Introduction :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
An independent kingdom for much of its long history, Korea was occupied by Japan beginning in 1905 following the Russo-Japanese War. In 1910, Tokyo formally annexed the entire Peninsula. Korea regained its independence following Japan's surrender to the US in 1945. After World War II, a democratic-based government (Republic of Korea, ROK) was set up in the southern half of the Korean Peninsula while a communist-style government was installed in the north (Democratic People's Republic of Korea, DPRK). During the Korean War (1950-53), US troops and UN forces fought alongside ROK soldiers to defend South Korea from a DPRK invasion supported by China and the Soviet Union. A 1953 armistice split the Peninsula along a demilitarized zone at about the 38th parallel. PARK Chung-hee took over leadership of the country in a 1961 coup. During his regime, from 1961 to 1979, South Korea achieved rapid economic growth, with per capita income rising to roughly 17 times the level of North Korea.
South Korea held its first free presidential election under a revised democratic constitution in 1987, with former ROK Army general ROH Tae-woo winning a close race. In 1993, KIM Young-sam (1993-98) became the first civilian president of South Korea's new democratic era. President KIM Dae-jung (1998-2003) won the Nobel Peace Prize in 2000 for his contributions to South Korean democracy and his "Sunshine" policy of engagement with North Korea. President PARK Geun-hye, daughter of former ROK President PARK Chung-hee, took office in February 2013 as South Korea's first female leader. In December 2016, the National Assembly passed an impeachment motion against President PARK over her alleged involvement in a corruption and influence-peddling scandal, immediately suspending her presidential authorities. The impeachment was upheld in March 2017, triggering an early presidential election in May 2017 won by MOON Jae-in. South Korea will host the Winter Olympic Games in February 2018. Discord with North Korea has permeated inter-Korean relations for much of the past decade, highlighted by the North's attacks on a South Korean ship and island in 2010, the exchange of artillery fire across the DMZ in 2015, and multiple nuclear and missile tests in 2016 and 2017.
Geography :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
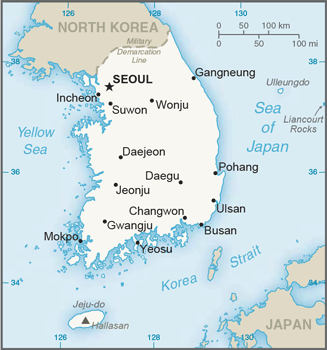
Eastern Asia, southern half of the Korean Peninsula bordering the Sea of Japan and the Yellow Sea
37 00 N, 127 30 E
Asia
total: 99,720 sq km
land: 96,920 sq km
water: 2,800 sq km
country comparison to the world: 110
slightly smaller than Pennsylvania; slightly larger than Indiana
Area comparison map:

East & Southeast Asia
::KOREA, SOUTH

Area Comparison
slightly smaller than Pennsylvania; slightly larger than Indiana
total: 237 km
border countries (1): North Korea 237 km
2,413 km
territorial sea: 12 nm; between 3 nm and 12 nm in the Korea Strait
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: not specified
temperate, with rainfall heavier in summer than winter; cold winters
mostly hills and mountains; wide coastal plains in west and south
mean elevation: 282 m
elevation extremes: lowest point: Sea of Japan 0 m
highest point: Halla-san 1,950 m
coal, tungsten, graphite, molybdenum, lead, hydropower potential
agricultural land: 18.1%
arable land 15.3%; permanent crops 2.2%; permanent pasture 0.6%
forest: 63.9%
other: 18% (2011 est.)
