1,972,126 (July 2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
noun: Slovene(s)
adjective: Slovenian
Slovene 83.1%, Serb 2%, Croat 1.8%, Bosniak 1.1%, other or unspecified 12% (2002 census)
Slovenian (official) 91.1%, Serbo-Croatian 4.5%, other or unspecified 4.4%, Italian (official, only in municipalities where Italian national communities reside), Hungarian (official, only in municipalities where Hungarian national communities reside) (2002 census)
Catholic 57.8%, Muslim 2.4%, Orthodox 2.3%, other Christian 0.9%, unaffiliated 3.5%, other or unspecified 23%, none 10.1% (2002 census)
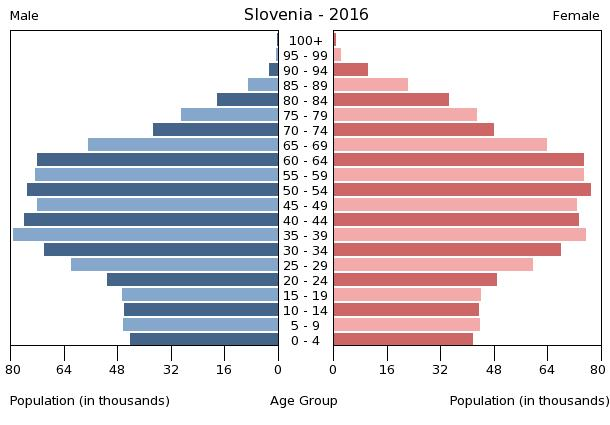
0-14 years: 13.32% (male 135,371/female 127,246)
15-24 years: 9.45% (male 95,546/female 90,744)
25-54 years: 42.9% (male 427,723/female 418,349)
55-64 years: 14.83% (male 143,642/female 148,821)
65 years and over: 19.51% (male 157,794/female 226,890) (2017 est.)
population pyramid:

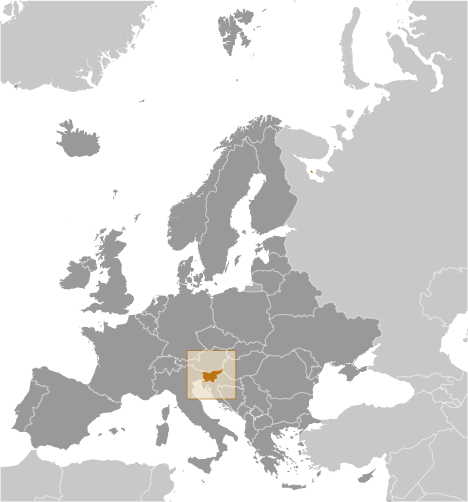
Europe
::SLOVENIA

Population Pyramid
A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.
total dependency ratio: 48.7
youth dependency ratio: 21.9
elderly dependency ratio: 26.8
potential support ratio: 3.7 (2015 est.)
total: 44.5 years
male: 42.8 years
female: 46.2 years (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
-0.31% (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 219
8.2 births/1,000 population (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 221
11.6 deaths/1,000 population (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
0.4 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
a fairly even distribution throughout most of the country, with urban areas attracting larger and denser populations; pockets in the mountainous northwest exhibit less density than elsewhere
urban population: 49.6% of total population (2017)
rate of urbanization: 0.18% annual rate of change (2015-20 est.)
LJUBLJANA (capital) 279,000 (2014)
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.68 male(s)/female
total population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2016 est.)
29.1 years (2014 est.)
9 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
total: 3.9 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 4.4 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 3.4 deaths/1,000 live births (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 194
total population: 78.3 years
male: 74.8 years
female: 82.2 years (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
1.36 children born/woman (2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 213
9.2% of GDP (2014)
country comparison to the world: 37
2.77 physicians/1,000 population (2014)
4.6 beds/1,000 population (2013)
improved:
urban: 99.7% of population
rural: 99.4% of population
total: 99.5% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0.3% of population
rural: 0.6% of population
total: 0.5% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 99.1% of population
rural: 99.1% of population
total: 99.1% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0.9% of population
rural: 0.9% of population
total: 0.9% of population (2015 est.)
