

Europe :: ALBANIA
Introduction :: ALBANIA
-
Albania declared its independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1912, but was conquered by Italy in 1939 and occupied by Germany in 1943. Communist partisans took over the country in 1944. Albania allied itself first with the USSR (until 1960), and then with China (to 1978). In the early 1990s, Albania ended 46 years of xenophobic communist rule and established a multiparty democracy. The transition has proven challenging as successive governments have tried to deal with high unemployment, widespread corruption, dilapidated infrastructure, powerful organized crime networks, and combative political opponents.Albania has made progress in its democratic development since first holding multiparty elections in 1991, but deficiencies remain. Most of Albania's post-communist elections were marred by claims of electoral fraud; however, international observers judged elections to be largely free and fair since the restoration of political stability following the collapse of pyramid schemes in 1997. Albania joined NATO in April 2009 and in June 2014 became a candidate for EU accession. Albania in November 2016 received a European Commission recommendation to open EU accession negotiations conditioned upon implementation of a judicial reform package passed earlier the same year. Although Albania's economy continues to grow, it has slowed, and the country is still one of the poorest in Europe. A large informal economy and a weak energy and transportation infrastructure remain obstacles.
Geography :: ALBANIA
-
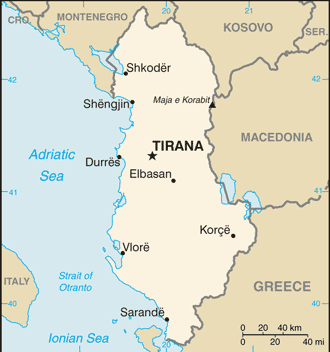
Southeastern Europe, bordering the Adriatic Sea and Ionian Sea, between Greece to the south and Montenegro and Kosovo to the north41 00 N, 20 00 EEuropetotal: 28,748 sq kmland: 27,398 sq kmwater: 1,350 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 145slightly smaller than Marylandtotal: 691 kmborder countries (4): Greece 212 km, Kosovo 112 km, Macedonia 181 km, Montenegro 186 km362 kmterritorial sea: 12 nmcontinental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitationmild temperate; cool, cloudy, wet winters; hot, clear, dry summers; interior is cooler and wettermostly mountains and hills; small plains along coastmean elevation: 708 melevation extremes: lowest point: Adriatic Sea 0 mhighest point: Maja e Korabit (Golem Korab) 2,764 mpetroleum, natural gas, coal, bauxite, chromite, copper, iron ore, nickel, salt, timber, hydropower, arable landagricultural land: 42.86%arable land 52.42%; permanent crops 6.84%; permanent pasture 40.73%forest: 28.19%other: 28.95% (2014 est.)3,537 sq km (2014)a fairly even distribution, with somewhat higher concentrations of people in the western and central parts of the countrydestructive earthquakes; tsunamis occur along southwestern coast; floods; droughtdeforestation; soil erosion; water pollution from industrial and domestic effluentsparty to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsstrategic location along Strait of Otranto (links Adriatic Sea to Ionian Sea and Mediterranean Sea)
People and Society :: ALBANIA
-
3,047,987 (July 2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 136noun: Albanian(s)adjective: AlbanianAlbanian 82.6%, Greek 0.9%, other 1% (including Vlach, Romani, Macedonian, Montenegrin, and Egyptian), unspecified 15.5% (2011 est.)Albanian 98.8% (official - derived from Tosk dialect), Greek 0.5%, other 0.6% (including Macedonian, Romani, Vlach, Turkish, Italian, and Serbo-Croatian), unspecified 0.1% (2011 est.)Muslim 56.7%, Roman Catholic 10%, Orthodox 6.8%, atheist 2.5%, Bektashi (a Sufi order) 2.1%, other 5.7%, unspecified 16.2%note: all mosques and churches were closed in 1967 and religious observances prohibited; in November 1990, Albania began allowing private religious practice (2011 est.)0-14 years: 18.05% (male 290,572/female 259,544)15-24 years: 17.47% (male 275,969/female 256,416)25-54 years: 41.06% (male 597,421/female 653,965)55-64 years: 11.54% (male 173,105/female 178,575)65 years and over: 11.89% (male 169,681/female 192,739) (2017 est.)total dependency ratio: 44youth dependency ratio: 26elderly dependency ratio: 18.1potential support ratio: 5.5 (2015 est.)total: 32.9 yearsmale: 31.6 yearsfemale: 34.3 years (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 960.31% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 17913.2 births/1,000 population (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 1496.8 deaths/1,000 population (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 136-3.3 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 