Introduction :: SAUDI ARABIA
-
Saudi Arabia is the birthplace of Islam and home to Islam's two holiest shrines in Mecca and Medina. The king's official title is the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques. The modern Saudi state was founded in 1932 by ABD AL-AZIZ bin Abd al-Rahman Al SAUD (Ibn Saud) after a 30-year campaign to unify most of the Arabian Peninsula. One of his male descendants rules the country today, as required by the country's 1992 Basic Law. King SALMAN bin Abd al-Aziz ascended to the throne in 2015 and placed the first next-generation prince, MUHAMMAD BIN NAYIF bin Abd al-Aziz, in the line of succession as Crown Prince. Following Iraq's invasion of Kuwait in 1990, Saudi Arabia accepted the Kuwaiti royal family and 400,000 refugees while allowing Western and Arab troops to deploy on its soil for the liberation of Kuwait the following year. The continuing presence of foreign troops on Saudi soil after the liberation of Kuwait became a source of tension between the royal family and the public until all operational US troops left the country in 2003. Major terrorist attacks in May and November 2003 spurred a strong on-going campaign against domestic terrorism and extremism.
King ABDALLAH from 2005 to 2015 incrementally modernized the Kingdom - driven by personal ideology and political pragmatism - through a series of social and economic initiatives, including expanding employment and social opportunities for women, attracting foreign investment, increasing the role of the private sector in the economy, and discouraging businesses from hiring foreign workers. The Arab Spring inspired protests - increasing in number since 2011 but usually small in size - over primarily domestic issues among Saudi Arabia's majority Sunni population. Riyadh has taken a cautious but firm approach by arresting some protesters but releasing most of them quickly, and by using its state-sponsored clerics to counter political and Islamist activism. In addition, Saudi Arabia has seen protests among Shias in the Eastern Province, who have protested primarily against the detention of political prisoners, endemic discrimination, and Bahraini and Saudi Government actions in Bahrain. Protests are met by a strong police presence, with some arrests, but not the level of bloodshed seen in protests elsewhere in the region.
In response to the unrest, King ABDALLAH in February and March 2011 announced a series of benefits for Saudi citizens including funds to build affordable housing, salary increases for government workers, and unemployment entitlements. To promote increased political participation, the government held elections nationwide in September 2011 for half the members of 285 municipal councils - a body that holds little influence in the Saudi Government. Also in September 2011, King ABDALLAH announced that women will be allowed to run for and vote in future municipal elections - first held in 2005 - and serve as full members of the advisory Consultative Council. The country remains a leading producer of oil and natural gas and holds about 16% of the world's proven oil reserves. The government continues to pursue economic reform and diversification, particularly since Saudi Arabia's accession to the WTO in 2005, and promotes foreign investment in the kingdom. A burgeoning population, aquifer depletion, and an economy largely dependent on petroleum output and prices are ongoing governmental concerns.
Geography :: SAUDI ARABIA
-
Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf and the Red Sea, north of Yemen
25 00 N, 45 00 E
Middle East
total: 2,149,690 sq km
land: 2,149,690 sq km
water: 0 sq km
country comparison to the world: 13
slightly more than one-fifth the size of the US
Area comparison map:

total: 4,272 km
border countries (7): Iraq 811 km, Jordan 731 km, Kuwait 221 km, Oman 658 km, Qatar 87 km, UAE 457 km, Yemen 1,307 km
2,640 km
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 18 nm
continental shelf: not specified
harsh, dry desert with great temperature extremes
mostly sandy desert
lowest point: Persian Gulf 0 m
highest point: Jabal Sawda' 3,133 m
petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, gold, copper
agricultural land: 80.7%
arable land 1.5%; permanent crops 0.1%; permanent pasture 79.1%
forest: 0.5%
other: 18.8% (2011 est.)
16,200 sq km (2004)
2.4 cu km (2011)
total: 23.67 cu km/yr (9%/3%/88%)
per capita: 928.1 cu m/yr (2006)
frequent sand and dust storms
volcanism: despite many volcanic formations, there has been little activity in the past few centuries; volcanoes include Harrat Rahat, Harrat Khaybar, Harrat Lunayyir, and Jabal Yar
desertification; depletion of underground water resources; the lack of perennial rivers or permanent water bodies has prompted the development of extensive seawater desalination facilities; coastal pollution from oil spills
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Saudi Arabia is the largest country in the world without a river; extensive coastlines on the Persian Gulf and Red Sea provide great leverage on shipping (especially crude oil) through the Persian Gulf and Suez Canal
People and Society :: SAUDI ARABIA
-
noun: Saudi(s)
adjective: Saudi or Saudi Arabian
Arab 90%, Afro-Asian 10%
Arabic (official)
Muslim (official; citizens are 85-90% Sunni and 10-15% Shia), other (includes Eastern Orthodox, Protestant, Roman Catholic, Jewish, Hindu, Buddhist, and Sikh) (2012 est.)
