Introduction :: SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES
-
Resistance by native Caribs prevented colonization on Saint Vincent until 1719. Disputed between France and the UK for most of the 18th century, the island was ceded to the latter in 1783. Between 1960 and 1962, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines was a separate administrative unit of the Federation of the West Indies. Autonomy was granted in 1969 and independence in 1979.
Geography :: SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES
-
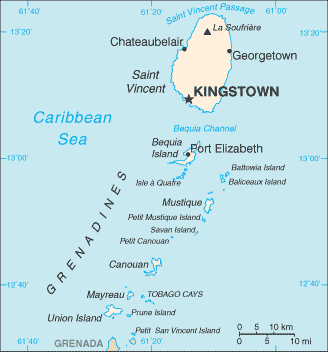
Caribbean, islands between the Caribbean Sea and North Atlantic Ocean, north of Trinidad and Tobago
13 15 N, 61 12 W
Central America and the Caribbean
total: 389 sq km (Saint Vincent 344 sq km)
land: 389 sq km
water: 0 sq km
country comparison to the world: 205
twice the size of Washington, DC
0 km
84 km
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm
tropical; little seasonal temperature variation; rainy season (May to November)
volcanic, mountainous
mean elevation: NA
elevation extremes: lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 m
highest point: La Soufriere 1,234 m
hydropower, arable land
agricultural land: 25.6%
arable land 12.8%; permanent crops 7.7%; permanent pasture 5.1%
forest: 68.7%
other: 5.7% (2011 est.)
10 sq km (2012)
most of the population is concentrated in and around the capital of Kingstown
hurricanes; La Soufriere volcano on the island of Saint Vincent is a constant threat
volcanism: La Soufriere (1,234 m) on the island of Saint Vincent last erupted in 1979; the island of Saint Vincent is part of the volcanic island arc of the Lesser Antilles that extends from Saba in the north to Grenada in the south
pollution of coastal waters and shorelines from discharges by pleasure yachts and other effluents; in some areas, pollution is severe enough to make swimming prohibitive
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
the administration of the islands of the Grenadines group is divided between Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and Grenada; Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is comprised of 32 islands and cays
People and Society :: SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES
-
102,089 (July 2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
noun: Saint Vincentian(s) or Vincentian(s)
adjective: Saint Vincentian or Vincentian
black 66%, mixed 19%, East Indian 6%, European 4%, Carib Amerindian 2%, other 3%
English, French patois
Protestant 75% (Anglican 47%, Methodist 28%), Roman Catholic 13%, other (includes Hindu, Seventh-Day Adventist, other Protestant) 12%
0-14 years: 21.3% (male 10,970/female 10,779)
15-24 years: 15.97% (male 8,226/female 8,080)
25-54 years: 42.66% (male 22,608/female 20,939)
55-64 years: 10.64% (male 5,595/female 5,272)
65 years and over: 9.42% (male 4,515/female 5,105) (2017 est.)
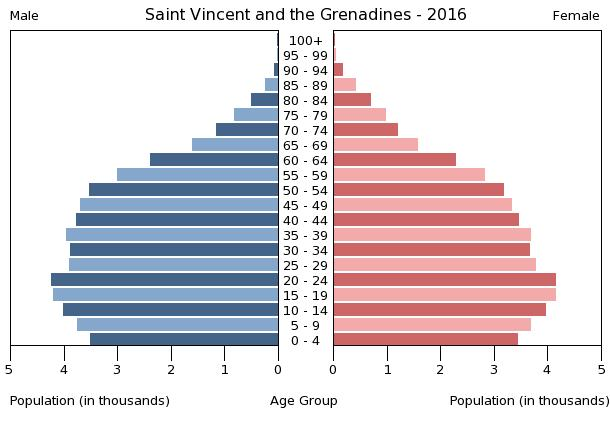
population pyramid:

Central America and Caribbean
::SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES

Population Pyramid
A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.
total dependency ratio: 46.8
youth dependency ratio: 36
elderly dependency ratio: 10.8
potential support ratio: 9.3 (2015 est.)
total: 33.6 years
male: 33.8 years
female: 33.4 years (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
-0.25% (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 218
13.2 births/1,000 population (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
7.3 deaths/1,000 population (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
-8.4 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 209
most of the population is concentrated in and around the capital of Kingstown
urban population: 51.2% of total population (2017)
rate of urbanization: 0.7% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)
KINGSTOWN (capital) 27,000 (2014)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.08 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.87 male(s)/female
total population: 1.03 male(s)/female (2016 est.)