180a fairly even distribution, with somewhat higher concentrations of people in the western and central parts of the countryurban population: 59.3% of total population (2017)rate of urbanization: 1.81% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)TIRANA (capital) 454,000 (2015)at birth: 1.1 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.12 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.07 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.91 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.98 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.89 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2016 est.)24.5 years (2014 est.)29 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 115total: 11.9 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 13.3 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 10.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 124total population: 78.5 yearsmale: 75.8 yearsfemale: 81.4 years (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 591.51 children born/woman (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 19569.3% (2008/09)5.9% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 1051.29 physicians/1,000 population (2013)2.6 beds/1,000 population (2012)improved:urban: 84.3% of populationrural: 81.8% of populationtotal: 83.6% of populationunimproved:urban: 15.7% of populationrural: 18.2% of populationtotal: 16.4% of population (2015 est.)improved:urban: 95.5% of populationrural: 90.2% of populationtotal: 93.2% of populationunimproved:urban: 4.5% of populationrural: 9.8% of populationtotal: 6.8% of population (2015 est.)0.1% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 991,700 (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 118<100 (2016 est.)21.7% (2016)country comparison to the world: 856.3% (2009)country comparison to the world: 803.5% of GDP (2013)country comparison to the world: 130definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 97.6%male: 98.4%female: 96.9% (2015 est.)total: 16 yearsmale: 15 yearsfemale: 16 years (2015)total: 39.8%male: 39.3%female: 40.8% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 46
Government :: ALBANIA
-
conventional long form: Republic of Albaniaconventional short form: Albanialocal long form: Republika e Shqiperiselocal short form: Shqiperiaformer: People's Socialist Republic of Albaniaetymology: the English-language country name seems to be derived from the ancient Illyrian tribe of the Albani; the native name "Shqiperia" is popularly interpreted to mean "Land of the Eagles"parliamentary republicname: Tirana (Tirane)geographic coordinates: 41 19 N, 19 49 Etime difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October12 counties (qarqe, singular - qark); Berat, Diber, Durres, Elbasan, Fier, Gjirokaster, Korce, Kukes, Lezhe, Shkoder, Tirane, Vlore28 November 1912 (from the Ottoman Empire)Independence Day, 28 November (1912) also known as Flag Dayhistory: several previous; latest approved by the Assembly 21 October 1998, adopted by referendum 22 November 1998, promulgated 28 November 1998amendments: proposed by at least one-fifth of the Assembly membership; passage requires at least a two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly; referendum required only if approved by two-thirds of the Assembly; amendments approved by referendum effective upon declaration by the president of the republic; amended several times, last in 2016 (2017)civil law system except in the northern rural areas where customary law known as the "Code of Leke" prevailshas not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictioncitizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Albaniadual citizenship recognized: yesresidency requirement for naturalization: 5 years18 years of age; universalchief of state: President of the Republic Ilir META (since 24 July 2017)head of government: Prime Minister Edi RAMA (since 10 September 2013); Deputy Prime Minister Niko PELESHIcabinet: Council of Ministers proposed by the prime minister, nominated by the president, and approved by the Assemblyelections/appointments: president indirectly elected by the Assembly for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); a candidate needs three-fifths majority vote of the Assembly in 1 of 3 rounds or a simple majority in 2 additional rounds to become president; election last held in 4 rounds on 19, 20, 27, and 28 April 2017 (next election to be held in 2022); prime minister appointed by the president on the proposal of the majority party or coalition of parties in the Assemblyelection results: Ilir META elected