Introduction :: URUGUAY
-
Montevideo, founded by the Spanish in 1726 as a military stronghold, soon took advantage of its natural harbor to become an important commercial center. Claimed by Argentina but annexed by Brazil in 1821, Uruguay declared its independence four years later and secured its freedom in 1828 after a three-year struggle. The administrations of President Jose BATLLE in the early 20th century launched widespread political, social, and economic reforms that established a statist tradition. A violent Marxist urban guerrilla movement named the Tupamaros, launched in the late 1960s, led Uruguay's president to cede control of the government to the military in 1973. By yearend, the rebels had been crushed, but the military continued to expand its hold over the government. Civilian rule was not restored until 1985. In 2004, the left-of-center Frente Amplio Coalition won national elections that effectively ended 170 years of political control previously held by the Colorado and Blanco parties. Uruguay's political and labor conditions are among the freest on the continent.
Geography :: URUGUAY
-
Southern South America, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Argentina and Brazil
33 00 S, 56 00 W
South America
total: 176,215 sq km
land: 175,015 sq km
water: 1,200 sq km
country comparison to the world: 91
slightly smaller than the state of Washington
total: 1,591 km
border countries (2): Argentina 541 km, Brazil 1,050 km
660 km
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or the edge of continental margin
warm temperate; freezing temperatures almost unknown
mostly rolling plains and low hills; fertile coastal lowland
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point: Cerro Catedral 514 m
arable land, hydropower, minor minerals, fish
agricultural land: 87.2%
arable land 10.1%; permanent crops 0.2%; permanent pasture 76.9%
forest: 10.2%
other: 2.6% (2011 est.)
1,810 sq km (2003)
139 cu km (2011)
total: 3.66 cu km/yr (11%/2%/87%)
per capita: 1,101 cu m/yr (2000)
seasonally high winds (the pampero is a chilly and occasional violent wind that blows north from the Argentine pampas), droughts, floods; because of the absence of mountains, which act as weather barriers, all locations are particularly vulnerable to rapid changes from weather fronts
water pollution from meat packing/tannery industry; inadequate solid/hazardous waste disposal
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation
second-smallest South American country (after Suriname); most of the low-lying landscape (three-quarters of the country) is grassland, ideal for cattle and sheep raising
People and Society :: URUGUAY
-
noun: Uruguayan(s)
adjective: Uruguayan
white 88%, mestizo 8%, black 4%, Amerindian (practically nonexistent)
Spanish (official), Portunol, Brazilero (Portuguese-Spanish mix on the Brazilian frontier)
Roman Catholic 47.1%, non-Catholic Christians 11.1%, nondenominational 23.2%, Jewish 0.3%, atheist or agnostic 17.2%, other 1.1% (2006)
Uruguay rates high for most development indicators and is known for its secularism, liberal social laws, and well-developed social security, health, and educational systems. It is one of the few countries in Latin America and the Caribbean where the entire population has access to clean water. Uruguay's provision of free primary through university education has contributed to the country's high levels of literacy and educational attainment. However, the emigration of human capital has diminished the state's return on its investment in education. Remittances from the roughly 18% of Uruguayans abroad amount to less than 1 percent of national GDP. The emigration of young adults and a low birth rate are causing Uruguay's population to age rapidly.
In the 1960s, Uruguayans for the first time emigrated en masse - primarily to Argentina and Brazil - because of economic decline and the onset of more than a decade of military dictatorship. Economic crises in the early 1980s and 2002 also triggered waves of emigration, but since 2002 more than 70% of Uruguayan emigrants have selected the US and Spain as destinations because of better job prospects. Uruguay had a tiny population upon its independence in 1828 and welcomed thousands of predominantly Italian and Spanish immigrants, but the country has not experienced large influxes of new arrivals since the aftermath of World War II. More recent immigrants include Peruvians and Arabs.
3,341,893 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
0-14 years: 20.73% (male 352,470/female 340,275)
15-24 years: 15.89% (male 269,034/female 262,117)
25-54 years: 39.09% (male 644,816/female 661,635)
55-64 years: 10.25% (male 161,190/female 181,478)
65 years and over: 14.03% (male 187,051/female 281,827) (2015 est.)
population pyramid:

total dependency ratio: 55.9%
youth dependency ratio: 33.4%
elderly dependency ratio: 22.5%
potential support ratio: 4.4% (2015 est.)
total: 34.5 years
male: 32.8 years
female: 36.2 years (2015 est.)
