Introduction :: DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
-
The Taino - indigenous inhabitants of Hispaniola prior to the arrival of the Europeans - divided the island into five chiefdoms and territories. Christopher COLUMBUS explored and claimed the island on his first voyage in 1492; it became a springboard for Spanish conquest of the Caribbean and the American mainland. In 1697, Spain recognized French dominion over the western third of the island, which in 1804 became Haiti. The remainder of the island, by then known as Santo Domingo, sought to gain its own independence in 1821 but was conquered and ruled by the Haitians for 22 years; it finally attained independence as the Dominican Republic in 1844. In 1861, the Dominicans voluntarily returned to the Spanish Empire, but two years later they launched a war that restored independence in 1865. A legacy of unsettled, mostly non-representative rule followed, capped by the dictatorship of Rafael Leonidas TRUJILLO from 1930 to 1961. Juan BOSCH was elected president in 1962 but was deposed in a military coup in 1963. In 1965, the US led an intervention in the midst of a civil war sparked by an uprising to restore BOSCH. In 1966, Joaquin BALAGUER defeated BOSCH in the presidential election. BALAGUER maintained a tight grip on power for most of the next 30 years when international reaction to flawed elections forced him to curtail his term in 1996. Since then, regular competitive elections have been held in which opposition candidates have won the presidency. Former President Leonel FERNANDEZ Reyna (first term 1996-2000) won election to a new term in 2004 following a constitutional amendment allowing presidents to serve more than one term, and was later reelected to a second consecutive term. In 2012, Danilo MEDINA Sanchez became president; he was reelected in 2016.
Geography :: DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
-
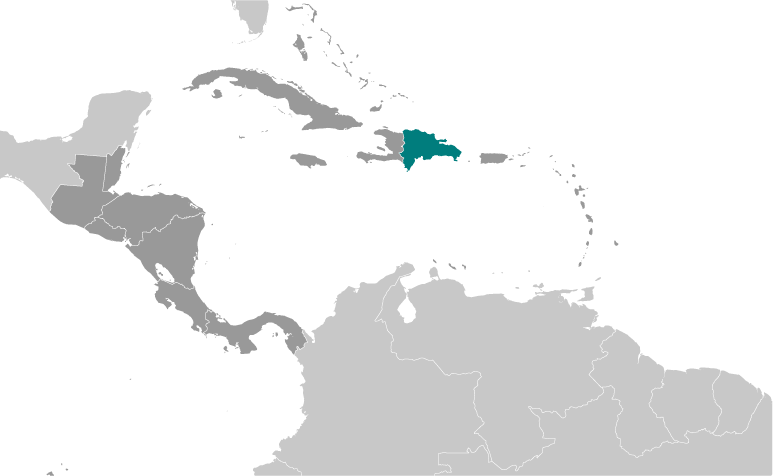
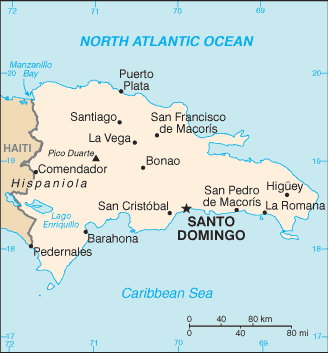
Caribbean, eastern two-thirds of the island of Hispaniola, between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east of Haiti
19 00 N, 70 40 W
Central America and the Caribbean
total: 48,670 sq km
land: 48,320 sq km
water: 350 sq km
country comparison to the world: 132
slightly more than twice the size of New Jersey
total: 376 km
border countries (1): Haiti 376 km
1,288 km
measured from claimed archipelagic straight baselines
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
tropical maritime; little seasonal temperature variation; seasonal variation in rainfall
rugged highlands and mountains interspersed with fertile valleys
mean elevation: 424 m
elevation extremes: lowest point: Lago Enriquillo -46 m
highest point: Pico Duarte 3,098 m
nickel, bauxite, gold, silver, arable land
agricultural land: 51.5%
arable land 16.6%; permanent crops 10.1%; permanent pasture 24.8%
forest: 40.8%
other: 7.7% (2011 est.)