president; Assembly vote - 87 - 2 in fourth rounddescription: unicameral Assembly or Kuvendi (140 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote to serve 4-year terms)elections: last held on 25 June 2017 (next to be held in 2021)election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PS 74, PD 43, LSI 19, PDIU 3, PSD 1highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of 17 judges, including the chief justice); Constitutional Court (consists of 9 judges, including the chairman)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges, including the chairman, appointed by the president with the consent of the Assembly to serve single 9-year terms; Constitutional Court judges appointed by the president with the consent of the Assembly to serve single 9-year terms with one-third of the membership renewed every 3 years; chairman elected by the People's Assembly for a single 3-year termsubordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; Courts of First InstanceDemocratic Party or PD [Lulzim BASHA]Party for Justice, Integration and Unity or PDIU [Shpetim IDRIZI] (formerly part of APMI)Social Democratic Party or PSD [Skender GJINUSHI]Socialist Movement for Integration or LSI [Monika KRYEMADHI]Socialist Party or PS [Edi RAMA]Confederation of Trade Unions of Albania or KSSH [Kol NIKOLLAJ]Omonia [Leonidha PAPA]Union of Independent Trade Unions of Albania or BSPSH [Gezim KALAJA]BSEC, CD, CE, CEI, EAPC, EBRD, EITI (compliant country), FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NATO, OAS (observer), OIC, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, SELEC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTOchief of mission: Ambassador Floreta FABER (since 18 May 2015)chancery: 2100 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 223-4942FAX: [1] (202) 628-7342consulate(s) general: New Yorkchief of mission: Ambassador Donald LU (since 13 January 2015)embassy: Rruga e Elbasanit, 103, Tiranamailing address: US Department of State, 9510 Tirana Place, Dulles, VA 20189-9510telephone: [355] (4) 2247-285FAX: [355] (4) 2232-222red with a black two-headed eagle in the center; the design is claimed to be that of 15th-century hero George Kastrioti SKANDERBEG, who led a successful uprising against the Ottoman Turks that resulted in a short-lived independence for some Albanian regions (1443-78); an unsubstantiated explanation for the eagle symbol is the tradition that Albanians see themselves as descendants of the eagle; they refer to themselves as "Shqiptare," which translates as "sons of the eagle"double-headed eagle; national colors: red, blackname: "Hymni i Flamurit" (Hymn to the Flag)lyrics/music: Aleksander Stavre DRENOVA/Ciprian PORUMBESCUnote: adopted 1912
Economy :: ALBANIA
-
Albania, a formerly closed, centrally-planned state, is a developing country with a modern open-market economy. Albania managed to weather the first waves of the global financial crisis but, the negative effects of the crisis caused a significant economic slowdown. Since 2014, Albania’s economy has steadily improved and economic growth is projected to increase to 3.8% in 2017. However, close trade, remittance, and banking sector ties with Greece and Italy make Albania vulnerable to spillover effects of possible debt crises and weak growth in the euro zone.Remittances, a significant catalyst for economic growth, declined from 12-15% of GDP before the 2008 financial crisis to 5.8% of GDP in 2015, mostly from Albanians residing in Greece and Italy. The agricultural sector, which accounts for almost half of employment but only about one-fifth of GDP, is limited primarily to small family operations and subsistence farming, because of a lack of modern equipment, unclear property rights, and the prevalence of small, inefficient plots of land. Complex tax codes and licensing requirements, a weak judicial system, endemic corruption, poor enforcement of contracts and property issues, and antiquated infrastructure contribute to Albania's poor business environment making attracting foreign investment difficult. Since 2015, Albania has launched an ambitious program to increase tax compliance and bring more businesses into the formal economy. In July 2016, Albania passed constitutional amendments reforming the judicial system in order to strengthen the rule of law and to reduce deeply entrenched corruption.Albania’s electricity supply is uneven despite upgraded transmission capacities with neighboring countries. However, the government has recently taken steps to stem non-technical losses and has begun to upgrade the distribution grid. Better