0.27% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 176
13.07 births/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
9.45 deaths/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
-0.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
urban population: 95.3% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: 0.53% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
MONTEVIDEO (capital) 1.707 million (2015)
at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.89 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.66 male(s)/female
total population: 0.94 male(s)/female (2015 est.)
total: 8.74 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 9.7 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 7.75 deaths/1,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
total population: 77 years
male: 73.86 years
female: 80.26 years (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
1.82 children born/woman (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
8.8% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 41
3.74 physicians/1,000 population (2008)
2.5 beds/1,000 population (2012)
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 93.9% of population
total: 99.7% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 6.1% of population
total: 0.3% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 96.6% of population
rural: 92.6% of population
total: 96.4% of population
unimproved:
urban: 3.4% of population
rural: 7.4% of population
total: 3.6% of population (2015 est.)
0.7% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
14,400 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
600 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
27.6% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 64
4.5% (2011)
country comparison to the world: 94
4.4% of GDP (2011)
country comparison to the world: 92
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 98.5%
male: 98.2%
female: 98.8% (2015 est.)
total: 16 years
male: 14 years
female: 17 years (2010)
total number: 51,879
percentage: 7% (2006 est.)
total: 18.5%
male: 14.7%
female: 23.6% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
Government :: URUGUAY
-
conventional long form: Oriental Republic of Uruguay
conventional short form: Uruguay
local long form: Republica Oriental del Uruguay
local short form: Uruguay
former: Banda Oriental, Cisplatine Province
constitutional republic
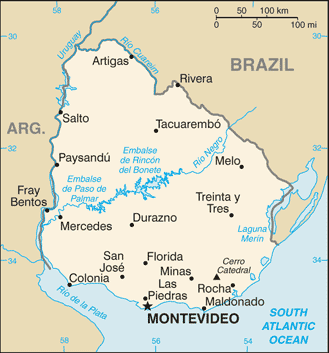
name: Montevideo
geographic coordinates: 34 51 S, 56 10 W
time difference: UTC-3 (2 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
19 departments (departamentos, singular - departamento); Artigas, Canelones, Cerro Largo, Colonia, Durazno, Flores, Florida, Lavalleja, Maldonado, Montevideo, Paysandu, Rio Negro, Rivera, Rocha, Salto, San Jose, Soriano, Tacuarembo, Treinta y Tres
25 August 1825 (from Brazil)
Independence Day, 25 August (1825)
several previous; latest approved by plebiscite 27 November 1966, effective 15 February 1967; amended several times, last in 2004 (2013)
civil law system based on the Spanish civil code
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
18 years of age; universal and compulsory
chief of state: President Tabare VAZQUEZ (since 1 March 2015); Vice President Raul Fernando SENDIC Rodriguez (since 1 March 2015); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Tabare VAZQUEZ (since 1 March 2015); Vice President Raul Fernando SENDIC Rodriguez (since 1 March 2015)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president with approval of the General Assembly
elections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot by absolute majority vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for nonconsecutive terms); election last held on 29 November 2009 (next to be held on 26 October 2014, and a runoff if needed on 30 November 2014)
election results: Tabare VAZQUEZ elected president in a runoff election; percent of vote - Tabare VAZQUEZ (Socialist Party) 56.5%, Luis Alberto LACALLE Pou (Blanco) 43.4%
description: bicameral General Assembly or Asamblea General consists of the Chamber of Senators or Camara de Senadores (31 seats; members directly elected in a single nationwide constituency by proportional representation vote; the vice-president serves as the presiding ex-officio member; elected members serve 5-year terms) and the Chamber of Representatives or Camara de Representantes (99 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote to serve 5-year terms)
elections: Chamber of Senators - last held on 26 October 2014 (next to be held in October 2019); Chamber of Representatives - last held on 26 October 2014 (next to be held in October 2019)