7,780 sq km (2012)
with approximately 70% of the country considered mountainous, the country's population is primarily concentrated in the lowland areas, where density is quite high; Gyeonggi Province in the northwest, which surrounds the capital of Seoul and contains the port of Incheon, is the most densely populated province; Gangwon in the northeast is the least populated
occasional typhoons bring high winds and floods; low-level seismic activity common in southwest
volcanism: Halla (1,950 m) is considered historically active although it has not erupted in many centuries
air pollution in large cities; acid rain; water pollution from the discharge of sewage and industrial effluents; drift net fishing
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
strategic location on Korea Strait; about 3,000 mostly small and uninhabited islands lie off the western and southern coasts
People and Society :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
51,181,299 (July 2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
noun: Korean(s)
adjective: Korean
homogeneous
Korean, English (widely taught in junior high and high school)
Protestant 19.7%, Buddhist 15.5%, Catholic 7.9%, none 56.9%
note: many people practice Confucianism, regardless of their religion or not having a religious affiliation (2015 est.)
0-14 years: 13.21% (male 3,484,398/female 3,276,984)
15-24 years: 12.66% (male 3,415,998/female 3,065,144)
25-54 years: 45.52% (male 11,992,462/female 11,303,726)
55-64 years: 14.49% (male 3,660,888/female 3,756,947)
65 years and over: 14.12% (male 3,080,601/female 4,144,151) (2017 est.)
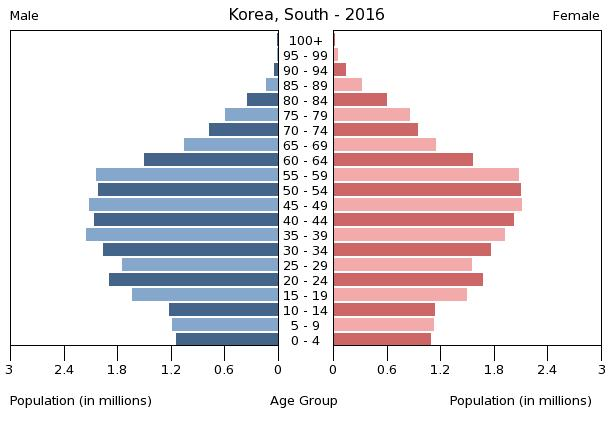
population pyramid:

East & Southeast Asia
::KOREA, SOUTH

Population Pyramid
A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.
total dependency ratio: 36.7
youth dependency ratio: 19
elderly dependency ratio: 17.7
potential support ratio: 5.6 (2015 est.)
total: 41.8 years
male: 40.2 years
female: 43.4 years (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
0.48% (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
8.3 births/1,000 population (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 220
6 deaths/1,000 population (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
2.5 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
with approximately 70% of the country considered mountainous, the country's population is primarily concentrated in the lowland areas, where density is quite high; Gyeonggi Province in the northwest, which surrounds the capital of Seoul and contains the port of Incheon, is the most densely populated province; Gangwon in the northeast is the least populated
urban population: 82.7% of total population (2017)
rate of urbanization: 0.55% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)
SEOUL (capital) 9.774 million; Busan (Pusan) 3.216 million; Incheon (Inch'on) 2.685 million; Daegu (Taegu) 2.244 million; Daejon (Taejon) 1.564 million; Gwangju (Kwangju) 1.536 million (2015)
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.12 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.71 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2016 est.)
31 years (2014 est.)
11 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
total: 3 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 3.2 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 2.8 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 215
total population: 82.5 years
male: 79.3 years
female: 85.8 years (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
1.26 children born/woman (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 219
80%
note: percent of women aged 15-44 (2009)
7.4% of GDP (2014)
country comparison to the world: 72
2.23 physicians/1,000 population (2014)
10.3 beds/1,000 population (2009)
improved:
urban: 99.7% of population
rural: 87.9% of population
total: 97.8% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0.3% of population
rural: 12.1% of population
total: 2.2% of population (2012 est.)
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2015 est.)