note: despite having a large expatriate community of various faiths (more than 30% of the population), most forms of public religious expression inconsistent with the government-sanctioned interpretation of Sunni Islam are restricted; non-Muslims are not allowed to have Saudi citizenship and non-Muslim places of worship are not permitted (2013)
religious affiliation:

27,752,316
note: immigrants make up more than 30% of the total population, according to UN data (2013) (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
0-14 years: 27.07% (male 3,850,992/female 3,661,194)
15-24 years: 19.11% (male 2,839,161/female 2,463,216)
25-54 years: 45.9% (male 7,244,386/female 5,495,284)
55-64 years: 4.68% (male 710,827/female 587,281)
65 years and over: 3.24% (male 460,209/female 439,766) (2015 est.)
population pyramid:

total dependency ratio: 45.9%
youth dependency ratio: 41.7%
elderly dependency ratio: 4.2%
potential support ratio: 24% (2015 est.)
total: 26.8 years
male: 27.6 years
female: 25.8 years (2015 est.)
1.46% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
18.51 births/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
3.33 deaths/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 219
-0.55 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
urban population: 83.1% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: 2.1% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
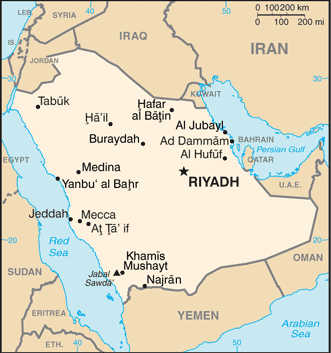
RIYADH (capital) 6.195 million; Jeddah 4.076 million; Mecca 1.771 million; Medina 1.28 million; Ad Dammam 1.064 million (2015)
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.15 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.32 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.21 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 1.05 male(s)/female
total population: 1.19 male(s)/female (2015 est.)
12 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
total: 14.09 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 16.16 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 11.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
total population: 75.05 years
male: 73 years
female: 77.2 years (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
2.12 children born/woman (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
23.8% (2007)
3.2% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 178
2.49 physicians/1,000 population (2012)
2.1 beds/1,000 population (2012)
improved:
urban: 97% of population
rural: 97% of population
total: 97% of population
unimproved: urban: 3% of population
rural: 3% of population
total: 3% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2015 est.)
NA
NA
NA
33.7% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 19
5.3% (2005)
country comparison to the world: 88
5.1% of GDP (2008)
country comparison to the world: 68
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 94.7%
male: 97%
female: 91.1% (2015 est.)
total: 16 years
male: 16 years
female: 17 years (2013)
total: 29.5%
male: 21.1%
female: 55.3% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
Government :: SAUDI ARABIA
-
conventional long form: Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
conventional short form: Saudi Arabia
local long form: Al Mamlakah al Arabiyah as Suudiyah
local short form: Al Arabiyah as Suudiyah
monarchy
name: Riyadh
geographic coordinates: 24 39 N, 46 42 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
13 provinces (mintaqat, singular - mintaqah); Al Bahah, Al Hudud ash Shamaliyah (Northern Border), Al Jawf, Al Madinah (Medina), Al Qasim, Ar Riyad (Riyadh), Ash Sharqiyah (Eastern), 'Asir, Ha'il, Jazan, Makkah (Mecca), Najran, Tabuk
23 September 1932 (unification of the kingdom)
Unification of the Kingdom, 23 September (1932)
1 March 1992 - Basic Law of Government, issued by royal decree, serves as the constitutional framework and is based on the Qur'an and the life and tradition of the Prophet Muhammad (2015)
Islamic (sharia) legal system with some elements of Egyptian, French, and customary law; note - several secular codes have been introduced; commercial disputes handled by special committees
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Saudi Arabia; a child born out of wedlock in Saudi Arabia to a Saudi mother and unknown father
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
21 years of age; male; male and female for municipal elections
chief of state: King and Prime Minister SALMAN bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud (since 23 January 2015); Crown Prince and Deputy Prime Minister MUHAMMAD BIN NAYIF bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud (born 30 August 1959); Crown Prince and Second Deputy Prime Minister MUHAMMAD BIN SALMAN bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud (born 31 August 1985); note - the monarch is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: King and Prime Minister SALMAN bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud (since 23 January 2015); Crown Prince and Deputy Prime Minister MUHAMMAD BIN NAYIF bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud (born 30 August 1959); Crown Prince and Second Deputy Prime Minister MUHAMMAD BIN SALMAN bin Abd al-Aziz Al Saud (born 31 August 1985)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the monarch every 4 years and includes many royal family members