election results: Chamber of Senators - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Frente Amplio 15, Blanco 10, Colorado Party 4, Independent Party 1; Chamber of Representatives - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - Frente Amplio 50, Blanco 32, Colorado Party 13, Independent Party 3, Popular Assembly 1
highest court(s): Supreme Court of Justice (consists of 5 judges)
judge selection and term of office: judges nominated by the president and appointed in joint conference of the General Assembly; judges appointed for 10-year terms, with reelection after a lapse of 5 years following the previous term
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; District Courts (Juzagados Letrados); Peace Courts (Juzagados de Paz); Rural Courts (Juzgados Rurales)
Broad Front (Frente Amplio) or EP-FA [Monica XAVIER] (a broad governing coalition that includes Liber Seregni Front (FLS) [Danilo ASTORI], Socialist Party [Monica XAVIER], Artigas Wing [Mariano ARANA], Christian Democratic Party [Juan Andres ROBALLO], Popular Participation Movement (MPP) [Jose MUJICA], Broad Front Commitment [Raul SENDIC], Action and Thought Current-Freedom (CAP-L) [Eleuterio FERNADEZ HUIDOBRO], Big House [Constanza MOREIRA], Communist Party [Marcos CARAMBULA], The Federal League
Colorado Party (including Vamos Uruguay [Pedro Bordaberry] and Propuesta Batllista [Jorge AMORIN BATLLE])
Independent Party [Pablo MIERES]
National Party or Blanco (including All Forward [Luis LACALLE POU] and National Alliance [Jorge LARRANAGA])
Popular Assembly [Gonzalo ABELLA]
B'nai Brith
Catholic Church
Chamber of Commerce and Export of Agriproducts
Chamber of Industries (manufacturer's association)
Exporters Union of Uruguay
National Chamber of Commerce and Services
PIT/CNT (powerful federation of Uruguayan Unions - umbrella labor organization)
Rural Association of Uruguay (rancher's association)
Uruguayan Network of Political Women
other: students
CAN (associate), CD, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, Mercosur, MIGA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM (observer), OAS, OIF (observer), OPANAL, OPCW, Pacific Alliance (observer), PCA, SICA (observer), UN, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNMOGIP, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
chief of mission: Ambassador Juan Carlos PITA Alvariza (since 3 August 2015)
chancery: 1913 I Street NW, Washington, DC 20006
telephone: [1] (202) 331-1313
FAX: [1] (202) 331-8142
consulate(s) general: Chicago, Los Angeles, Miami, New York
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Brad FREDEN (since 10 December 2014)
embassy: Lauro Muller 1776, Montevideo 11200
mailing address: APO AA 34035
telephone: [598] (2) 1770-2000
FAX: [598] (2) 1770-2128
nine equal horizontal stripes of white (top and bottom) alternating with blue; a white square in the upper hoist-side corner with a yellow sun bearing a human face known as the Sun of May with 16 rays that alternate between triangular and wavy; the stripes represent the nine original departments of Uruguay; the sun symbol evokes the legend of the sun breaking through the clouds on 25 May 1810 as independence was first declared from Spain (Uruguay subsequently won its independence from Brazil); the sun features are said to represent those of Inti, the Inca god of the sun
note: the banner was inspired by the national colors of Argentina and by the design of the US flag
Sun of May (a sun-with-face symbol); national colors: blue, white, yellow
name: "Himno Nacional" (National Anthem of Uruguay)
lyrics/music: Francisco Esteban ACUNA de Figueroa/Francisco Jose DEBALI
note: adopted 1848; the anthem is also known as "Orientales, la Patria o la tumba!" ("Uruguayans, the Fatherland or Death!"); it is the world's longest national anthem in terms of music (105 bars; almost five minutes); generally only the first verse and chorus are sung
Economy :: URUGUAY
-
Uruguay has a free market economy characterized by an export-oriented agricultural sector, a well-educated work force, and high levels of social spending. Following financial difficulties in the late 1990s and early 2000s, Uruguay's economic growth averaged 8% annually during the period 2004-08. The 2008-09 global financial crisis put a brake on Uruguay's vigorous growth, which decelerated to 2.6% in 2009. Nevertheless, the country managed to avoid a recession and keep positive growth rates, mainly through higher public expenditure and investment; GDP growth reached 8.9% in 2010 but slowed in 2012-13 as a result of a renewed slowdown in the global economy and in Uruguay's main trade partners and Common Market of the South (Mercosur) counterparts, Argentina and Brazil. Uruguay has sought to expand trade within Mercosur and with non-Mercosur members, and President VAZQUEZ has said he will maintain his predecessor’s mix of pro-market policies and a strong social safety net.