45 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
total: 12 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 13.1 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 10.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
total population: 75.5 years
male: 73.5 years
female: 77.6 years (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 104
1.8 children born/woman (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
8.6% of GDP (2014)
country comparison to the world: 46
5.2 beds/1,000 population (2012)
improved:
urban: 95.1% of population
rural: 95.1% of population
total: 95.1% of population
unimproved:
urban: 4.9% of population
rural: 4.9% of population
total: 4.9% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 76.1% of population
rural: 76.1% of population
total: 76.1% of population
unimproved:
urban: 23.9% of population
rural: 23.9% of population
total: 23.9% of population (2007 est.)
NA
NA
NA
note: active local transmission of Zika virus by Aedes species mosquitoes has been identified in this country (as of August 2016); it poses an important risk (a large number of cases possible) among US citizens if bitten by an infective mosquito; other less common ways to get Zika are through sex, via blood transfusion, or during pregnancy, in which the pregnant woman passes Zika virus to her fetus (2016)
23.7% (2016)
country comparison to the world: 64
5.1% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 69
total: 33.8%
male: 27.8%
female: 41.4% (2008 est.)
Government :: SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES
-
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
etymology: Saint Vincent was named by explorer Christopher COLUMBUS after Saint VINCENT of Saragossa because the 22 January 1498 day of discovery was the saint's feast day
parliamentary democracy (House of Assembly) under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm
name: Kingstown
geographic coordinates: 13 08 N, 61 13 W
time difference: UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
6 parishes; Charlotte, Grenadines, Saint Andrew, Saint David, Saint George, Saint Patrick
27 October 1979 (from the UK)
Independence Day, 27 October (1979)
several previous; latest passed by the House of Assembly 3 September 2009 (The Saint Vincent and The Grenadines Constitution Act, 2009) (2016)
English common law
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent: at least one parent must be a citizen of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years
18 years of age; universal
chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Governor General Sir Fredrick Nathaniel BALLANTYNE (since 2 September 2002)
head of government: Prime Minister Ralph E. GONSALVES (since 29 March 2001)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister
elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party usually appointed prime minister by the governor general; deputy prime minister appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister
description: unicameral House of Assembly (21 seats; 15 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 6 appointed by the governor general; members serve 5-year terms)
elections: last held on 9 December 2015 (next to be held in 2020)
election results: percent of vote by party - ULP 52.3%, NDP 47.4%, other 0.3%; seats by party - ULP 8, NDP 7
highest court(s): the Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court (ECSC) is the superior court of the Organization of Eastern Caribbean States; the ECSC - headquartered on St. Lucia - consists of the Court of Appeal - headed by the chief justice and 4 judges - and the High Court with 18 judges; the Court of Appeal is itinerant, travelling to member states on a schedule to hear appeals from the High Court and subordinate courts; High Court judges reside at the member states with 2 assigned to Saint Vincent and the Grenadines; note - Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is also a member of the Caribbean Court of Justice
judge selection and term of office: chief justice of Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court appointed by Her Majesty, Queen ELIZABETH II; other justices and judges appointed by the Judicial and Legal Services Commission, an independent body of judicial officials; Court of Appeal justices appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 65; High Court judges appointed for life with mandatory retirement at age 62
subordinate courts: magistrates' courts
Democratic Republican Party or DRP [Anesia BAPTISTE]
New Democratic Party or NDP [Godwin L. FRIDAY]
Unity Labor Party or ULP [Dr. Ralph GONSALVES] (formed by the coalition of Saint Vincent Labor Party or SVLP and the Movement for National Unity or MNU)
SVG Green Party or SVGP [Ivan O'NEAL]
St. Vincent & the Grenadines Teachers' Union [Oswald CHAMBERS]
other: several labor unions
ACP, AOSIS, C, Caricom, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ISO (subscriber), ITU, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OECS, OPANAL, OPCW, Petrocaribe, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WTO
chief of mission: Ambassador Lou-Anne Gaylene GILCHRIST (since 18 January 2017)
chancery: 3216 New Mexico Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20016
telephone: [1] (202) 364-6730
FAX: [1] (202) 364-6736
consulate(s) general: New York
the US does not have an embassy in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines; the US Ambassador to Barbados is accredited to Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
three vertical bands of blue (hoist side), gold (double width), and green; the gold band bears three green diamonds arranged in a V pattern, which stands for Vincent; the diamonds recall the islands as "the Gems of the Antilles" and are set slightly lowered in the gold band to reflect the nation's position in the Antilles; blue conveys the colors of a tropical sky and crystal waters, yellow signifies the golden Grenadine sands, and green represents lush vegetation
Saint Vincent parrot; national colors: blue, gold, green
name: "St. Vincent! Land So Beautiful!"
