

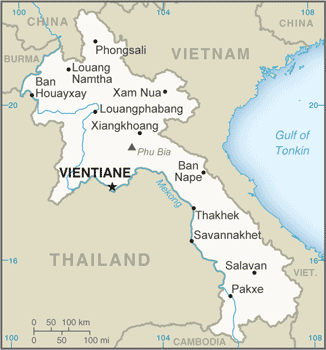
East & Southeast Asia :: LAOS
Introduction :: LAOS
-
Modern-day Laos has its roots in the ancient Lao kingdom of Lan Xang, established in the 14th century under King FA NGUM. For 300 years Lan Xang had influence reaching into present-day Cambodia and Thailand, as well as over all of what is now Laos. After centuries of gradual decline, Laos came under the domination of Siam (Thailand) from the late 18th century until the late 19th century, when it became part of French Indochina. The Franco-Siamese Treaty of 1907 defined the current Lao border with Thailand. In 1975, the communist Pathet Lao took control of the government, ending a six-century-old monarchy and instituting a strict socialist regime closely aligned to Vietnam. A gradual, limited return to private enterprise and the liberalization of foreign investment laws began in 1988. Laos became a member of ASEAN in 1997 and the WTO in 2013.
Geography :: LAOS
-
Southeastern Asia, northeast of Thailand, west of Vietnam18 00 N, 105 00 ESoutheast Asiatotal: 236,800 sq kmland: 230,800 sq kmwater: 6,000 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 85about twice the size of Pennsylvania; slightly larger than Utahtotal: 5,274 kmborder countries (5): Burma 238 km, Cambodia 555 km, China 475 km, Thailand 1,845 km, Vietnam 2,161 km0 km (landlocked)none (landlocked)tropical monsoon; rainy season (May to November); dry season (December to April)mostly rugged mountains; some plains and plateausmean elevation: 710 melevation extremes: lowest point: Mekong River 70 mhighest point: Phu Bia 2,817 mtimber, hydropower, gypsum, tin, gold, gemstonesagricultural land: 10.6%arable land 6.2%; permanent crops 0.7%; permanent pasture 3.7%forest: 67.9%other: 21.5% (2011 est.)3,100 sq km (2012)most densely populated area is in and around the capital city of Vientiane; large communities are primarily found along the Mekong River along the southwestern border; overall density is considered one of the lowest in Southeast Asiafloods, droughtsunexploded ordnance; deforestation; soil erosion; most of the population does not have access to potable waterparty to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protectionsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementslandlocked; most of the country is mountainous and thickly forested; the Mekong River forms a large part of the western boundary with Thailand
People and Society :: LAOS
-
7,126,706 (July 2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 101noun: Lao(s) or Laotian(s)adjective: Lao or LaotianLao 53.2%, Khmou 11%, Hmong 9.2%, Phouthay 3.4%, Tai 3.1%, Makong 2.5%, Katong 2.2%, Lue 2%, Akha 1.8%, other 11.6%note: the Laos Government officially recognizes 49 ethnic groups, but the total number of ethnic groups is estimated to be well over 200 (2015 est.)Lao (official), French, English, various ethnic languagesBuddhist 64.7%, Christian 1.7%, none 31.4%, other/not stated 2.1% (2015 est.)0-14 years: 32.76% (male 1,180,227/female 1,154,550)15-24 years: 21.17% (male 749,312/female 759,677)25-54 years: 36.7% (male 1,290,768/female 1,324,390)55-64 years: 5.48% (male 190,627/female 199,673)65 years and over: 3.89% (male 125,682/female 151,800) (2017 est.)total dependency ratio: 60.2youth dependency ratio: 54elderly dependency ratio: 6.2potential support ratio: 16.1 (2015 est.)total: 23 yearsmale: 22.7 yearsfemale: 23.3 years (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 1721.51% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 7823.6 births/1,000 population (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 637.4 deaths/1,000 population (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 115-1.1 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 139most densely populated area is in and around the capital city of Vientiane; large communities are primarily found along the Mekong River along the southwestern border; overall density is considered one of the lowest in Southeast Asiaurban population: 40.7% of total population (2017)rate of urbanization: 4.13% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)VIENTIANE (capital) 997,000 (2015)at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.99 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.97 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.83 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2016 est.)197 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 52total: 49.9 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 55.2 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 44.4 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 30total population: 64.6 yearsmale: 62.6 yearsfemale: 66.7 years (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 1842.7 