$69.98 billion (2014 est.)
$67.73 billion (2013 est.)
$64.88 billion (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 95
$55.14 billion (2014 est.)
3.3% (2014 est.)
4.4% (2013 est.)
3.7% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
$20,600 (2014 est.)
$19,900 (2013 est.)
$19,100 (2012 est.)
note: data are in 2014 US dollars
country comparison to the world: 80
17.3% of GDP (2014 est.)
18.3% of GDP (2013 est.)
18.2% of GDP (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
household consumption: 66.1%
government consumption: 14%
investment in fixed capital: 22.9%
investment in inventories: 0.7%
exports of goods and services: 24.2%
imports of goods and services: -28%
(2014 est.)
agriculture: 7.5%
industry: 20.4%
services: 72.1% (2014 est.)
soybeans, rice, wheat; beef, dairy products; fish; lumber, cellulose
food processing, electrical machinery, transportation equipment, petroleum products, textiles, chemicals, beverages
1.8% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136
1.712 million (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
agriculture: 13%
industry: 14%
services: 73% (2010 est.)
6.5% (2014 est.)
6.6% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
18.6% (2010 est.)
lowest 10%: 1.9%
highest 10%: 34.4% (2010 est.)
45.3 (2010)
44.8 (1999)
country comparison to the world: 40
revenues: $16.8 billion
expenditures: $18.71 billion (2014 est.)
30.2% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
-3.4% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
64.7% of GDP (2014 est.)
62.1% of GDP (2013 est.)
note: data cover general government debt, and include debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions.
country comparison to the world: 48
calendar year
8.9% (2014 est.)
8.6% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
9% (31 December 2012)
8.75% (31 December 2011)
note: Uruguay's central bank uses the benchmark interest rate, rather than the discount rate, to conduct monetary policy; the rates shown here are the benchmark rates
country comparison to the world: 26
15.7% (31 December 2014 est.)
12.44% (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
$5.201 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$5.455 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
$8.568 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$8.919 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
$19.82 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$19.48 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
$175.4 million (31 December 2012 est.)
$174.6 million (31 December 2011)
$156.9 million (31 December 2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 117
-$2.615 billion (2014 est.)
-$3.144 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
$11 billion (2014 est.)
$10.29 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
beef, soybeans, cellulose, rice, wheat, wood, dairy products; wool
China 22.4%, Brazil 17.9%, Argentina 6.3%, Venezuela 5% (2014)
$12.05 billion (2014 est.)
$11.6 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
refined oil, crude oil, passenger and other transportation vehicles, vehicle parts, cellular phones
Brazil 20.3%, China 16.9%, Argentina 13.1%, US 10.2%, Venezuela 4.6% (2014)
$17.96 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$16.28 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
$17.54 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$16.27 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
$23.41 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$20.59 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
$411.7 million (31 December 2014 est.)
$376.6 million (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
Uruguayan pesos (UYU) per US dollar -
23.18 (2014 est.)
20.482 (2013 est.)
20.31 (2012 est.)
19.314 (2011 est.)
20.059 (2010 est.)