3,070 sq km (2012)
coastal development is significant, especially in the southern coastal plains and the Cibao Valley, where population density is highest; smaller population clusters exist in the interior mountains (Cordillera Central)
lies in the middle of the hurricane belt and subject to severe storms from June to October; occasional flooding; periodic droughts
water shortages; soil eroding into the sea damages coral reefs; deforestation
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea
shares island of Hispaniola with Haiti (eastern two-thirds makes up the Dominican Republic, western one-third is Haiti); the second largest country in the Antilles (after Cuba); geographically diverse with the Caribbean's tallest mountain, Pico Duarte, and lowest elevation and largest lake, Lago Enriquillo
People and Society :: DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
-
10,734,247 (July 2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
noun: Dominican(s)
adjective: Dominican
mixed 70.4% (mestizo/indio 58%, mulatto 12.4%), black 15.8%, white 13.5%, other 0.3%
note: respondents self-identified their race; the term "indio" in the Dominican Republic is not associated with people of indigenous ancestry but people of mixed ancestry or skin color between light and dark (2014 est.)
Spanish (official)
Roman Catholic 95%, other 5%
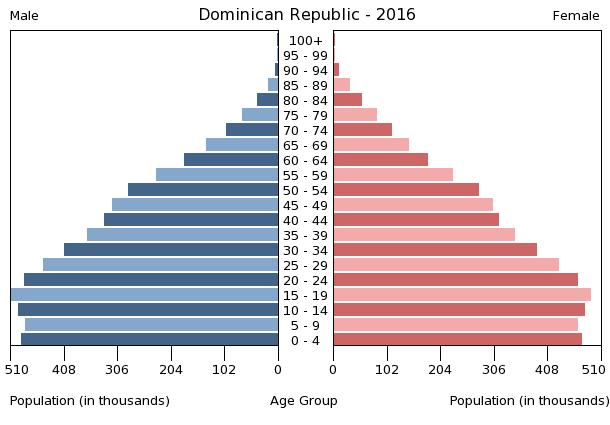
0-14 years: 26.63% (male 1,454,527/female 1,404,538)
15-24 years: 18.18% (male 993,642/female 957,466)
25-54 years: 39.66% (male 2,178,477/female 2,078,371)
55-64 years: 7.9% (male 426,810/female 421,727)
65 years and over: 7.63% (male 378,226/female 440,463) (2017 est.)
population pyramid:

Central America and Caribbean
::DOMINICAN REPUBLIC

Population Pyramid
A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.
total dependency ratio: 57.8
youth dependency ratio: 47.3
elderly dependency ratio: 10.5
potential support ratio: 9.5 (2015 est.)
total: 28.1 years
male: 27.9 years
female: 28.3 years (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
1.18% (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
18.4 births/1,000 population (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
4.7 deaths/1,000 population (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 202
-1.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
coastal development is significant, especially in the southern coastal plains and the Cibao Valley, where population density is highest; smaller population clusters exist in the interior mountains (Cordillera Central)
urban population: 80.6% of total population (2017)
rate of urbanization: 2% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)
SANTO DOMINGO (capital) 2.945 million (2015)
at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.86 male(s)/female
total population: 1.03 male(s)/female (2016 est.)
21.3 years
note: median age at first birth among women 25-29 (2013 est.)
92 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
total: 17.5 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 19.3 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 15.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
total population: 78.3 years
male: 76 years
female: 80.6 years (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
2.29 children born/woman (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 92
69.5% (2014)
4.4% of GDP (2014)
country comparison to the world: 157
1.49 physicians/1,000 population (2011)
1.7 beds/1,000 population (2011)
improved:
urban: 85.4% of population
rural: 81.9% of population
total: 84.7% of population
unimproved:
urban: 14.6% of population
rural: 18.1% of population
total: 15.3% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 86.2% of population
rural: 75.7% of population
total: 84% of population
unimproved:
urban: 13.8% of population
rural: 24.3% of population
total: 16% of population (2015 est.)
1% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
67,000 (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
2,200 (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne disease: dengue fever
note: active local transmission of Zika virus by Aedes species mosquitoes has been identified in this country (as of August 2016); it poses an important risk (a large number of cases possible) among US citizens if bitten by an infective mosquito; other less common ways to get Zika are through sex, via blood transfusion, or during pregnancy, in which the pregnant woman passes Zika virus to her fetus (2016)
27.6% (2016)
country comparison to the world: 37
4% (2013)
country comparison to the world: 106
2.1% of GDP (2007)
country comparison to the world: 163
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 91.8%
male: 91.2%
female: 92.3% (2015 est.)
