
Europe :: NORWAY
Introduction :: NORWAY
-
Two centuries of Viking raids into Europe tapered off following the adoption of Christianity by King Olav TRYGGVASON in 994; conversion of the Norwegian kingdom occurred over the next several decades. In 1397, Norway was absorbed into a union with Denmark that lasted more than four centuries. In 1814, Norwegians resisted the cession of their country to Sweden and adopted a new constitution. Sweden then invaded Norway but agreed to let Norway keep its constitution in return for accepting the union under a Swedish king. Rising nationalism throughout the 19th century led to a 1905 referendum granting Norway independence. Although Norway remained neutral in World War I, it suffered heavy losses to its shipping. Norway proclaimed its neutrality at the outset of World War II, but was nonetheless occupied for five years by Nazi Germany (1940-45). In 1949, Norway abandoned neutrality and became a member of NATO. Discovery of oil and gas in adjacent waters in the late 1960s boosted Norway's economic fortunes. In referenda held in 1972 and 1994, Norway rejected joining the EU. Key domestic issues include immigration and integration of ethnic minorities, maintaining the country's extensive social safety net with an aging population, and preserving economic competitiveness.
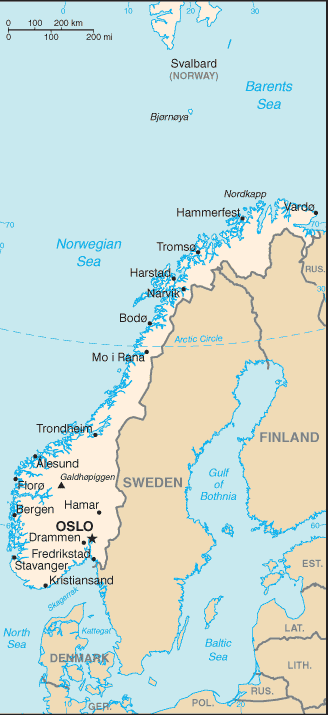
Geography :: NORWAY
-
Northern Europe, bordering the North Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, west of Sweden62 00 N, 10 00 EEuropetotal: 323,802 sq kmland: 304,282 sq kmwater: 19,520 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 69slightly larger than twice the size of Georgia; slightly larger than New Mexicototal: 2,566 kmborder countries (3): Finland 709 km, Sweden 1,666 km, Russia 191 km25,148 km (includes mainland 2,650 km, as well as long fjords, numerous small islands, and minor indentations 22,498 km; length of island coastlines 58,133 km)territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 10 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nmtemperate along coast, modified by North Atlantic Current; colder interior with increased precipitation and colder summers; rainy year-round on west coastglaciated; mostly high plateaus and rugged mountains broken by fertile valleys; small, scattered plains; coastline deeply indented by fjords; arctic tundra in northmean elevation: 460 melevation extremes: lowest point: Norwegian Sea 0 mhighest point: Galdhopiggen 2,469 mpetroleum, natural gas, iron ore, copper, lead, zinc, titanium, pyrites, nickel, fish, timber, hydropoweragricultural land: 2.7%arable land 2.2%; permanent crops 0%; permanent pasture 0.5%forest: 27.8%other: 69.5% (2011 est.)900 sq km (2012)most Norwegians live in the south where the climate is milder and there is better connectivity to mainland Europe; population clusters are found all along the North Sea coast in the southwest, and Skaggerak in the southeast; the interior areas of the north remain sparsely populatedrockslides, avalanchesvolcanism: Beerenberg (2,227 m) on Jan Mayen Island in the Norwegian Sea is the country's only active volcanowater pollution; acid rain damaging forests and adversely affecting lakes, threatening fish stocks; air pollution from vehicle emissionsparty to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsabout two-thirds mountains; some 50,000 islands off its much-indented coastline; strategic location adjacent to sea lanes and air routes in North Atlantic; one of the most rugged and longest coastlines in the world
People and Society :: NORWAY
-
5,320,045 (July 2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 120noun: Norwegian(s)adjective: NorwegianNorwegian 94.4% (includes about 60,000 Sami), other European 3.6%, other 2% (2007 est.)Bokmal Norwegian (official), Nynorsk Norwegian (official), small Sami- and Finnish-speaking minoritiesnote: Sami is an official language in nine municipalitiesChurch of Norway (Evangelical Lutheran - official) 82.1%, other Christian 3.9%, Muslim 2.3%, Roman Catholic 1.8%, other 2.4%, unspecified 7.5% (2011 est.)0-14 years: 18% (male 490,915/female 466,515)15-24 years: 12.58% (male 343,103/female 326,053)25-54 years: 41.01% (male 1,125,334/female 1,056,330)55-64 years: 11.71% (male 315,223/female 307,639)65 years and over: 16.71% (male 409,057/female 479,876) (2017 est.)total dependency ratio: 52.1youth dependency ratio: 27.3elderly dependency ratio: 24.8potential support ratio: 4note: data include Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands (2015 est.)total: 39.2 yearsmale: 38.4 yearsfemale: 40 years (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 551.01% (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 11412.2 births/1,000 population (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 1648.1 deaths/1,000 population (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 875.