Energy :: URUGUAY
-
10.16 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
9.333 billion kWh (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
194 million kWh (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
742 million kWh (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
2.707 million kW (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
41.6% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 168
0% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 197
56.8% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
1.6% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
400 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
0 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 199
38,680 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
0 bbl (1 January 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 202
43,440 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
49,140 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
4,656 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
16,420 bbl/day (2010 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
0 cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
60 million cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
0 cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200
60 million cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
0 cu m (1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
7.591 million Mt (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
Communications :: URUGUAY
-
total subscriptions: 1.08 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 32 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
total: 5.5 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 165 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
general assessment: fully digitalized
domestic: most modern facilities concentrated in Montevideo; nationwide microwave radio relay network; overall fixed-line and mobile-cellular teledensity has reached 170 telephones per 100 persons
international: country code - 598; the UNISOR submarine cable system provides direct connectivity to Brazil and Argentina; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2011)
mixture of privately owned and state-run broadcast media; more than 100 commercial radio stations and about 20 TV channels; cable TV is available; many community radio and TV stations; adopted the hybrid Japanese/Brazilian HDTV standard (ISDB-T) in December 2010 (2010)
AM 93, FM 191, shortwave 7 (2005)
62 (2005)
.uy
total: 2 million
percent of population: 59.0% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
Transportation :: URUGUAY
-
133 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 42
total: 11
over 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4
914 to 1,523 m: 4
under 914 m: 2 (2013)
total: 122
1,524 to 2,437 m: 3
914 to 1,523 m: 40
under 914 m:
79 (2013)
gas 257 km; oil 160 km (2013)
total: 1,641 km
standard gauge: 1,641 km 1.435-m gauge (2014)
country comparison to the world: 77
total: 77,732 km
paved: 7,743 km
unpaved: 69,989 km (2010)
country comparison to the world: 62
1,600 km (2011)
country comparison to the world: 48
total: 16
by type: bulk carrier 1, cargo 2, chemical tanker 3, passenger/cargo 6, petroleum tanker 3, roll on/roll off 1
foreign-owned: 8 (Argentina 1, Denmark 1, Greece 1, Spain 5)
registered in other countries: 1 (Liberia 1) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 100
major seaport(s): Montevideo
Military :: URUGUAY
-
Uruguayan Armed Forces: Uruguayan National Army (Ejercito Nacional Uruguaya, ENU), Uruguayan National Navy (Armada Nacional del Uruguay; includes naval air arm, Naval Rifle Corps (Cuerpo de Fusileros Navales, Fusna), Maritime Prefecture in wartime), Uruguayan Air Force (Fuerza Aerea Uruguaya, FAU) (2012)
18-30 years of age (18-22 years of age for navy) for male or female voluntary military service; up to 40 years of age for specialists; enlistment is voluntary in peacetime, but the government has the authority to conscript in emergencies; minimum 6-year education (2013)
males age 16-49: 771,159
females age 16-49: 780,932 (2010 est.)
males age 16-49: 649,025
females age 16-49: 654,903 (2010 est.)
male: 27,564
female: 26,811 (2010 est.)
1.95% of GDP (2012)
1.94% of GDP (2011)
1.95% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 42
Transnational Issues :: URUGUAY
-
in 2010, the ICJ ruled in favor of Uruguay's operation of two paper mills on the Uruguay River, which forms the border with Argentina; the two countries formed a joint pollution monitoring regime; uncontested boundary dispute between Brazil and Uruguay over Braziliera/Brasiliera Island in the Quarai/Cuareim River leaves the tripoint with Argentina in question; smuggling of firearms and narcotics continues to be an issue along the Uruguay-Brazil border
current situation: Uruguay is a source country for women and children subjected to sex trafficking and, to a lesser extent, a transit and destination country for men, women, and children exploited in forced labor and sex trafficking; most victims are women and girls exploited in sex trafficking domestically; some Uruguayan women lured by fraudulent job employment offers in Spain, Italy, and Argentina are forced into prostitution; foreign workers in domestic service, agriculture, and lumber processing are vulnerable to forced labor in Uruguay; some human trafficking cases are reportedly linked to international crime rings
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – Uruguay does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; authorities investigated and prosecuted several trafficking cases in 2013 but reported no convictions; limited anti-trafficking data makes it difficult to assess law enforcement efforts; the government provides limited services to human trafficking victims outside the capital and to forced labor victims; two public awareness campaigns were launched with foreign funding in 2013 (2014)
small-scale transit country for drugs mainly bound for Europe, often through sea-borne containers; law enforcement corruption; money laundering because of strict banking secrecy laws; weak border control along Brazilian frontier; increasing consumption of cocaine base and synthetic drugs
 Central Intelligence Agency
Central Intelligence Agency