NA
NA
NA
4.7% (2016)
country comparison to the world: 184
0.7% (2010)
country comparison to the world: 135
4.6% of GDP (2012)
country comparison to the world: 75
total: 17 years
male: 17 years
female: 16 years (2013)
total: 10.7%
male: 11%
female: 10.5% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
Government :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
conventional long form: Republic of Korea
conventional short form: South Korea
local long form: Taehan-min'guk
local short form: Han'guk
abbreviation: ROK
etymology: derived from the Chinese name for Goryeo, which was the Korean dynasty that united the peninsula in the 10th century A.D.; the South Korean name "Han'guk" means "Land of the Han," where "han" may have its origins in the native root for "great [leader]" (similar to the title "khan")
presidential republic
name: Seoul; note - Sejong, located some 120 km (75 mi) south of Seoul, is being developed as a new capital
geographic coordinates: 37 33 N, 126 59 E
time difference: UTC+9 (14 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
9 provinces (do, singular and plural), 6 metropolitan cities (gwangyeoksi, singular and plural), 1 special city (teugbyeolsi), and 1 special self-governing city (teukbyeoljachisi)
provinces: Chungbuk (North Chungcheong), Chungnam (South Chungcheong), Gangwon, Gyeongbuk (North Gyeongsang), Gyeonggi, Gyeongnam (South Gyeongsang), Jeju, Jeonbuk (North Jeolla), Jeonnam (South Jeolla)
metropolitan cities: Busan (Pusan), Daegu (Taegu), Daejeon (Taejon), Gwangju (Kwangju), Incheon (Inch'on), Ulsan
special city: Seoul
special self-governing city: Sejong
15 August 1945 (from Japan)
Liberation Day, 15 August (1945)
effective 17 July 1948; amended many times, last in 1987 (2017)
mixed legal system combining European civil law, Anglo-American law, and Chinese classical thought
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of South Korea
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
19 years of age; universal
chief of state: President MOON Jae-in (since 10 May 2017); note - President PARK Geun-hye (since 25 February 2013) was impeached by the National Assembly on 9 December 2016; PARK's impeachment was upheld by the Constitutional Court and she was removed from office on 9 March 2017
head of government: Prime Minister LEE Nak-yon (since 1 June 2017); Deputy Prime Ministers KIM Dong-yeon (since 9 June 2017), KIM Sang-kon (since 4 July 2017)
cabinet: State Council appointed by the president on the prime minister's recommendation
elections/appointments: president directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a single 5-year term; election last held on 9 May 2017 (next to be held in 2022); prime minister appointed by president with consent of National Assembly
election results: MOON Jae-in elected president; percent of vote - MOON Jae-in (DP) 41.1%, HONG Joon-pyo (LKP) 25.5%, AHN Cheol-soo (PP) 21.4%, other 12.0%
description: unicameral National Assembly or Kuk Hoe (300 seats; 246 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 54 directly elected in a single national constituency by proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)
elections: last held on 13 April 2016 (next to be held in 2020)
election results: percent of vote by party - NFP 33.5%, PP 26.7%, MPK 25.5%, JP 7.2%, other 7.1%; seats by party - MPK 123, NFP 122, PP 38, JP 6, independent 11
note: as of January 2018, seats by party - DP 121, LKP 118, PP 39, BP 9, JP 6, MP 1, Patriotic Party 1, independent 2, vacant 3
highest court(s): Supreme Court of South Korea (consists of a chief justice and 13 justices); Constitutional Court (consists of a court head and 8 justices)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the president with the consent of the National Assembly; other justices appointed by the president upon the recommendation of the chief justice and consent of the National Assembly; position of the chief justice is a 6-year non-renewable term; other justices serve 6-year renewable terms; Constitutional Court justices appointed - 3 by the president, 3 by the National Assembly, and 3 by the Supreme Court chief justice; court head serves until retirement at age 70, while other justices serve 6-year renewable terms with mandatory retirement at age 65
subordinate courts: High Courts; District Courts; Branch Courts (organized under the District Courts); specialized courts for family and administrative issues
Bareun Party or BP [YOO Seong-min] (split from the NFP)
Democratic Party or DP [CHOO Mi-ae] (renamed from Minjoo Party of Korea or MPK in October 2016; formerly New Politics Alliance for Democracy or NPAD, which was a merger of the Democratic Party or DP (formerly DUP) [KIM Han-gil] and the New Political Vision Party or NPVP [AHN Cheol-soo] in March 2014)