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 18most Norweigans live in the south where the climate is milder and there is better connectivity to mainland Europe; population clusters are found all along the North Sea coast in the southwest, and Skaggerak in the southeast; the interior areas of the north remain sparsely populatedurban population: 81% of total population (2017)rate of urbanization: 1.31% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)note: data include Svalbard and Jan Mayen IslandsOSLO (capital) 986,000 (2015)at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.06 male(s)/female55-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.84 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1.02 male(s)/female (2016 est.)28.9 yearsnote: data is calculated based on actual age at first births (2015 est.)5 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 174total: 2.5 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 2.8 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 2.2 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 221total population: 81.9 yearsmale: 79.8 yearsfemale: 84 years (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 181.85 children born/woman (2017 est.)country comparison to the world: 1459.7% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 274.42 physicians/1,000 population (2014)3.85 beds/1,000 population (2014)improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 100% of populationtotal: 100% of populationunimproved:urban: 0% of populationrural: 0% of populationtotal: 0% of population (2015 est.)improved:urban: 98% of populationrural: 98.3% of populationtotal: 98.1% of populationunimproved:urban: 2% of populationrural: 1.7% of populationtotal: 1.9% of population (2015 est.)NANANA23.1% (2016)country comparison to the world: 677.4% of GDP (2013)country comparison to the world: 21total: 18 yearsmale: 17 yearsfemale: 18 years (2015)total: 11.1%male: 13%female: 9.3% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 109
Government :: NORWAY
-
conventional long form: Kingdom of Norwayconventional short form: Norwaylocal long form: Kongeriket Norgelocal short form: Norgeetymology: derives from the Old Norse words "nordr" and "vegr" meaning "northern way" and refers to the long coastline of western Norwayparliamentary constitutional monarchyname: Oslogeographic coordinates: 59 55 N, 10 45 Etime difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October19 counties (fylker, singular - fylke); Akershus, Aust-Agder, Buskerud, Finnmark, Hedmark, Hordaland, More og Romsdal, Nordland, Nord-Trondelag, Oppland, Oslo, Ostfold, Rogaland, Sogn og Fjordane, Sor-Trondelag, Telemark, Troms, Vest-Agder, VestfoldBouvet Island, Jan Mayen, Svalbard7 June 1905 (declared the union with Sweden dissolved); 26 October 1905 (Sweden agreed to the repeal of the union)Constitution Day, 17 May (1814)history: drafted spring 1814, adopted 16 May 1814, signed by Constituent Assembly 17 May 1814amendments: proposals submitted by members of Parliament or by the government within the first three years of Parliament's four-year term; passage requires two-thirds majority vote of a two-thirds quorum in the next elected Parliament; amended over 400 times, last in 2015 (2016)mixed legal system of civil, common, and customary law; Supreme Court can advise on legislative actsaccepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdictioncitizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Norwaydual citizenship recognized: noresidency requirement for naturalization: 7 years18 years of age; universalchief of state: King HARALD V (since 17 January 1991); Heir Apparent Crown Prince HAAKON MAGNUS, son of the monarch (born 20 July 1973)head of government: Prime Minister Erna SOLBERG (since 16 October 2013)cabinet: State Council appointed by the monarch, approved by Parliamentelections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; following parliamentary elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the monarch with the approval of the parliamentdescription: unicameral Parliament or Storting (169 