the spring 2013 draft campaign were fit for military service, and over 12% of these were sent for an additional medical examination (by way of comparison, 69.9% in 2012 and 57.7% in 2011 were deemed fit for military service); approximately 50% of draft-age Russian males receive some type of legal deferment each draft cycle (2014)
males age 16-49: 34,765,736
females age 16-49: 35,410,779 (2013 est.)
males age 16-49: 22,597,728
females age 16-49: 23,017,006 (2013 est.)
male: 696,768
female: 664,847 (2013 est.)
3.49% of GDP (2014)
3.18% of GDP (2013)
2.92% of GDP (2012)
2.71% of GDP (2011)
country comparison to the world: 16
Transnational Issues :: RUSSIA
-
Russia remains concerned about the smuggling of poppy derivatives from Afghanistan through Central Asian countries; China and Russia have demarcated the once disputed islands at the Amur and Ussuri confluence and in the Argun River in accordance with the 2004 Agreement, ending their centuries-long border disputes; the sovereignty dispute over the islands of Etorofu, Kunashiri, Shikotan, and the Habomai group, known in Japan as the "Northern Territories" and in Russia as the "Southern Kurils," occupied by the Soviet Union in 1945, now administered by Russia, and claimed by Japan, remains the primary sticking point to signing a peace treaty formally ending World War II hostilities; Russia's military support and subsequent recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia independence in 2008 continue to sour relations with Georgia; Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, and Russia ratified Caspian seabed delimitation treaties based on equidistance, while Iran continues to insist on a one-fifth slice of the sea; Norway and Russia signed a comprehensive maritime boundary agreement in 2010; various groups in Finland advocate restoration of Karelia (Kareliya) and other areas ceded to the Soviet Union following World War II but the Finnish Government asserts no territorial demands; Russia and Estonia signed a technical border agreement in May 2005, but Russia recalled its signature in June 2005 after the Estonian parliament added to its domestic ratification act a historical preamble referencing the Soviet occupation and Estonia's pre-war borders under the 1920 Treaty of Tartu; Russia contends that the preamble allows Estonia to make territorial claims on Russia in the future, while Estonian officials deny that the preamble has any legal impact on the treaty text; Russia demands better treatment of the Russian-speaking population in Estonia and Latvia; Lithuania and Russia committed to demarcating their boundary in 2006 in accordance with the land and maritime treaty ratified by Russia in May 2003 and by Lithuania in 1999; Lithuania operates a simplified transit regime for Russian nationals traveling from the Kaliningrad coastal exclave into Russia, while still conforming, as an EU member state with an EU external border, where strict Schengen border rules apply; preparations for the demarcation delimitation of land boundary with Ukraine have commenced; the dispute over the boundary between Russia and Ukraine through the Kerch Strait and Sea of Azov is suspended due to the occupation of Crimea by Russia; Kazakhstan and Russia boundary delimitation was ratified on November 2005 and field demarcation should commence in 2007; Russian Duma has not yet ratified 1990 Bering Sea Maritime Boundary Agreement with the US; Denmark (Greenland) and Norway have made submissions to the Commission on the Limits of the Continental shelf (CLCS) and Russia is collecting additional data to augment its 2001 CLCS submission
refugees (country of origin): 383,323 asylum seekers and 911,549 applicants for other forms of legal stay (Ukraine) (2015)
IDPs: at least 25,378 (armed conflict, human rights violations, generalized violence in North Caucasus, particularly Chechnya and North Ossetia) (2014)
stateless persons: 113,474 (2014); note - Russia's stateless population consists of Roma, Meskhetian Turks, and ex-Soviet citizens from the former republics; between 2003 and 2010 more than 600,000 stateless people were naturalized; most Meskhetian Turks, followers of Islam with origins in Georgia, fled or were evacuated from Uzbekistan after a 1989 pogrom and have lived in Russia for more than the required five-year residency period; they continue to be denied registration for citizenship and basic rights by local Krasnodar Krai authorities on the grounds that they are temporary illegal migrants
current situation: Russia is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children who are subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking, although labor trafficking is the predominant problem; workers from Russia and other countries in Europe, Central Asia, and Asia, including Vietnam and North Korea, are subjected to conditions of forced labor in Russia’s construction, manufacturing, agriculture, grocery store, maritime, and domestic services industries, as well as forced begging, waste sorting, and street sweeping; North Koreans contracted under bilateral government arrangements to work in the timber industry in the Russian Far East reportedly are subjected to forced labor; Russian women and children were reported to be victims of sex trafficking in Russia, Northeast Asia, Europe, Central Asia, Africa, and the Middle East, while women from European, Southeast Asian, African, and Central Asian countries were reportedly forced into prostitution in Russia
tier rating: Tier 3 - Russia does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making a significant effort to do so; prosecutions of trafficking offenders remains low in comparison to the scope of Russia’s trafficking problem; in 2013, the government did not develop or deploy a formal system for the identification of trafficking victims or their referral to protective services, although some victims were reportedly cared for through ad hoc efforts; victims were routinely detained and deported; the government has not investigated allegations of slave-like conditions of North Korean workers in Russia; the Russian Security Council has not made a decision on an anti-trafficking national action plan (2014)
limited cultivation of illicit cannabis and opium poppy and producer of methamphetamine, mostly for domestic consumption; government has active illicit crop eradication program; used as transshipment point for Asian opiates, cannabis, and Latin American cocaine bound for growing domestic markets, to a lesser extent Western and Central Europe, and occasionally to the US; major source of heroin precursor chemicals; corruption and organized crime are key concerns; major consumer of opiates
 Central Intelligence Agency
Central Intelligence Agency