Justice Party or JP [SIM Sang-jeong]
Liberty Korea Party or LKP [HONG Joon-pyo] (formerly the New Frontier Party (NFP) or Saenuri and before that the Grand National Party [HONG Joon-Pyo])
Minjung Party or MP (formed from the merger of the New People's Party (formerly the New People's Political Party or NPP) and the People's United Party or PUP)
Patriotic Party
People's Party or PP [AHN Cheol-soo]
Saenuri Party [CHUNG Kwang-Taek) (split from Liberty Korea Party in April 2017)
Christian Council of Korea
Citizen's Coalition for Economic Justice
Federation of Korean Trade Unions
Korea Women's Association United
Korea Women's Hotline
Korean Confederation of Trade Unions
Korean Veterans' Association
Lawyers for a Democratic Society
National Council of Churches in Korea
People's Solidarity for Participatory Democracy
ADB, AfDB (nonregional member), APEC, Arctic Council (observer), ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, CD, CICA, CP, EAS, EBRD, FAO, FATF, G-20, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAIA (observer), MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE (partner), Pacific Alliance (observer), Paris Club (associate), PCA, PIF (partner), SAARC (observer), SICA (observer), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNMOGIP, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
chief of mission: Ambassador CHO Yoon-je (since 29 November 2017)
chancery: 2450 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 939-5600
FAX: [1] (202) 797-0595
consulate(s) general: Agana (Guam), Anchorage (AK), Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Honolulu, Houston, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco, Seattle
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Marc KNAPPER (since 20 January 2017)
embassy: 188 Sejong-daero, Jongno-gu, Seoul 110-710
mailing address: US Embassy Seoul, Unit
telephone: [82] (2) 397-4114
FAX: [82] (2) 725-0152
white with a red (top) and blue yin-yang symbol in the center; there is a different black trigram from the ancient I Ching (Book of Changes) in each corner of the white field; the South Korean national flag is called Taegukki; white is a traditional Korean color and represents peace and purity; the blue section represents the negative cosmic forces of the yin, while the red symbolizes the opposite positive forces of the yang; each trigram (kwae) denotes one of the four universal elements, which together express the principle of movement and harmony
taegeuk (yin yang symbol), Hibiscus syriacus (Rose of Sharon); national colors: red, white, blue, black
name: "Aegukga" (Patriotic Song)
lyrics/music: YUN Ch'i-Ho or AN Ch'ang-Ho/AHN Eaktay
note: adopted 1948, well-known by 1910; both North Korea's and South Korea's anthems share the same name and have a vaguely similar melody but have different lyrics
Economy :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
After emerging from the 1950-53 war with North Korea, South Korea emerged as one of the 20th century’s most remarkable economic success stories, becoming a developed, globally connected, high-technology society within decades. In the 1960s, GDP per capita was comparable with levels in the poorest countries in the world. In 2004, South Korea joined the trillion-dollar club of world economies.
Beginning in the 1960s under President PARK Chung-hee, the government promoted the import of raw materials and technology, encouraged saving and investment over consumption, kept wages low, and directed resources to export-oriented industries that remain important to the economy to this day. Growth surged under these policies, and frequently reached double-digits in the 1960s and 1970s. Growth gradually moderated in the 1990s as the economy matured, but remained strong enough to propel South Korea into the ranks of the advanced economies of the OECD by 1997. These policies also led to the emergence of family-owned chaebol conglomerates such as Daewoo, Hyundai, and Samsung, which retained their dominant positions even as the government loosened its grip on the economy amid the political changes of the 1980s and 1990s.
The Asian financial crisis of 1997-98 hit South Korea’s companies hard because of their excessive reliance on short-term borrowing, and GDP ultimately plunged by 7% in 1998. South Korea tackled difficult economic reforms following the crisis, including restructuring some chaebols, increasing labor market flexibility, and opening up to more foreign investment and imports. These steps lead to a relatively rapid economic recovery. South Korea also began expanding its network of free trade agreements to help bolster exports, and has since implemented 16 free trade agreements covering 58 countries—including the United State and China—that collectively cover more than three-quarters of global GDP.