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)elections: last held on 11 September 2017 (next to be held in September 2021)election results: percent of vote by party - Ap 27.4%, H 25%, FrP 15.2%, SP 10.3%, SV 6%, V 4.4%, KrF 4.2%, MDG 3.2%, R 2.4%, other/invalid 1.9%; seats by party - Ap 49, H 45, FrP 27, SP 19, SV 11, V 8, KrF 8, MDG 1, R 1highest court(s): Supreme Court or Hoyesterett (consists of the chief justice and 18 associate justices)judge selection and term of office: justices appointed by the monarch (King in Council) upon the recommendation of the Judicial Appointments Board; justice retirement mandatory at age 70subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal or Lagmensrett; regional and district courts; Conciliation Boards; ordinary and special courts; note - in addition to professionally trained judges, elected lay judges sit on the bench with professional judges in the Courts of Appeal and district courtsCenter Party or Sp [Trygve Slagsvold VEDUM]Christian Democratic Party or KrF [Knut Arild HAREIDE]Conservative Party or H [Erna SOLBERG]Green Party or MDG [Rasmus HANSSON and Une Aina BASTHOLM]Labor Party or Ap [Jonas Gahr STORE]Liberal Party or V [Trine SKEI GRANDE]Progress Party or FrP [Siv JENSEN]Socialist Left Party or SV [Audun LYSBAKKEN]Confederation of Norwegian Enterprise or NHO [Tore ULSTEIN, Kristin SKOGEN LUND]Norwegian Confederation of Trade Unions or LO [Hans-Christian GABRIELSEN]other: environmental groups; media; digital privacy movementsADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EFTA, EITI (implementing country), ESA, FAO, FATF, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINUSMA, NATO, NC, NEA, NIB, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNITAR, UNMISS, UNRWA, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZCchief of mission: Ambassador Kare Reidar AAS (since 17 September 2013)chancery: 2720 34th Street NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 333-6000FAX: [1] (202) 459-3990consulate(s) general: Houston, New York, San Franciscochief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires James P. DEHART (since 12 January 2017)embassy: Morgedalsvegen 36, 0378 Oslo;mailing address: PSC 69, Box 1000, APO AE 09707telephone: [47] 21-30-85-40FAX: [47] 22-44-33-63, 22-56-27-51red with a blue cross outlined in white that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side in the style of the Dannebrog (Danish flag); the colors recall Norway's past political unions with Denmark (red and white) and Sweden (blue)lion; national colors: red, white, bluename: "Ja, vi elsker dette landet" (Yes, We Love This Country)lyrics/music: lyrics/music: Bjornstjerne BJORNSON/Rikard NORDRAAKnote: adopted 1864; in addition to the national anthem, "Kongesangen" (Song of the King), which uses the tune of "God Save the Queen," serves as the royal anthem
Economy :: NORWAY
-
Norway has a stable economy with a vibrant private sector, a large state sector, and an extensive social safety net. Norway opted out of the EU during a referendum in November 1994; nonetheless, as a member of the European Economic Area, it contributes sizably to the EU budget.The country is richly endowed with natural resources in addition to oil and gas, including hydropower, fish, forests, and minerals. Norway is a leading producer and the world’s second largest exporter of seafood, after China. The government manages the country’s petroleum resources through extensive regulation. The petroleum sector provides about 9% of jobs, 12% of GDP, 13% of the state’s revenue, and 37% of exports, according to official national estimates. Norway is one of the world's leading petroleum exporters, though oil production in 2016 was close to 50% below its peak in 2000; annual gas production, conversely, more than doubled over the same time period. After a continual decline from 2001 to 2013, oil production rose in 2016 for the third year running, due to the higher production of existing oil fields and to new fields coming on stream.In anticipation of eventual declines in oil and gas production, Norway saves state revenue from petroleum sector activities in the world's largest sovereign wealth fund, valued at almost $900 billion as of early 2017. To help balance the federal budget each year, the government follows a “fiscal rule,” which states that spending of revenues from petroleum and fund investments shall correspond to the expected real rate of return on the fund, an amount it estimates is sustainable over time. In February 2017, the government revised the expected rate of return for the fund downward from 4% to 3%.After solid GDP growth in the 2004-07 period, the economy slowed in 2008, and contracted in 2009, before returning to modest, positive growth from 2010 to 2016. Lower oil prices in 2015 and 2016 caused growth to slow, increased unemployment, and weakened the Norwegian krone. The latter trend has mitigated the negative impact of lower oil and gas prices by making Norwegian exports cheaper for foreign buyers. The government has expressed willingness to increase public spending from the sovereign wealth fund to help prevent a recession.