elections/appointments: none; the monarchy is hereditary; note - an Allegiance Commission created by royal decree in October 2006 established a committee of Saudi princes to a role in selecting future Saudi kings
description: unicameral Consultative Council or Majlis al-Shura (150 seats; members appointed by the monarch to serve 4-year terms); note - in early 2013, the monarch granted women 30 seats on the Council
highest court(s): High Court (consists of the court chief and organized into circuits with 3-judge panels except the criminal circuit which has a 5-judge panel for cases involving major punishments)
judge selection and term of office: the High Court chief and chiefs of the High Court Circuits appointed by royal decree following the recommendation of the Supreme Judiciary Council, a 10-member body of high level judges and other judicial heads; new judges and assistant judges serve 1- and 2- year probations, respectively, before permanent assignment
subordinate courts: Court of Appeals; first-degree courts composed of general, criminal, personal status, and commercial courts, and the Labor Court; hierarchy of administrative courts
note: in 2005, former King Abdullah issued decrees approving an overhaul of the judicial system and which were incorporated in the Judiciary Law of 2007; changes include the establishment of a High Court and special commercial, labor, and administrative courts
none
other: gas companies; religious groups
ABEDA, AfDB (nonregional member), AFESD, AMF, BIS, CAEU, CP, FAO, G-20, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OAPEC, OAS (observer), OIC, OPCW, OPEC, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
chief of mission: Ambassador Abdallah bin Faysal bin Turki bin Abdallah bin Saud Abu Hala
chancery: 601 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20037
telephone: [1] (202) 342-3800
FAX: [1] (202) 944-3113
consulate(s) general: Houston, Los Angeles, New York
chief of mission: Ambassador Joseph William WESTPHAL (since 26 March 2014)
embassy: Collector Road M, Diplomatic Quarter, Riyadh
mailing address: American Embassy, Unit 61307, APO AE 09803-1307; International Mail: P. O. Box 94309, Riyadh 11693
telephone: [966] (1) 488-3800
FAX: [966] (1) 488-7360
consulate(s) general: Dhahran, Jiddah (Jeddah)
green, a traditional color in Islamic flags, with the Shahada or Muslim creed in large white Arabic script (translated as "There is no god but God; Muhammad is the Messenger of God") above a white horizontal saber (the tip points to the hoist side); design dates to the early twentieth century and is closely associated with the Al Saud family which established the kingdom in 1932; the flag is manufactured with differing obverse and reverse sides so that the Shahada reads - and the sword points - correctly from right to left on both sides
note: the only national flag to display an inscription as its principal design; one of only three national flags that differ on their obverse and reverse sides - the others are Moldova and Paraguay
palm tree surmounting two crossed swords; national colors: green, white
name: "Aash Al Maleek" (Long Live Our Beloved King)
lyrics/music: Ibrahim KHAFAJI/Abdul Rahman al-KHATEEB
note: music adopted 1947, lyrics adopted 1984
Economy :: SAUDI ARABIA
-
Saudi Arabia has an oil-based economy with strong government controls over major economic activities. It possesses about 16% of the world's proven petroleum reserves, ranks as the largest exporter of petroleum, and plays a leading role in OPEC. The petroleum sector accounts for roughly 80% of budget revenues, 45% of GDP, and 90% of export earnings. Saudi Arabia is encouraging the growth of the private sector in order to diversify its economy and to employ more Saudi nationals. Diversification efforts are focusing on power generation, telecommunications, natural gas exploration, and petrochemical sectors. Over 6 million foreign workers play an important role in the Saudi economy, particularly in the oil and service sectors, while Riyadh is struggling to reduce unemployment among its own nationals. Saudi officials are particularly focused on employing its large youth population, which generally lacks the education and technical skills the private sector needs. In 2014 the Kingdom ran its first budget deficit since 2009, and faces budget deficits for the foreseeable future because it requires an oil price greater than $100 per barrel to balance its budget. Although the Kingdom can finance high deficits for several years by drawing down its considerable foreign assets or borrowing, it probably will begin to reduce capital spending if oil prices stay low through the next year.
$1.61 trillion (2014 est.)
$1.556 trillion (2013 est.)
$1.515 trillion (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 15
$746.2 billion (2014 est.)
3.5% (2014 est.)