children born/woman (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 6749.8% (2011/12)1.9% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 1910.18 physicians/1,000 population (2012)1.5 beds/1,000 population (2012)improved:urban: 85.6% of populationrural: 69.4% of populationtotal: 75.7% of populationunimproved:urban: 14.4% of populationrural: 30.6% of populationtotal: 24.3% of population (2015 est.)improved:urban: 94.5% of populationrural: 56% of populationtotal: 70.9% of populationunimproved:urban: 5.5% of populationrural: 44% of populationtotal: 29.1% of population (2015 est.)0.3% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 8611,000 (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 94<500 (2016 est.)degree of risk: very highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria (2016)5.3% (2016)country comparison to the world: 18026.5% (2011)country comparison to the world: 223.3% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 147definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 79.9%male: 87.1%female: 72.8% (2015 est.)total: 11 yearsmale: 11 yearsfemale: 11 years (2015)
Government :: LAOS
-
conventional long form: Lao People's Democratic Republicconventional short form: Laoslocal long form: Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Laolocal short form: Mueang Lao (unofficial)etymology: name means "Land of the Lao [people]"communist statename: Vientiane (Viangchan)geographic coordinates: 17 58 N, 102 36 Etime difference: UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)17 provinces (khoueng, singular and plural) and 1 capital city* (nakhon luang, singular and plural); Attapu, Bokeo, Bolikhamxai, Champasak, Houaphan, Khammouan, Louangnamtha, Louangphabang, Oudomxai, Phongsali, Salavan, Savannakhet, Viangchan (Vientiane)*, Viangchan, Xaignabouli, Xaisomboun, Xekong, Xiangkhouang19 July 1949 (from France)Republic Day (National Day), 2 December (1975)previous 1947 (preindependence); latest promulgated 13-15 August 1991; amended 2003, 2015 (2016)civil law system similar in form to the French systemhas not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtcitizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Laosdual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 10 years18 years of age; universalchief of state: President BOUNNYANG Vorachit (since 20 April 2016); Vice President PHANKHAM Viphavan (since 20 April 2016)head of government: Prime Minister THONGLOUN Sisoulit (since 20 April 2016); Deputy Prime Ministers BOUNTHONG Chitmani, SONXAI Siphandon, SOMDI Douangdi (since 20 April 2016)cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president, approved by the National Assemblyelections/appointments: president and vice president indirectly elected by the National Assembly for a 5-year term (no term limits); election last held on 20 April 2016 (next to be held in 2021); prime minister nominated by the president, elected by the National Assembly for 5-year termelection results: BOUNNYANG Vorachit (LPRP) elected president; PHANKHAM Viphavan (LPRP) elected vice president; percent of National Assembly vote - NA; THONGLOUN Sisoulit (LPRP) elected prime minister; percent of National Assembly vote - NAdescription: unicameral National Assembly or Sapha Heng Xat (149 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by simple majority vote from candidate lists provided by the Lao People's Revolutionary Party; members serve 5-year terms)elections: last held on 20 March 2016 (next to be held in 2021)election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - LPRP 144, independent 5highest court(s): People's Supreme Court (consists of the court president and organized into criminal, civil, administrative, commercial, family, and juvenile chambers, each with a vice president and several judges)judge selection and term of office: president of People's Supreme Court appointed by National Assembly on recommendation of the president of the republic for a 5-year term; vice presidents of People's Supreme Court appointed by the president of the republic on recommendation of the National Assembly; appointment of chamber judges NA; tenure of court vice presidents and chamber judges NAsubordinate courts: appellate courts; provincial, municipal, district, and military courtsLao People's Revolutionary Party or LPRP [BOUNNYANG Vorachit]note: other parties proscribedInternational Labor OrganizationADB, ARF, ASEAN, CP, EAS, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO (subscriber), ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTOchief of mission: Ambassador MAI Xaignavong (since 3 August 2015)chancery: 2222 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 332-6416FAX: [1] (202) 332-4923consulate(s): New Yorkchief of mission: Ambassador