$364.5 billion (2016 est.)$356.1 billion (2015 est.)$346.7 billion (2014 est.)note: data are in 2016 dollarscountry comparison to the world: 49$370.6 billion (2016 est.)1.1% (2016 est.)1.6% (2015 est.)1.9% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 173$69,400 (2016 est.)$69,300 (2015 est.)$68,800 (2014 est.)note: data are in 2016 dollarscountry comparison to the world: 1334.1% of GDP (2016 est.)36.9% of GDP (2015 est.)39.2% of GDP (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 18household consumption: 45.2%government consumption: 24.5%investment in fixed capital: 24%investment in inventories: 5.3%exports of goods and services: 34%imports of goods and services: -33% (2016 est.)agriculture: 2.5%industry: 31.7%services: 65.8% (2016 est.)barley, wheat, potatoes; pork, beef, veal, milk; fishpetroleum and gas, shipping, fishing, aquaculture, food processing, shipbuilding, pulp and paper products, metals, chemicals, timber, mining, textiles0.4% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1532.78 million (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 108agriculture: 2.1%industry: 19.3%services: 78.6% (2016 est.)4.7% (2016 est.)4.4% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 61NA%lowest 10%: 3.8%highest 10%: 21.2% (2014)26.8 (2010)25.8 (1995)country comparison to the world: 139revenues: $200.6 billionexpenditures: $189.4 billion (2016 est.)54.2% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 113% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1135.7% of GDP (2016 est.)32% of GDP (2015 est.)note: data cover general government debt, and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data exclude treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data exclude debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctionscountry comparison to the world: 144calendar year3.6% (2016 est.)2.2% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1546.25% (31 December 2010)1.75% (31 December 2009)country comparison to the world: 671.5% (31 December 2016 est.)1.75% (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 183$214 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$199.6 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 20$323.9 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$310 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 31$571.7 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$527.8 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 23$193.9 billion (31 December 2015 est.)$219.4 billion (31 December 2014 est.)$265.4 billion (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 34$18.43 billion (2016 est.)$33.75 billion (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 16$88.88 billion (2016 est.)$103.4 billion (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 37petroleum and petroleum products, machinery and equipment, metals, chemicals, ships, fishUK 21%, Germany 14.4%, Netherlands 10.7%, France 6.9%, Sweden 6.5%, Belgium 4.4%, US 4.3%, Denmark 4% (2016)$73.62 billion (2016 est.)$75.41 billion (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 39machinery and equipment, chemicals, metals, foodstuffsGermany 12.2%, Sweden 12.2%, China 11.2%, US 6.6%, Denmark 5.7%, UK 5.2%, Netherlands 4.1% (2016)$60.45 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$57.46 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 35$642.3 billion (31 March 2016 est.)$640.1 billion (31 March 2015 est.)note: Norway is a net external creditorcountry comparison to the world: 19$219.1 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$210.6 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 28$191.7 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$203 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 26Norwegian kroner (NOK) per US dollar -8.3978 (2016 est.)8.3978 (2015 est.)8.0646 (2014 est.)6.3021 (2013 est.)5.82 (2012 est.)