lyrics/music: Phyllis Joyce MCCLEAN PUNNETT/Joel Bertram MIGUEL
note: adopted 1967
Economy :: SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES
-
Success of the economy hinges upon seasonal variations in agriculture, tourism, and construction activity, as well as remittances. Much of the workforce is employed in banana production and tourism. Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is home to a small offshore banking sector and continues to fully adopt international regulatory standards.
This lower-middle-income country remains vulnerable to natural and external shocks. The economy has shown some signs of recovery due to increased tourist arrivals, falling oil prices and renewed growth in the construction sector. The much anticipated international airport opened in early 2017 with hopes for increased airlift and tourism activity. The government's ability to invest in social programs and respond to external shocks is constrained by its high public debt burden, which was 67% of GDP at the end of 2013.
$1.232 billion (2016 est.)
$1.207 billion (2015 est.)
$1.184 billion (2014 est.)
note: data are in 2016 dollars
country comparison to the world: 201
$770 million (2016 est.)
0.8% (2016 est.)
0.9% (2015 est.)
0.3% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
$11,200 (2016 est.)
$11,100 (2015 est.)
$11,000 (2014 est.)
note: data are in 2016 dollars
country comparison to the world: 133
-5.1% of GDP (2016 est.)
-3.1% of GDP (2015 est.)
-0.7% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 172
household consumption: 87.8%
government consumption: 18.5%
investment in fixed capital: 19.7%
investment in inventories: -0.2%
exports of goods and services: 21.1%
imports of goods and services: -47.1% (2016 est.)
agriculture: 7.1%
industry: 17.4%
services: 75.4% (2016 est.)
bananas, coconuts, sweet potatoes, spices; small numbers of cattle, sheep, pigs, goats; fish
tourism; food processing, cement, furniture, clothing, starch
2.3% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 100
57,520 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 189
agriculture: 26%
industry: 17%
services: 57% (1980 est.)
18.8% (2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181
NA%
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%: NA%
revenues: $222.2 million
expenditures: $222.2 million (2016 est.)
28.7% of GDP (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
0% of GDP (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
79.2% of GDP (2016 est.)
81.3% of GDP (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
calendar year
-0.2% (2016 est.)
-1.7% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
6.5% (31 December 2010)
6.5% (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 59
9.17% (31 December 2016 est.)
9.3% (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
$177.7 million (31 December 2016 est.)
$162.2 million (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 186
$563.2 million (31 December 2016 est.)
$546.6 million (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
$424.6 million (31 December 2016 est.)
$439 million (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 179
$-122 million (2016 est.)
$-183.4 million (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
$47.3 million (2016 est.)
$48.5 million (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
bananas, eddoes and dasheen (taro), arrowroot starch; tennis racquets
Barbados 18.3%, St. Lucia 17.6%, Antigua and Barbuda 14.8%, Trinidad and Tobago 12.3%, Dominica 9.5%, St. Kitts and Nevis 7.3%, Grenada 5.9% (2016)
$289.9 million (2016 est.)
$297.3 million (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 201
foodstuffs, machinery and equipment, chemicals and fertilizers, minerals and fuels
US 44%, Trinidad and Tobago 14.1%, UK 6.5%, France 4.8% (2016)
$192.3 million (31 December 2016 est.)
$166 million (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
$330.8 million (31 December 2016 est.)
$338.6 million (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 184
East Caribbean dollars (XCD) per US dollar -
2.7 (2016 est.)
2.7 (2015 est.)
2.7 (2014 est.)