total: 13 years
male: 13 years
female: 14 years (2014)
total: 10.8%
male: 7.7%
female: 15.8% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
Government :: DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
-
conventional long form: Dominican Republic
conventional short form: The Dominican
local long form: Republica Dominicana
local short form: La Dominicana
etymology: the country name derives from the capital city of Santo Domingo (Saint Dominic)
presidential republic
name: Santo Domingo
geographic coordinates: 18 28 N, 69 54 W
time difference: UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
10 regions (regiones, singular - region); Cibao Nordeste, Cibao Noroeste, Cibao Norte, Cibao Sur, El Valle, Enriquillo, Higuamo, Ozama, Valdesia, Yuma
27 February 1844 (from Haiti)
Independence Day, 27 February (1844)
many previous (38 total); latest proclaimed 26 January 2010; note - the Dominican Republic Government has a practice of promulgating a "new" constitution whenever an amendment is ratified (2016)
civil law system based on the French civil code; Criminal Procedures Code modified in 2004 to include important elements of an accusatory system
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of the Dominican Republic
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 2 years
18 years of age, universal and compulsory; married persons regardless of age can vote; note - members of the armed forces and national police by law cannot vote
chief of state: President Danilo MEDINA Sanchez (since 16 August 2012); Vice President Margarita CEDENO DE FERNANDEZ (since 16 August 2012); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Danilo MEDINA Sanchez (since 16 August 2012); Vice President Margarita CEDENO DE FERNANDEZ (since 16 August 2012)
cabinet: Cabinet nominated by the president
elections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot by absolute vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 4-year term (eligible for consecutive terms); election last held on 15 May 2016 (next to be held in 2020)
election results: Danilo MEDINA Sanchez reelected president; percent of vote - Danilo MEDINA Sanchez (PLD) 61.7%, Luis Rodolfo ABINADER Corona (PRM) 35%, other 3.3%; Margarita CEDENO DE FERNANDEZ (PLD) reelected vice president
description: bicameral National Congress or Congreso Nacional consists of the Senate or Senado (32 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 4-year terms) and the House of Representatives or Camara de Diputados (190 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)
elections: Senate - last held on 15 May 2016 (next to be held in May 2020); House of Representatives - last held on 15 May 2016 (next to be held in May 2020)
election results: Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PLD 26, PRM 2, BIS 1, PLRD 1, PRD 1, PRSC 1
House of Representatives - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PLD 106, PRM 42, PRSC 18, PRD 16, PLRD 3, other 5
highest court(s): Supreme Court of Justice or Suprema Corte de Justicia (consists of a minimum of 16 magistrates); Constitutional Court or Tribunal Constitucional (consists of 13 judges); note - the Constitutional Court was established in 2010 by constitutional amendment
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court and Constitutional Court judges appointed by the National Council of the Judiciary comprised of the president, the leaders of both chambers of congress, the president of the Supreme Court, and a non-governing party congressional representative; Supreme Court judges appointed for 7-year terms; Constitutional Court judges appointed for 9-year terms
subordinate courts: courts of appeal; courts of first instance; justices of the peace; special courts for juvenile, labor, and land cases; Contentious Administrative Court for cases filed against the government
Dominican Liberation Party or PLD [Leonel FERNANDEZ Reyna]
Dominican Revolutionary Party or PRD [Miguel VARGAS Maldonado]
Institutional Social Democratic Bloc or BIS
Liberal Reformist Party or PRL
Modern Revolutionary Party or PRM [Andres BAUTISTA Garcia]
National Progressive Front or FNP [Vinicio CASTILLO, Pelegrin CASTILLO]
Social Christian Reformist Party or PRSC [Federico ANTUN]
Citizen Participation Group (Participacion Ciudadania)
Collective of Popular Organizations or COP
Foundation for Institution-Building and Justice or FINJUS
ACP, AOSIS, BCIE, Caricom (observer), CD, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA, MIGA, MINUSMA, NAM, OAS, OIF (observer), OPANAL, OPCW, Pacific Alliance (observer), PCA, Petrocaribe, SICA (associated member), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
chief of mission: Ambassador Jose Tomas PEREZ Vazquez(since 23 February 2015)
chancery: 1715 22nd Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 332-6280
FAX: [1] (202) 265-8057
consulate(s) general: Boston, Chicago, Los Angeles, Mayaguez (Puerto Rico), Miami, New Orleans, New York, San Juan (Puerto Rico)
consulate(s): San Francisco
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Robert COPLEY (since 21 July 2017)
embassy: Av. Republica de Colombia
mailing address: Unit 5500, APO AA 34041-5500
telephone: [1] (809) 567-7775
FAX: [1] (809) 686-7437
a centered white cross that extends to the edges divides the flag into four rectangles - the top ones are ultramarine blue (hoist side) and vermilion red, and the bottom ones are vermilion red (hoist side) and ultramarine blue; a small coat of arms featuring a shield supported by a laurel branch (left) and a palm branch (right) is at the center of the cross; above the shield a blue ribbon displays the motto, DIOS, PATRIA, LIBERTAD (God, Fatherland, Liberty), and below the shield, REPUBLICA DOMINICANA appears on a red ribbon; in the shield a bible is opened to a verse that reads "Y la verdad nos hara libre" (And the truth shall set you free); blue stands for liberty, white for salvation, and red for the blood of heroes
palmchat (bird); national colors: red, white, blue
name: "Himno Nacional" (National Anthem)
lyrics/music: Emilio PRUD'HOMME/Jose REYES
note: adopted 1934; also known as "Quisqueyanos valientes" (Valient Sons of Quisqueye); the anthem never refers to the people as Dominican but rather calls them "Quisqueyanos," a reference to the indigenous name of the island
Economy :: DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
-
The Dominican Republic was for most of its history primarily an exporter of sugar, coffee, and tobacco, but in recent years the service sector has overtaken agriculture as the economy's largest employer, due to growth in construction, tourism, and free trade zones. The mining sector has also played a greater role in the export market since late 2012 with the commencement of the extraction phase of the Pueblo Viejo Gold and Silver mine, one of the largest gold mines in the world. The country suffers from marked income inequality; the poorest half of the population receives less than one-fifth of GDP, while the richest 10% enjoys nearly 40% of GDP. High unemployment, a large informal sector, and underemployment remain important long-term challenges.