2.7% (2013 est.)
5.4% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
$52,300 (2014 est.)
$50,600 (2013 est.)
$49,200 (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 20
38.1% of GDP (2014 est.)
44.4% of GDP (2013 est.)
48.8% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
household consumption: 32.5%
government consumption: 26.4%
investment in fixed capital: 24.3%
investment in inventories: 3.5%
exports of goods and services: 47.5%
imports of goods and services: -34.2%
(2014 est.)
agriculture: 1.9%
industry: 57%
services: 41.1% (2014 est.)
wheat, barley, tomatoes, melons, dates, citrus; mutton, chickens, eggs, milk
crude oil production, petroleum refining, basic petrochemicals, ammonia, industrial gases, sodium hydroxide (caustic soda), cement, fertilizer, plastics, metals, commercial ship repair, commercial aircraft repair, construction
2.7% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
11.22 million
note: about 80% of the labor force is non-national (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
agriculture: 6.7%
industry: 21.4%
services: 71.9% (2005 est.)
11.6% (2014 est.)
11.5% (2013 est.)
note: data are for Saudi males only (local bank estimates; some estimates are as high as 25%)
country comparison to the world: 127
NA%
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%: NA%
revenues: $278.9 billion
expenditures: $293.3 billion (2014 est.)
37.4% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
-1.9% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
1.6% of GDP (2014 est.)
2.7% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 173
calendar year
2.7% (2014 est.)
3.5% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
2.5% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 114
6.8% (31 December 2014 est.)
6.7% (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
$304.8 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$266.8 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
$461.2 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$412 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
$-38.16 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$-58.7 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 191
$373.4 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
$338.9 billion (31 December 2011)
$353.4 billion (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
$76.92 billion (2014 est.)
$135.4 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
$342.3 billion (2014 est.)
$375.9 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
petroleum and petroleum products 90% (2012 est.)
China 13.3%, Japan 13%, US 12.9%, South Korea 10%, India 8.9%, Singapore 4% (2014)
$158.5 billion (2014 est.)
$153.3 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
machinery and equipment, foodstuffs, chemicals, motor vehicles, textiles
China 13.3%, US 12.1%, India 8.3%, Germany 6.5%, South Korea 5.4%, Japan 4.9% (2014)
$660.1 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$732.4 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
$166.1 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$155.7 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
$242.6 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$234.5 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
$32.46 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$27.06 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
Saudi riyals (SAR) per US dollar -
3.75 (2014 est.)
3.75 (2013 est.)
3.75 (2012 est.)
3.75 (2011 est.)
3.75 (2010 est.)
Energy :: SAUDI ARABIA
-
255.4 billion kWh (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
231.6 billion kWh (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 189
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
53.62 million kW (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
99.9% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 196
0.1% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
9.735 million bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
7.658 million bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
0 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
268.3 billion bbl (1 January 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
1.971 million bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
2.961 million bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
1.524 million bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
338,800 bbl/day (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
102.4 billion cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
102.4 billion cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
0 cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 171
0 cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
8.235 trillion cu m (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
582.7 million Mt (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
Communications :: SAUDI ARABIA
-
total subscriptions: 3.92 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 14 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
total: 52.7 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 193 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 29
general assessment: modern system including a combination of extensive microwave radio relays, coaxial cables, and fiber-optic cables
domestic: mobile-cellular subscribership has been increasing rapidly
international: country code - 966; landing point for the international submarine cable Fiber-Optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG) and for both the SEA-ME-WE-3 and SEA-ME-WE-4 submarine cable networks providing connectivity to Asia, Middle East, Europe, and US; microwave radio relay to Bahrain, Jordan, Kuwait, Qatar, UAE, Yemen, and Sudan; coaxial cable to Kuwait and Jordan; satellite earth stations - 5 Intelsat (3 Atlantic Ocean and 2 Indian Ocean), 1 Arabsat, and 1 Inmarsat (Indian Ocean region) (2011)