Rena BITTER (since 2 November 2016)embassy: Thadeua Road, Kilometer 9, Ban Somvang Tai, Hatsayfong District, Vientianemailing address: American Embassy Vientiane, Unit 46222, APO AP 96546-6222telephone: [856] 21-48-7000FAX: [856] 21-48-7190three horizontal bands of red (top), blue (double width), and red with a large white disk centered in the blue band; the red bands recall the blood shed for liberation; the blue band represents the Mekong River and prosperity; the white disk symbolizes the full moon against the Mekong River, but also signifies the unity of the people under the Lao People's Revolutionary Party, as well as the country's bright futureelephant; national colors: red, white, bluename: "Pheng Xat Lao" (Hymn of the Lao People)lyrics/music: SISANA Sisane/THONGDY Sounthonevichitnote: music adopted 1945, lyrics adopted 1975; the anthem's lyrics were changed following the 1975 Communist revolution that overthrew the monarchy
Economy :: LAOS
-
The government of Laos, one of the few remaining one-party communist states, began decentralizing control and encouraging private enterprise in 1986. Economic growth averaged more than 6% per year in the period 1988-2008, and Laos' growth has more recently been amongst the fastest in Asia, averaging nearly 8% per year for most of the last decade. However, growth has declined over the past year and is expected to be about 6.8% in 2017, according to the IMF.Nevertheless, Laos remains a country with an underdeveloped infrastructure, particularly in rural areas. It has a basic, but improving, road system, and limited external and internal land-line telecommunications. Electricity is available to 83% of the population. Agriculture, dominated by rice cultivation in lowland areas, accounts for about 25% of GDP and 73% of total employment. Recently, the country has faced a persistent current account deficit, falling foreign currency reserves, and growing public debt, as slow recovery of the global economy, especially that of China, has driven down the prices of its mineral exports.Laos' economy is heavily dependent on capital-intensive natural resource exports. The economy has benefited from high-profile foreign direct investment in hydropower dams along the Mekong River, copper and gold mining, logging, and construction, although some projects in these industries have drawn criticism for their environmental impacts.Laos gained Normal Trade Relations status with the US in 2004 and applied for Generalized System of Preferences trade benefits in 2013 after being admitted to the World Trade Organization earlier in the year. Laos held the chairmanship of ASEAN in 2016. Laos is in the process of implementing a value-added tax system. The government appears committed to raising the country's profile among foreign investors and has developed special economic zones replete with generous tax incentives, but a limited labor pool, a small domestic market, and corruption remain impediments to investment. Laos also has ongoing problems with the business environment, including onerous registration requirements, a gap between legislation and implementation, and unclear or conflicting regulations.$45.25 billion (2016 est.)$41.75 billion (2015 est.)$38.5 billion (2014 est.)note: data are in 2016 dollarscountry comparison to the world: 114$15.77 billion (2016 est.)7% (2016 est.)7.3% (2015 est.)7.6% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 10$6,900 (2016 est.)$6,500 (2015 est.)$6,200 (2014 est.)note: data are in 2016 dollarscountry comparison to the world: 16514.8% of GDP (2016 est.)14.5% of GDP (2015 est.)19.9% of GDP (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 129household consumption: 62.9%government consumption: 13.2%investment in fixed capital: 33.1%investment in inventories: 4.9%exports of goods and services: 34.9%imports of goods and services: -49% (2016 est.)agriculture: 21.6%industry: 32.8%services: 38.9% (2016 est.)sweet potatoes, vegetables, corn, coffee, sugarcane, tobacco, cotton, tea, peanuts, rice; cassava (manioc, tapioca), water buffalo, pigs, cattle, poultrymining (copper, tin, gold, gypsum); timber, electric power, agricultural processing, rubber, construction, garments, cement, tourism8% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 183.521 million (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 101agriculture: 73.1%industry: 6.1%services: 20.6% (2012 est.)1.5% (2016 est.)1.4% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1022% (2013 est.)lowest 10%: 3.3%highest 10%: 30.3% (2008)36.7 (2008)34.6 (2002)country comparison to the world: 84revenues: $2.921 billionexpenditures: $3.824 billion (2016 est.)21.2% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 139-6.6% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 