2.7 (2013 est.)
2.7 (2012 est.)
Energy :: SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES
-
population without electricity: 25,587
electrification - total population: 76%
electrification - urban areas: 100%
electrification - rural areas: 32% (2012)
155 million kWh (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
144.2 million kWh (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 197
0 kWh (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 211
0 kWh (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 214
48,000 kW (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
83.3% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
0% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
14.6% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
2.1% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
0 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
0 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 207
0 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
0 bbl (1 January 2017 es)
country comparison to the world: 208
0 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 209
1,600 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 197
0 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 210
1,519 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 194
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
0 cu m (1 January 2014 es)
country comparison to the world: 204
300,000 Mt (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 194
Communications :: SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES
-
total subscriptions: 20,550
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 20 (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 175
total: 112,649
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 110 (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 188
general assessment: adequate islandwide, fully automatic telephone system
domestic: fixed-line teledensity exceeds 20 per 100 persons and mobile-cellular teledensity is about 110 per 100 persons
international: country code - 1-784; the East Caribbean Fiber System and Southern Caribbean Fiber submarine cables carry international calls; connectivity also provided by VHF/UHF radiotelephone from Saint Vincent to Barbados; SHF radiotelephone to Grenada and Saint Lucia; access to Intelsat earth station in Martinique through Saint Lucia (2016)
St. Vincent and the Grenadines Broadcasting Corporation operates 1 TV station and 5 repeater stations that provide near total coverage to the multi-island state; multi-channel cable TV service available; a partially government-funded national radio service broadcasts on 1 station and has 2 repeater stations; about a dozen privately owned radio stations and repeater stations (2007)
.vc
total: 53,000
percent of population: 51.8% (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 177
Transportation :: SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES
-
number of registered air carriers: 2
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 11 (2015)
J8 (2016)
6 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 175
total: 5
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 3
under 914 m: 1 (2017)
total: 1
under 914 m: 1 (2013)
total: 829 km
paved: 580 km
unpaved: 249 km (2003)
country comparison to the world: 189
total: 412
by type: bulk carrier 64, cargo 263, carrier 14, chemical tanker 4, container 18, liquefied gas 3, passenger 2, passenger/cargo 7, petroleum tanker 9, refrigerated cargo 12, roll on/roll off 15, specialized tanker 1
foreign-owned: 325 (Austria 1, Azerbaijan 1, Bangladesh 1, Belgium 7, Bermuda 1, Bulgaria 9, China 65, Croatia 8, Cyprus 3, Czech Republic 1, Denmark 9, Dominica 1, Egypt 2, Estonia 8, France 2, Germany 3, Greece 42, Guyana 2, Hong Kong 5, Israel 3, Italy 4, Japan 3, Kenya 2, Latvia 15, Lebanon 2, Lithuania 9, Monaco 2, Netherlands 1, Norway 13, Poland 3, Romania 1, Russia 11, Singapore 5, Slovenia 1, Sweden 10, Switzerland 7, Syria 9, Turkey 13, UAE 3, UK 6, Ukraine 12, US 18, Venezuela 1) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 26
major seaport(s): Kingstown
Military and Security :: SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES
-
no regular military forces; Royal Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Police Force (RSVPF) (2013)
Transnational Issues :: SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES
-
joins other Caribbean states to counter Venezuela's claim that Aves Island sustains human habitation, a criterion under UN Convention on the Law of the Sea, which permits Venezuela to extend its EEZ/continental shelf over a large portion of the eastern Caribbean Sea
current situation: Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; some children under 18 are pressured to engage in sex acts in exchange for money or gifts; foreign workers may experience forced labor and are particularly vulnerable when employed by small, foreign-owned companies; adults and children are vulnerable to forced labor domestically, especially in the agriculture sector
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – Saint Vincent and the Grenadines does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; the government for the first time acknowledged a trafficking problem, launched an anti-trafficking public awareness campaign, and conducted anti-trafficking training for law enforcement, immigration, and labor officials; in 2014, authorities initiated three trafficking investigations, two of which were ultimately determined not to be trafficking cases, and did not prosecute or convict any trafficking offenders; the government did not identify or refer any potential trafficking victims to care (2015)
transshipment point for South American drugs destined for the US and Europe; small-scale cannabis cultivation