enforcement of electricity contracts has improved the financial viability of the sector, decreasing its reliance on budget support. Also, with help from international donors, the government is taking steps to improve the poor road and rail networks, a long standing barrier to sustained economic growth.Inward FDI has increased significantly in recent years as the government has embarked on an ambitious program to improve the business climate through fiscal and legislative reforms. The government is focused on the simplification of licensing requirements and tax codes, and it entered into a new arrangement with the IMF for additional financial and technical support. Albania’s three-year IMF program, an extended fund facility arrangement, was successfully concluded in February 2017. Albania’s 2017 budget aims to reach a small primary surplus, which the Albanian Government plans to achieve by strengthening tax collection amid moderate public wage and pension increases. The country continues to face high public debt, exceeding its former statutory limit of 60% of GDP in 2013 and reaching 71% in 2016.$34 billion (2016 est.)$32.48 billion (2015 est.)$31.43 billion (2014 est.)note: data are in 2016 dollarsunreported output may be as large as 50% of official GDPcountry comparison to the world: 124$11.87 billion (2016 est.)3.4% (2016 est.)2.2% (2015 est.)1.8% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 82$11,800 (2016 est.)$11,400 (2015 est.)$11,100 (2014 est.)note: data are in 2016 dollarscountry comparison to the world: 12715.9% of GDP (2016 est.)16.3% of GDP (2015 est.)16% of GDP (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 112household consumption: 78.8%government consumption: 11%investment in fixed capital: 27.1%investment in inventories: 0%exports of goods and services: 28.7%imports of goods and services: -45.6% (2016 est.)agriculture: 23%industry: 23.8%services: 53.2%(2016 est.)wheat, corn, potatoes, vegetables, fruits, olives and olive oil, grapes; meat, dairy products; sheep and goatsfood; footwear, apparel and clothing; lumber, oil, cement, chemicals, mining, basic metals, hydropower3.2% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 771.358 million (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 134agriculture: 41.8%industry: 11.4%services: 46.8% (December 2014 est)15.2% (2016 est.)13.3% (2015 est.)note: these official rates may not include those working at near-subsistence farmingcountry comparison to the world: 13314.3% (2012 est.)lowest 10%: 4.1%highest 10%: 19.6% (2015 est.)29 (2012 est.)30 (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 131revenues: $3.279 billionexpenditures: $3.494 billion (2016 est.)27% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 103-1.8% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 8572% of GDP (2016 est.)72.6% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 47calendar year1.3% (2016 est.)1.9% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 991.25% (31 December 2016)1.75% (31 December 2015)country comparison to the world: 1249.65% (31 December 2016 est.)8.73% (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 85$3.397 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$3.054 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 113$5.75 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$5.747 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 122$7.065 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$7.178 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 117$NA$-899 million (2016 est.)$-1.222 billion (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 131$789.1 million (2016 est.)$854.7 million (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 163apparel and clothing, footwear; asphalt, metals and metallic ores, crude oil; cement and construction materials, vegetables, fruits, tobaccoItaly 50.5%, Serbia 8.1%, Kosovo 7.5%, Greece 4.2% (2016)$3.671 billion (2016 est.)$3.402 billion (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 131machinery and equipment, foodstuffs, textiles, chemicalsItaly 29%, Germany 9.4%, China 8.7%, Greece 7.8%, Turkey 7.8%, Serbia 4.1% (2016)$3.109 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$3.139 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 104$8.421 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$8.269 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 116$6.056 billion (31 December 2014)$5.459 billion (31 December 2013)country comparison to the world: 101leke (ALL) per US dollar -124.14 (2016 est.)124.14 (2015 est.)125.96 (2014 est.)105.48 (2013 est.)108.19 (2012 est.)