The economy is highly dependent upon the US, the destination for approximately half of exports. Remittances from the US amount to about 7% of GDP, equivalent to about a third of exports and two-thirds of tourism receipts. The Central America-Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement came into force in March 2007, boosting investment and manufacturing exports.
The Dominican Republic's economy rebounded from the global recession in 2010-16, and the fiscal situation is improving. A tax reform package passed in November 2012, a reduction in government spending, and lower energy costs helped to narrow the central government budget deficit from 6.6% of GDP in 2012 to 2.6% in 2016. A liability management operation in January 2015, in which the government paid down over $4 billion of the country’s Petrocaribe debt at a discount of 52% with proceeds from the sale of $2.5 billion in global bonds, reduced the country’s debt load by approximately by 4% of GDP. Since 2015 the Dominican Republic has posted the fastest economic growth in Latin America.
$161.9 billion (2016 est.)
$149.9 billion (2015 est.)
$138.5 billion (2014 est.)
note: data are in 2016 dollars
country comparison to the world: 74
$71.67 billion (2016 est.)
6.6% (2016 est.)
7% (2015 est.)
7.6% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
$16,100 (2016 est.)
$15,200 (2015 est.)
$14,400 (2014 est.)
note: data are in 2016 dollars
country comparison to the world: 103
household consumption: 69.7%
government consumption: 11%
investment in fixed capital: 22.4%
investment in inventories: 0.6%
exports of goods and services: 25.2%
imports of goods and services: -28.9% (2016 est.)
agriculture: 5.5%
industry: 33.4%
services: 61.1% (2016 est.)
cocoa, tobacco, sugarcane, coffee, cotton, rice, beans, potatoes, corn, bananas; cattle, pigs, dairy products, beef, eggs
tourism, sugar processing, gold mining, textiles, cement, tobacco, electrical components, medical devices
7.3% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
4.639 million (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
agriculture: 14.4%
industry: 20.8%
services: 64.7% (2014)
5.5% (2016 est.)
14% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
30.5% (2016 est.)
lowest 10%: 1.9%
highest 10%: 37.4% (2013 est.)
47.1 (2013 est.)
45.7 (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
revenues: $10.59 billion
expenditures: $12.63 billion (2016 est.)
14.7% of GDP (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 193
-2.8% of GDP (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
47.4% of GDP (2016 est.)
44.7% of GDP (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
calendar year
1.6% (2016 est.)
0.8% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
15.08% (31 December 2016 est.)
14.88% (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 42
$6.491 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$5.986 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
$19.81 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$18.43 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
$33.6 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$30.9 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 74
$NA
$-1.066 billion (2016 est.)
$-1.299 billion (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
$9.86 billion (2016 est.)
$9.442 billion (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
gold, silver, cocoa, sugar, coffee, tobacco, meats, consumer goods
US 47.3%, Haiti 12%, Canada 7.8%, India 6.2% (2016)
$17.48 billion (2016 est.)
$16.91 billion (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
petroleum, foodstuffs, cotton and fabrics, chemicals and pharmaceuticals
US 40.4%, China 12.5%, Mexico 5.2% (2016)
$6.134 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$5.266 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
$27.7 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$26.63 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
$33.56 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$31.04 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
$387.8 million (31 December 2016 est.)