17967.3% of GDP (2016 est.)65.6% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 541 October - 30 September2% (2016 est.)1.3% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1074.3% (31 December 2010)4% (31 December 2009)country comparison to the world: 8418% (31 December 2016 est.)18.2% (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 23$1.243 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$1.192 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 148$8.197 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$7.341 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 111$8.381 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$7.288 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 112$1.012 billion (2012 est.)$576.8 million (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 106$-1.678 billion (2016 est.)$-2.265 billion (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 159$2.705 billion (2016 est.)$2.769 billion (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 127wood products, coffee, electricity, tin, copper, gold, cassavaThailand 40.1%, China 28.5%, Vietnam 13.7% (2016)$5.547 billion (2016 est.)$5.233 billion (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 117machinery and equipment, vehicles, fuel, consumer goodsThailand 64.6%, China 16.5%, Vietnam 9.4% (2016)$940.1 million (31 December 2016 est.)$1.058 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 126$12.9 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$11.65 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 105$15.14 billion (31 December 2012 est.)$12.44 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 87kips (LAK) per US dollar -8,129.1 (2016 est.)8,129.1 (2015 est.)8,147.9 (2014 est.)8,049 (2013 est.)8,007.3 (2012 est.)
Energy :: LAOS
-
population without electricity: 900,000electrification - total population: 87%electrification - urban areas: 97%electrification - rural areas: 82% (2013)11.46 billion kWh (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 954.239 billion kWh (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1268.469 billion kWh (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 262.05 billion kWh (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 554.541 million kW (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 811.1% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 2100% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 12598.2% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 50.7% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1460 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1570 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1500 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1470 bbl (1 January 2017 es)country comparison to the world: 1540 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1613,500 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1840 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1693,480 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1750 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1560 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 2000 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1340 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1460 cu m (1 January 2014 es)country comparison to the world: 158500,000 Mt (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 182
Communications :: LAOS
-
total subscriptions: 1,266,605subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 18 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 81total: 3.727 millionsubscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 54 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 122general assessment: service to public is generally improving; the government relies on a radiotelephone network to communicate with remote areasdomestic: mobile cellular network coverage including 3G is relatively widespread, although usage has slowed as the regulator imposed a strict policy on pricing and competition is effectively discouraged; network performance has suffered because of insufficient maintenance and upgradesinternational: country code - 856; satellite earth station - 1 Intersputnik (Indian Ocean region) and a second to be developed by China (2017)6 TV stations operating out of Vientiane - 3 government-operated and the others commercial; 17 provincial stations operating with nearly all programming relayed via satellite from the government-operated stations in Vientiane; Chinese and Vietnamese programming relayed via satellite from Lao National TV; broadcasts available from stations in Thailand and Vietnam in border areas; multi-channel satellite and cable TV systems provide access to a wide range of foreign stations; state-controlled radio with state-operated Lao National Radio (LNR) broadcasting on 5 frequencies - 1 AM, 1 SW, and 3 FM; LNR's AM and FM programs are relayed via satellite constituting a large part of the programming schedules of the provincial radio stations; Thai radio broadcasts available in border areas and transmissions of multiple international broadcasters are also accessible (2012).latotal: 1.258 millionpercent of population: 18.2% (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 142