In 2017, the election of President MOON Jae-in brought a surge in consumer confidence, in part, because of his successful efforts to increase wages and government spending. These factors combined with an uptick in export growth to drive real GDP growth to more than 3%, despite disruptions in South Korea’s trade with China over the deployment of a US missile defense system in South Korea.
In 2018 and beyond, South Korea will contend with gradually slowing economic growth - in the 2-3% range - not uncommon for advanced economies. This could be partially offset by efforts to address challenges arising from its rapidly aging population, inflexible labor market, continued dominance of the chaebols, and heavy reliance on exports rather than domestic consumption. Socioeconomic problems also persist, and include rising inequality, poverty among the elderly, high youth unemployment, long working hours, low worker productivity, and corruption.
$2.027 trillion (2017 est.)
$1.967 trillion (2016 est.)
$1.913 trillion (2015 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 15
$1.53 trillion (2016 est.)
3% (2017 est.)
2.8% (2016 est.)
2.8% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
$39,400 (2017 est.)
$38,400 (2016 est.)
$37,500 (2015 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 48
37.2% of GDP (2017 est.)
36.2% of GDP (2016 est.)
36.6% of GDP (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
household consumption: 47.8%
government consumption: 15.2%
investment in fixed capital: 29.4%
investment in inventories: 0.3%
exports of goods and services: 43.9%
imports of goods and services: -36.7% (2017 est.)
agriculture: 2.2%
industry: 38.8%
services: 59.1% (2017 est.)
rice, root crops, barley, vegetables, fruit, cattle, pigs, chickens, milk, eggs, fish
electronics, telecommunications, automobile production, chemicals, shipbuilding, steel
3.5% (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
27.47 million (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
agriculture: 4.9%
industry: 24.1%
services: 71% (2016 est.)
3.8% (2017 est.)
3.7% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
12.5% (2015 est.)
lowest 10%: 6.8%
highest 10%: 48.5% (2015 est.)
34.1 (2015 est.)
34.1 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
revenues: $351.6 billion
expenditures: $338 billion (2017 est.)
23% of GDP (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
0.9% of GDP (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
43.3% of GDP (2017 est.)
45.6% of GDP (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
calendar year
1.9% (2017 est.)
1% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
1.25% (31 December 2016 est.)
1.5% (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
3.4% (31 December 2017 est.)
3.37% (31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
$742.5 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$658.7 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
$2.167 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)
$1.993 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
$2.683 trillion (31 December 2017 est.)
$2.515 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
$1.305 trillion (31 December 2016 est.)
$1.28 trillion (31 December 2015 est.)
$1.269 trillion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
$85.14 billion (2017 est.)
$98.68 billion (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
$552.3 billion (2017 est.)
$511.8 billion (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
semiconductors, petrochemicals, automobile/auto parts, ships, wireless communication equipment, flat displays, steel, electronics, plastics, computers
China 25.1%, US 13.5%, Vietnam 6.6%, Hong Kong 6.6%, Japan 4.9% (2016)
$448.4 billion (2017 est.)
$391.3 billion (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
crude oil/petroleum products, semiconductors, natural gas, coal, steel, computers, wireless communication equipment, automobiles, fine chemicals, textiles
China 21.4%, Japan 11.7%, US 10.7%, Germany 4.7% (2016)
$374.8 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$371.1 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
$376.9 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$358.2 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
$193.6 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$185 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
$342.4 billion (31 December 2017 est.)
$310.3 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
South Korean won (KRW) per US dollar -
1,136.7 (2017 est.)
1,160.77 (2016 est.)
1,160.77 (2015 est.)
1,130.95 (2014 est.)
1,052.96 (2013 est.)