broadcast media are state-controlled; state-run TV operates 4 networks; Saudi Arabia is a major market for pan-Arab satellite TV broadcasters; state-run radio operates several networks; multiple international broadcasters are available (2007)
AM 43, FM 31, shortwave 2 (1998)
117 (1997)
.sa
total: 16.2 million
percent of population: 59.2% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
Transportation :: SAUDI ARABIA
-
214 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 26
total: 82
over 3,047 m: 33
2,438 to 3,047 m: 16
1,524 to 2,437 m: 27
914 to 1,523 m: 2
under 914 m: 4 (2013)
total: 132
2,438 to 3,047 m: 7
1,524 to 2,437 m: 72
914 to 1,523 m: 37
under 914 m:
16 (2013)
10 (2013)
condensate 209 km; gas 2,940 km; liquid petroleum gas 1,183 km; oil 5,117 km; refined products 1,151 km (2013)
total: 1,378 km
standard gauge: 1,378 km 1.435-m gauge (with branch lines and sidings) (2014)
country comparison to the world: 81
total: 221,372 km
paved: 47,529 km (includes 3,891 km of expressways)
unpaved: 173,843 km (2006)
country comparison to the world: 22
total: 72
by type: cargo 1, chemical tanker 25, container 4, liquefied gas 2, passenger/cargo 10, petroleum tanker 20, refrigerated cargo 3, roll on/roll off 7
foreign-owned: 15 (Egypt 1, Greece 4, Kuwait 4, UAE 6)
registered in other countries: 55 (Bahamas 16, Dominica 2, Liberia 20, Malta 2, Norway 3, Panama 11, Tanzania 1) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 61
major seaport(s): Ad Dammam, Al Jubayl, Jeddah, Yanbu al Bahr
container port(s) (TEUs): Ad Dammam (1,492,315), Jeddah (4,010,448)
Military :: SAUDI ARABIA
-
Ministry of Defense: Royal Saudi Land Forces, Royal Saudi Naval Forces (includes Marine Forces and Special Forces), Royal Saudi Air Force (Al-Quwwat al-Jawwiya al-Malakiya as-Sa'udiya), Royal Saudi Air Defense Forces, Royal Saudi Strategic Rocket Forces, Ministry of the National Guard (SANG) (2015)
17 is the legal minimum age for voluntary military service; no conscription (2012)
males age 16-49: 8,644,522
females age 16-49: 6,601,985 (2010 est.)
males age 16-49: 7,365,624
females age 16-49: 5,677,819 (2010 est.)
male: 261,105
female: 244,763 (2010 est.)
7.98% of GDP (2012)
7.25% of GDP (2011)
7.98% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 4
Transnational Issues :: SAUDI ARABIA
-
Saudi Arabia has reinforced its concrete-filled security barrier along sections of the now fully demarcated border with Yemen to stem illegal cross-border activities; Kuwait and Saudi Arabia continue discussions on a maritime boundary with Iran; Saudi Arabia claims Egyptian-administered islands of Tiran and Sanafir
refugees (country of origin): 30,000 (Yemen) (2015)
stateless persons: 70,000 (2014); note - thousands of biduns (stateless Arabs) are descendants of nomadic tribes who were not officially registered when national borders were established, while others migrated to Saudi Arabia in search of jobs; some have temporary identification cards that must be renewed every five years, but their rights remain restricted; most Palestinians have only legal resident status; some naturalized Yemenis were made stateless after being stripped of their passports when Yemen backed Iraq in its invasion of Kuwait in 1990; Saudi women cannot pass their citizenship on to their children, so if they marry a non-national, their children risk statelessness
current situation: Saudi Arabia is a destination country for men and women subjected to forced labor and, to a lesser extent, forced prostitution; many men and women from Central Asia, the Middle East, and Africa who voluntarily travel to Saudi Arabia as domestic servants or low-skilled laborers subsequently face conditions of involuntary servitude, including nonpayment, withholding of passports, restriction of movement, food deprivation, and abuse; some migrant workers are forced to work indefinitely beyond the term of their contract because their employers will not grant them a required exit visa; foreign domestic workers are particularly vulnerable because of their isolation in private homes; women, primarily from Asian and African countries, are believed to be forced into prostitution in Saudi Arabia, while other foreign women were reportedly kidnapped and forced into prostitution after running away from abusive employers; Yemeni, Nigerian, Pakistani, Afghan, Chadian, and Sudanese children were subjected to forced labor as beggars and street vendors in Saudi Arabia, facilitated by criminal gangs
tier rating: Tier 3 - Saudi Arabia does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so; in 2013, the government did not report prosecuting or convicting any trafficking offenders and identified and referred fewer victims to protection services than in the previous reporting period; the sponsorship system, including the exit visa requirement, continues to restrict the freedom of movement of migrant workers and to hamper the ability of victims to pursue legal cases against their employers; the withholding workers’ passports remains widespread because legislation prohibiting the practice was not enforced; officials continue to arrest, detain, deport, and sometimes prosecute trafficking victims for unlawful acts committed as a direct result of being trafficked (2014)
regularly enforces the death penalty for drug traffickers, with foreigners being convicted and executed disproportionately; improving anti-money-laundering legislation and enforcement
 Central Intelligence Agency
Central Intelligence Agency