Energy :: ALBANIA
-
electrification - total population: 100% (2016)7.135 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1137.094 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1101.869 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 451.827 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 561.897 million kW (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1155.2% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 2050% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 3994.8% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 70.1% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 16322,750 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 6619,100 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 521,000 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 80168.3 million bbl (1 January 2017 es)country comparison to the world: 61290 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 10827,000 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 12516,250 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 7513,250 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 13535 million cu m (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 87200 million cu m (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1100 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 600 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 83821.2 million cu m (1 January 2017 es)country comparison to the world: 1064.3 million Mt (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 130
Communications :: ALBANIA
-
total subscriptions: 245,336subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 8 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 123total: 3,369,756subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 111 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 133general assessment: fixed line, teledensity continues to decline due to heavy use of mobile-cellular telephone services; mobile-cellular telephone use is widespread and generally effective; of 3.4 million active mobile telephone users, 1.3 million use mobile broadband services (3G/4G)domestic: offsetting the shortage of fixed-line capacity, mobile-cellular phone service has been available since 1996; by 2015, four companies were providing mobile services and mobile teledensity had reached 110 per 100 persons; Internet broadband services initiated in 2005, and the penetration rate rose to over 65% by 2016; Internet cafes are popular in major urban areasinternational: country code - 355; submarine cable provides connectivity to Italy, Croatia, and Greece; the Trans-Balkan Line, a combination submarine cable and land fiber-optic system, provides additional connectivity to Bulgaria, Macedonia, and Turkey; international traffic carried by fiber-optic cable and, when necessary, by microwave radio relay from the Tirana exchange to Italy and Greece (2016)Albania has more than 65 TV stations, including several that broadcast nationally; Albanian TV broadcasts are also available to Albanian-speaking populations in neighboring countries; many viewers have access to Italian and Greek TV broadcasts via terrestrial reception; Albania's TV stations have begun a government-mandated conversion from analog to digital broadcast; the government has pledged to provide analog-to-digital converters to low-income families affected by this decision; cable TV service is available; 2 public radio networks and roughly 78 private radio stations; several international broadcasters are available (2017).altotal: 2,016,516percent of population: 66.4% (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 104
Transportation :: ALBANIA
-
number of registered air carriers: 1inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 1annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 151,632annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 0 mt-km (2015)ZA (2016)4 (2016)country comparison to the world: 183total: 42,438 to 3,047 m: 31,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2017)total: 1914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2012)1 (2013)gas 498 km (a majority of the network is in disrepair and parts of it are missing); oil 249 km (2015)total: 677 km (447 km of major railway lines and 230 km of secondary lines)standard gauge: 677 km 1.435-m gauge (2015)country comparison to the world: 104total: 18,000 kmpaved: 7,020 kmunpaved: 10,980 km (2002)country comparison to the world: 11641 km (on the Bojana River) (2011)country comparison to the world: 103total: 17by type: cargo 16, roll on/roll off 1foreign-owned: 1 (Turkey 1)registered in other countries: 5 (Antigua and Barbuda 1, Panama 4) (2010)country comparison to the world: 99major seaport(s): Durres, Sarande, Shengjin, Vlore
Military and Security :: ALBANIA
-
1.23% of GDP (2016)1.16% of GDP (2015)1.35% of GDP (2014)1.41% of GDP (2013)1.49% of GDP (2012)country comparison to the world: 112Land Forces Command, Navy Force Command, Air Forces Command (2013)19 is the legal minimum age for voluntary military service; 18 is the legal minimum age in case of general/partial compulsory mobilization (2012)
Transnational Issues :: ALBANIA
-
nonestateless persons: 4,921 (2016)active transshipment point for Southwest Asian opiates, hashish, and cannabis transiting the Balkan route and - to a lesser extent - cocaine from South America destined for Western Europe; significant source country for cannabis production; ethnic Albanian narcotrafficking organizations active and expanding in Europe; vulnerable to money laundering associated with regional trafficking in narcotics, arms, contraband, and illegal aliens