<.1% (2016 est.)
<1000 (2016 est.)
<100 (2016 est.)
20.2% (2016)
country comparison to the world: 102
5.5% of GDP (2013)
country comparison to the world: 51
definition: NA
total population: 99.7%
male: 99.7%
female: 99.7% (2015 est.)
total: 17 years
male: 17 years
female: 18 years (2014)
total: 16.3%
male: 17.6%
female: 14.6% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
conventional long form: Republic of Slovenia
conventional short form: Slovenia
local long form: Republika Slovenija
local short form: Slovenija
former: People's Republic of Slovenia, Socialist Republic of Slovenia
etymology: related to the Slavic autonym (self-designation) "Slovenin," a derivation from "slovo" (word), denoting "people who speak (the same language)" (i.e., people who understand each other)
parliamentary republic
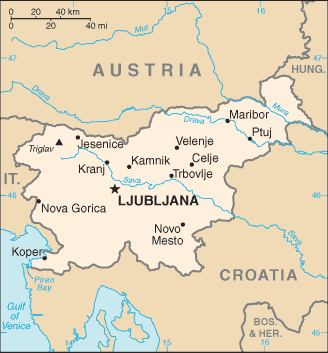
name: Ljubljana
geographic coordinates: 46 03 N, 14 31 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
201 municipalities (obcine, singular - obcina) and 11 urban municipalities (mestne obcine, singular - mestna obcina)
municipalities: Ajdovscina, Ankaran, Apace, Beltinci, Benedikt, Bistrica ob Sotli, Bled, Bloke, Bohinj, Borovnica, Bovec, Braslovce, Brda, Brezice, Brezovica, Cankova, Cerklje na Gorenjskem, Cerknica, Cerkno, Cerkvenjak, Cirkulane, Crensovci, Crna na Koroskem, Crnomelj, Destrnik, Divaca, Dobje, Dobrepolje, Dobrna, Dobrova-Polhov Gradec, Dobrovnik/Dobronak, Dolenjske Toplice, Dol pri Ljubljani, Domzale, Dornava, Dravograd, Duplek, Gorenja Vas-Poljane, Gorisnica, Gorje, Gornja Radgona, Gornji Grad, Gornji Petrovci, Grad, Grosuplje, Hajdina, Hoce-Slivnica, Hodos, Horjul, Hrastnik, Hrpelje-Kozina, Idrija, Ig, Ilirska Bistrica, Ivancna Gorica, Izola/Isola, Jesenice, Jezersko, Jursinci, Kamnik, Kanal, Kidricevo, Kobarid, Kobilje, Kocevje, Komen, Komenda, Kosanjevica na Krki, Kostel, Kozje, Kranjska Gora, Krizevci, Krsko, Kungota, Kuzma, Lasko, Lenart, Lendava/Lendva, Litija, Ljubno, Ljutomer, Log-Dragomer, Logatec, Loska Dolina, Loski Potok, Lovrenc na Pohorju, Luce, Lukovica,
Majsperk, Makole, Markovci, Medvode, Menges, Metlika, Mezica, Miklavz na Dravskem Polju, Miren-Kostanjevica, Mirna, Mirna Pec, Mislinja, Mokronog-Trebelno, Moravce, Moravske Toplice, Mozirje, Muta, Naklo, Nazarje, Odranci, Oplotnica, Ormoz, Osilnica, Pesnica, Piran/Pirano, Pivka, Podcetrtek, Podlehnik, Podvelka, Poljcane, Polzela, Postojna, Prebold, Preddvor, Prevalje, Puconci, Race-Fram, Radece, Radenci, Radlje ob Dravi, Radovljica, Ravne na Koroskem, Razkrizje, Recica ob Savinji, Rence-Vogrsko, Ribnica, Ribnica na Pohorju, Rogaska Slatina, Rogasovci, Rogatec, Ruse, Selnica ob Dravi, Semic, Sevnica, Sezana, Slovenska Bistrica, Slovenske Konjice, Sodrazica, Solcava, Sredisce ob Dravi, Starse, Straza, Sveta Ana, Sveta Trojica v Slovenskih Goricah, Sveti Andraz v Slovenskih Goricah, Sveti Jurij ob Scavnici, Sveti Jurij v Slovenskih Goricah, Sveti Tomaz, Salovci, Sempeter-Vrtojba, Sencur, Sentilj, Sentjernej, Sentjur, Sentrupert, Skocjan, Skofja Loka, Skofljica, Smarje pri Jelsah, Smarjeske Toplice, Smartno ob Paki, Smartno pri Litiji, Sostanj, Store, Tabor, Tisina, Tolmin, Trbovlje, Trebnje, Trnovska Vas, Trzic, Trzin, Turnisce, Velika Polana, Velike Lasce, Verzej, Videm, Vipava, Vitanje, Vodice, Vojnik, Vransko, Vrhnika, Vuzenica, Zagorje ob Savi, Zalec, Zavrc, Zelezniki, Zetale, Ziri, Zirovnica, Zrece, Zuzemberk
urban municipalities: Celje, Koper-Capodistria, Kranj, Ljubljana, Maribor, Murska Sobota, Nova Gorica, Novo Mesto, Ptuj, Slovenj Gradec, Velenje
25 June 1991 (from Yugoslavia)
Independence Day/Statehood Day, 25 June (1991)
history: previous 1974 (preindependence); latest passed by Parliament 23 December 1991