$272 million (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
Dominican pesos (DOP) per US dollar -
46.078 (2016 est.)
46.078 (2015 est.)
45.052 (2014 est.)
43.556 (2013 est.)
39.34 (2012 est.)
Energy :: DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
-
population without electricity: 300,000
electrification - total population: 98%
electrification - urban areas: 99%
electrification - rural areas: 97% (2013)
15.53 billion kWh (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
13.25 billion kWh (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
0 kWh (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
0 kWh (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144
3.732 million kW (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
80.8% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
0% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
16.1% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
5.7% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
0 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 128
0 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
27,440 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
0 bbl (1 January 2017 es)
country comparison to the world: 128
27,060 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
114,000 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
0 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
84,370 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
1.895 billion cu m (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
1.108 billion cu m (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
0 cu m (1 January 2014 es)
country comparison to the world: 134
22 million Mt (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
Communications :: DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
-
total subscriptions: 1,345,091
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 13 (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
total: 8,708,131
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 82 (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
general assessment: relatively efficient system based on island-wide microwave radio relay network
domestic: fixed-line teledensity is about 13 per 100 persons; multiple providers of mobile-cellular service with a subscribership of over 80 per 100 persons
international: country code - 1-809; 1-829; 1-849; landing point for the Americas Region Caribbean Ring System (ARCOS-1), Antillas 1, AMX-1, and the Fibralink submarine cables that provide links to South and Central America, parts of the Caribbean, and US; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2016)
combination of state-owned and privately owned broadcast media; 1 state-owned TV network and a number of private TV networks; networks operate repeaters to extend signals throughout country; combination of state-owned and privately owned radio stations with more than 300 radio stations operating (2015)
.do
total: 6,504,998
percent of population: 61.3% (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 69
Transportation :: DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
-
number of registered air carriers: 1
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 6
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 14,463
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 0 mt-km (2015)
HI (2016)
36 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 110
total: 16
over 3,047 m: 3
2,438 to 3,047 m: 4
1,524 to 2,437 m: 4
914 to 1,523 m: 4
under 914 m: 1 (2017)
total: 20
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 1
under 914 m: 18 (2013)
1 (2013)
gas 27 km; oil 103 km (2013)
total: 496 km
standard gauge: 354 km 1.435-m gauge
narrow gauge: 142 km 0.762-m gauge (2014)
country comparison to the world: 115
total: 19,705 km
paved: 9,872 km
unpaved: 9,833 km (2002)
country comparison to the world: 110
major seaport(s): Puerto Haina, Puerto Plata, Santo Domingo
oil terminal(s): Punta Nizao oil terminal
LNG terminal(s) (import): Andres LNG terminal (Boca Chica)
Military and Security :: DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
-
0.64% of GDP (2016)
0.67% of GDP (2015)
0.67% of GDP (2014)
0.62% of GDP (2013)
0.65% of GDP (2012)
country comparison to the world: 121
Army (Ejercito Nacional, EN), Navy (Marina de Guerra, MdG, includes naval infantry), Dominican Air Force (Fuerza Aerea Dominicana, FAD) (2017)
17-21 years of age for voluntary military service; recruits must have completed primary school and be Dominican Republic citizens; women may volunteer (2012)
Transnational Issues :: DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
-
Haitian migrants cross the porous border into the Dominican Republic to find work; illegal migrants from the Dominican Republic cross the Mona Passage each year to Puerto Rico to find better work
stateless persons: 133,770 (2016); note - a September 2013 Constitutional Court ruling revoked the citizenship of those born after 1929 to immigrants without proper documentation, even though the constitution at the time automatically granted citizenship to children born in the Dominican Republic and the 2010 constitution provides that constitutional provisions cannot be applied retroactively; the decision overwhelmingly affected people of Haitian descent whose relatives had come to the Dominican Republic since the 1890s as a cheap source of labor for sugar plantations; a May 2014 law passed by the Dominican Congress regularizes the status of those with birth certificates but will require those without them to prove they were born in the Dominican Republic and to apply for naturalization; the government has issued documents to thousands of individuals who may claim citizenship under this law, but no official estimate has been released
note: revised estimate includes only individuals born to parents who were both born abroad; it does not include individuals born in the country to one Dominican-born and one foreign-born parent or subsequent generations of individuals of foreign descent; the estimate, as such, does not include all stateless persons (2015)
transshipment point for South American drugs destined for the US and Europe; has become a transshipment point for ecstasy from the Netherlands and Belgium destined for US and Canada; substantial money laundering activity in particular by Colombian narcotics traffickers; significant amphetamine consumption