Energy :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
electrification - total population: 100% (2016)
528.1 billion kWh (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
497 billion kWh (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
0 kWh (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
0 kWh (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
103 million kW (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
67.1% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
21.1% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
1.7% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 139
7.2% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 80
0 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
0 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
2.942 million bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
NA bbl (1 January 2017 es)
3.114 million bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
2.63 million bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
1.343 million bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
935,500 bbl/day (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
188 million cu m (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
69.63 billion cu m (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
0 cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
43.43 billion cu m (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
7.079 billion cu m (1 January 2017 es)
country comparison to the world: 88
599.3 million Mt (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
Communications :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
total subscriptions: 28,035,600
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 55 (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
total: 58.935 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 120 (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
general assessment: excellent domestic and international services featuring rapid incorporation of new technologies
domestic: fixed-line and mobile-cellular services widely available with the latter subscribership up to about 120 per 100 persons; rapid assimilation of a full range of telecommunications technologies leading to a boom in e-commerce
international: country code - 82; numerous submarine cables provide links throughout Asia, Australia, the Middle East, Europe, and US; satellite earth stations - 66 (2016)
multiple national TV networks with 2 of the 3 largest networks publicly operated; the largest privately owned network, Seoul Broadcasting Service (SBS), has ties with other commercial TV networks; cable and satellite TV subscription services available; publicly operated radio broadcast networks and many privately owned radio broadcasting networks, each with multiple affiliates, and independent local stations (2017)
.kr
total: 44.153 million
percent of population: 89.9% (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
Transportation :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
number of registered air carriers: 12
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 348
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 65,482,307
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 11.297 billion mt-km (2015)
HL (2016)
111 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 53
total: 71
over 3,047 m: 4
2,438 to 3,047 m: 19
1,524 to 2,437 m: 12
914 to 1,523 m: 13
under 914 m: 23 (2017)
total: 40
914 to 1,523 m: 2
under 914 m: 38 (2013)
466 (2013)
gas 2,216 km; oil 16 km; refined products 889 km (2013)
total: 3,874 km
standard gauge: 3,874 km 1.435-m gauge (2,727 km electrified) (2015)
country comparison to the world: 52
total: 99,025 km
paved: 91,195 km (includes 4,193 km of expressways)
unpaved: 7,830 km (2015)
country comparison to the world: 46
1,600 km (most navigable only by small craft) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 50
total: 1,907
by type: bulk carrier 100, container ship 89, general cargo 394, oil tanker 201, other 1,123 (2017)
country comparison to the world: 12
major seaport(s): Busan, Incheon, Gunsan, Kwangyang, Mokpo, Pohang, Ulsan, Yeosu
container port(s) (TEUs): Busan (19,469,000), Kwangyang (2,327,000), Incheon (2,368,000) (2015)
LNG terminal(s) (import): Incheon, Kwangyang, Pyeongtaek, Samcheok, Tongyeong, Yeosu
Military and Security :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
2.3% of GDP (2016)
2.3% of GDP (2015)
2.64% of GDP (2014)
2.63% of GDP (2013)
2.61% of GDP (2012)
country comparison to the world: 25
Republic of Korea Army, Navy (includes Marine Corps), Air Force (2011)
18-35 years of age for compulsory military service, with middle school education required; minimum conscript service obligation - 21 months (Army, Marines), 23 months (Navy), 24 months (Air Force); 18-26 years of age for voluntary military service; women, in service since 1950, admitted to 7 service branches, including infantry, but excluded from artillery, armor, anti-air, and chaplaincy corps; HIV-positive individuals are exempt from military service (2017)
Transnational Issues :: KOREA, SOUTH
-
Military Demarcation Line within the 4-km-wide Demilitarized Zone has separated North from South Korea since 1953; periodic incidents with North Korea in the Yellow Sea over the Northern Limit Line, which South Korea claims as a maritime boundary; South Korea and Japan claim Liancourt Rocks (Tok-do/Take-shima), occupied by South Korea since 1954
stateless persons: 197 (2016)