amendments: proposed by at least 20 National Assembly members, by the government, or by petition of at least 30,000 voters; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly; referendum required if agreed upon by at least 30 Assembly members; passage in a referendum requires participation of a majority of eligible voters and a simple majority of votes cast; amended several times, last in 2015 (2016)
civil law system
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Slovenia; both parents if the child is born outside of Slovenia
dual citizenship recognized: yes, for select cases
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years, the last 5 of which have been continuous
18 years of age, 16 if employed; universal
chief of state: President Borut PAHOR (since 22 December 2012)
head of government: Prime Minister Miro CERAR (since 18 September 2014)
cabinet: Council of Ministers nominated by the prime minister, elected by the National Assembly
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 22 October and 12 November 2017 (next election schedule for 2022); following National Assembly elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually nominated prime minister by the president and elected by the National Assembly
election results: Borut PAHOR is reelected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Borut PAHOR (independent) 47.1%, Marjan SAREC (Marjan Sarec List) 25%, Romana TOMC (SDS) 13.7%, Ljudmila NOVAK (NSi) 7.2%, other 7%; percent of vote in second round - Borut PAHOR 52.9%, Marjan SAREC 47.1%; note - a snap election was held on 13 July 2014 following the resignation of Prime Minister Alenka BRATUSEK on 5 May 2014; Miro CERAR (SMC) elected prime minister; National Assembly vote - 57 to 11
description: bicameral Parliament consists of the National Council or Drzavni Svet (40 seats; members indirectly elected by an electoral college to serve 5-year terms) and the National Assembly or Drzavni Zbor (90 seats; 88 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote and 2 directly elected in special constituencies for Italian and Hungarian minorities by simple majority vote; members serve 4-year terms); note - the National Council is primarily an advisory body with limited legislative powers
elections: National Assembly - last held on 13 July 2014 (next to be held by July 2018)
election results: percent of vote by party - SMC 34.5%, SDS 20.7%, DeSUS 10.2%, ZL 6%, SD 6%, NSi 5.6%, ZaAB 4.4%, other 12.6%; seats by party - SMC 36, SDS 21, DeSUS 10, ZL 6, SD 6, NSi, 5, ZaAB 4, Hungarian minority 1, Italian minority 1
note: as of January 2017, seats by party - SMC 35, SDS 19, DeSUS 11, ZL 6, SD 6, NSi 5, Hungarian minority 1, Italian minority 1, unaffiliated 6
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the court president and 37 judges organized into civil, criminal, commercial, labor and social security, administrative, and registry departments); Constitutional Court (consists of the court president, vice president, and 7 judges)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court president and vice president appointed by the National Assembly upon the proposal of the Minister of Justice based on the opinions of the Judicial Council, an 11-member independent body elected by the National Assembly from proposals submitted by the president, attorneys, law universities, and sitting judges; other Supreme Court judges elected by the National Assembly from candidates proposed by the Judicial Council; Supreme Court judges appointed for life; Constitutional Court judges appointed by the National Assembly from nominations by the president of the republic; Constitutional Court president selected from among their own for a 3-year term; other judges elected for single 9-year terms
subordinate courts: county, district, regional, and high courts; specialized labor-related and social courts; Court of Audit; Administrative Court
Alliance of Social Liberal Democrats or ZSD (formerly Alliance of Alenka Bratusek or ZaAB) [Alenka BRATUSEK]