Transportation :: LAOS
-
number of registered air carriers: 1inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 11annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 1,181,187annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 1,356,497 mt-km (2015)RDPL (2016)41 (2013)country comparison to the world: 103total: 82,438 to 3,047 m: 31,524 to 2,437 m: 4914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2017)total: 331,524 to 2,437 m: 2914 to 1,523 m: 9under 914 m: 22 (2013)refined products 540 km (2013)total: 39,586 kmpaved: 5,415 kmunpaved: 34,171 km (2009)country comparison to the world: 894,600 km (primarily on the Mekong River and its tributaries; 2,900 additional km are intermittently navigable by craft drawing less than 0.5 m) (2012)country comparison to the world: 23
Military and Security :: LAOS
-
0.2% of GDP (2013)0.22% of GDP (2012)0.23% of GDP (2011)Lao People's Armed Forces (LPAF): Lao People's Army (LPA, includes Riverine Force), Air Force (2011)18 years of age for compulsory or voluntary military service; conscript service obligation - minimum 18-months (2012)serving one of the world's least developed countries, the Lao People's Armed Forces (LPAF) is small, poorly funded, and ineffectively resourced; its mission focus is border and internal security, primarily in countering ethnic Hmong insurgent groups; together with the Lao People's Revolutionary Party and the government, the Lao People's Army (LPA) is the third pillar of state machinery, and as such is expected to suppress political and civil unrest and similar national emergencies; there is no perceived external threat to the state and the LPA maintains strong ties with the neighboring Vietnamese military (2012)
Transnational Issues :: LAOS
-
southeast Asian states have enhanced border surveillance to check the spread of avian flu; talks continue on completion of demarcation with Thailand but disputes remain over islands in the Mekong River; Cambodia and Laos have a longstanding border demarcation dispute; concern among Mekong River Commission members that China's construction of eight dams on the Upper Mekong River and construction of more dams on its tributaries will affect water levels, sediment flows, and fisheries; Cambodia and Vietnam are concerned about Laos' extensive plans for upstream dam construction for the same reasonscurrent situation: Laos is a source and, to a lesser extent, transit and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; Lao economic migrants may encounter conditions of forced labor or sexual exploitation in destination countries, most often Thailand; Lao women and girls are exploited in Thailand’s commercial sex trade, domestic service, factories, and agriculture; a small, possibly growing, number of Lao women and girls are sold as brides in China and South Korea and subsequently sex trafficked; Lao men and boys are victims of forced labor in the Thai fishing, construction, and agriculture industries; some Lao children, as well as Vietnamese and Chinese women and girls, are subjected to sex trafficking in Laos; other Vietnamese and Chinese, and possibly Burmese, adults and girls transit Laos for sexual and labor exploitation in neighboring countries, particularly Thailandtier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – Laos does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; authorities sustained moderate efforts to investigate, prosecute, and convict trafficking offenders; the government failed to make progress in proactively identifying victims exploited within the country or among those deported from abroad; the government continues to rely almost entirely on local and international organizations to provide and fund services to trafficking victims; although Lao men and boys are trafficked, most protective services are only available to women and girls, and long-term support is lacking; modest prevention efforts include the promotion of anti-trafficking awareness on state-controlled media (2015)estimated opium poppy cultivation in 2015 was estimated to be 5,700 hectares, compared with 6,200 hectares in 2014; estimated potential production of between 84 and 176 mt of raw opium; unsubstantiated reports of domestic methamphetamine production; growing domestic methamphetamine problem