Energy :: NORWAY
-
electrification - total population: 100% (2016)149.5 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 28133.1 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 2815.53 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 135.7 billion kWh (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 3633.85 million kW (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 314.1% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 2070% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 15588.4% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 113.3% of total installed capacity (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1081.648 million bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 151.395 million bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1110,630 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 756.611 billion bbl (1 January 2017)country comparison to the world: 21282,400 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 42227,700 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 53353,100 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 22124,500 bbl/day (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 53117.2 billion cu m (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 89.428 billion cu m (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 55112 billion cu m (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 30 cu m (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1661.856 trillion cu m (1 January 2017 es)country comparison to the world: 1953.9 million Mt (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 58
Communications :: NORWAY
-
total subscriptions: 863,855subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 16 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 72total: 5,718,740subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 109 (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 111general assessment: modern in all respects; one of the most advanced telecommunications networks in Europedomestic: Norway has a domestic satellite system; the prevalence of rural areas encourages the wide use of mobile-cellular systemsinternational: country code - 47; 2 buried coaxial cable systems; submarine cables provide links to other Nordic countries and Europe; satellite earth stations - NA Eutelsat, NA Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean), and 1 Inmarsat (Atlantic and Indian Ocean regions); note - Norway shares the Inmarsat earth station with the other Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, and Sweden) (2016)state-owned public radio-TV broadcaster operates 3 nationwide TV stations, 3 nationwide radio stations, and 16 regional radio stations; roughly a dozen privately owned TV stations broadcast nationally and roughly another 25 local TV stations broadcasting; nearly 75% of households have access to multi-channel cable or satellite TV; 2 privately owned radio stations broadcast nationwide and another 240 stations operate locally; Norway is the first country in the world to phase out FM radio in favor of Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB), a process scheduled for completion in late 2017 (2017).nototal: 5,122,904percent of population: 97.3% (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 70
Transportation :: NORWAY
-
number of registered air carriers: 3inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 106annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 12,277,220annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 0 mt-km (2015)LN (2016)95 (2013)country comparison to the world: 61total: 672,438 to 3,047 m: 141,524 to 2,437 m: 10914 to 1,523 m: 22under 914 m: 21 (2017)total: 28914 to 1,523 m: 6under 914 m: 22 (2013)1 (2013)gas 8,520 km; oil/condensate 1,304 km (2017)total: 4,250 kmstandard gauge: 4,250 km 1.435-m gauge (2,518 km electrified) (2014)country comparison to the world: 41total: 93,870 km (includes 393 km of expressways)paved: 75,754 kmunpaved: 18,116 km (2013)country comparison to the world: 531,577 km (2010)country comparison to the world: 51total: 585by type: bulk carrier 55, cargo 105, carrier 5, chemical tanker 121, combination ore/oil 12, liquefied gas 47, passenger 3, passenger/cargo 121, petroleum tanker 54, refrigerated cargo 9, roll on/roll off 4, vehicle carrier 49foreign-owned: 81 (Bermuda 24, Canada 1, Cyprus 1, Denmark 7, France 5, Iceland 2, Lithuania 1, Saudi Arabia 3, Sweden 27, US 10)registered in other countries: 974 (Antigua and Barbuda 9, Bahamas 186, Barbados 38, Belize 2, Bermuda 5, Brazil 3, Canada 4, Chile 1, Comoros 1, Cook Islands 8, Croatia 2, Curacao 2, Cyprus 14, Denmark 2, Dominica 1, Equatorial Guinea 1, Estonia 2, Faroe Islands 13, Gibraltar 46, Hong Kong 48, Indonesia 3, Isle of Man 30, Italy 6, Liberia 38, Libya 1, Malta 96, Marshall Islands 75, Netherlands 19, Panama 81, Portugal 2, Saint Kitts and Nevis 3, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 13, Singapore 153, Spain 10, Sweden 3, UK 32, US 17, Vanuatu 1, unknown 3) (2010)country comparison to the world: 20major seaport(s): Bergen, Haugesund, Maaloy, Mongstad, Narvik, StureLNG terminal(s) (export): Kamoy, Kollsnes, Melkoya IslandLNG terminal(s) (import): Fredrikstad, Mosjoen
Military and Security :: NORWAY
-
1.62% of GDP (2016)1.5% of GDP (2015)1.47% of GDP (2014)1.41% of GDP (2013)1.4% of GDP (2012)country comparison to the world: 72Norwegian Army (Haeren), Royal Norwegian Navy (Kongelige Norske Sjoeforsvaret; includes Coastal Rangers and Coast Guard (Kystvakt)), Royal Norwegian Air Force (Kongelige Norske Luftforsvaret), Home Guard (Heimevernet, HV) (2017)19-35 years of age for male and female compulsory military service; 16 years of age in wartime; 17 years of age for male volunteers; 18 years of age for women; 19-month service obligation (2017)
Transnational Issues :: NORWAY
-
Norway asserts a territorial claim in Antarctica (Queen Maud Land and its continental shelf); Denmark (Greenland) and Norway have made submissions to the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS) and Russia is collecting additional data to augment its 2001 CLCS submission; Norway and Russia signed a comprehensive maritime boundary agreement in 2010refugees (country of origin): 15,062 (Eritrea); 11,537 (Syria); 8,379 (Somalia); 6,568 (Afghanistan) (2016)stateless persons: 3,251 (2016)