Democratic Party of Pensioners of Slovenia or DeSUS [Karl ERJAVEC]
Marjan Sarej List [Marjan SAREC]
Modern Center Party or SMC [Miro CERAR]
New Slovenia or NSi [Ljudmila NOVAK]
Slovenian Democratic Party or SDS [Janez JANSA]
Social Democrats or SD [Dejan ZIDAN]
United Left or ZL (collective leadership)
inactive: Alliance for the Re-liberation of Somalia; reportedly inactive since 2009
Roman Catholic Church
other: various trade and public sector employee unions
Australia Group, BIS, CD, CE, CEI, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA (cooperating state), EU, FAO, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, MIGA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, SELEC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
chief of mission: Ambassador Stanislav VIDOVIC (since 21 July 2017)
chancery: 2410 California Street N.W., Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 386-6601
FAX: [1] (202) 386-6633
consulate(s) general: Cleveland (OH)
chief of mission: Ambassador Brent Robert HARTLEY (since 12 February 2015)
embassy: Presernova 31, 1000 Ljubljana
mailing address: American Embassy Ljubljana, US Department of State, 7140 Ljubljana Place, Washington, DC 20521-7140
telephone: [386] (1) 200-5500
FAX: [386] (1) 200-5555
three equal horizontal bands of white (top), blue, and red, derive from the medieval coat of arms of the Duchy of Carniola; the Slovenian seal (a shield with the image of Triglav, Slovenia's highest peak, in white against a blue background at the center; beneath it are two wavy blue lines depicting seas and rivers, and above it are three six-pointed stars arranged in an inverted triangle, which are taken from the coat of arms of the Counts of Celje, the prominent Slovene dynastic house of the late 14th and early 15th centuries) appears in the upper hoist side of the flag centered on the white and blue bands
Mount Triglav; national colors: white, blue, red
name: "Zdravljica" (A Toast)
lyrics/music: France PRESEREN/Stanko PREMRL
note: adopted 1989; originally written in 1848; the full poem, whose seventh verse is used as the anthem, speaks of pan-Slavic nationalism
With excellent infrastructure, a well-educated work force, and a strategic location between the Balkans and Western Europe, Slovenia has one of the highest per capita GDPs in Central Europe, despite having suffered a protracted recession in the 2008-09 period in the wake of the global financial crisis. Slovenia became the first 2004 EU entrant to adopt the euro (on 1 January 2007) and has experienced one of the most stable political transitions in Central and Southeastern Europe.
In March 2004, Slovenia became the first transition country to graduate from borrower status to donor partner at the World Bank. In 2007, Slovenia was invited to begin the process for joining the OECD; it became a member in 2012. However, long-delayed privatizations, particularly within Slovenia’s largely state-owned and increasingly indebted banking sector, have fueled investor concerns since 2012 that the country would need EU-IMF financial assistance. In 2013, the European Commission granted Slovenia permission to begin recapitalizing ailing lenders and transferring their nonperforming assets into a “bad bank” established to restore bank balance sheets. From 2014 to 2016, export-led growth, fueled by demand in larger European markets pushed GDP growth to 2.3% per year, while stubbornly high unemployment fell slightly to below 12%.
Prime Minister CERAR’s government took office in September 2014, pledging to press ahead with commitments to privatize a select group of state-run companies, rationalize public spending, and further stabilize the banking sector.
$66.5 billion (2016 est.)
$63.66 billion (2015 est.)
$61.58 billion (2014 est.)
note: data are in 2016 dollars
country comparison to the world: 99
$44.73 billion (2016 est.)
3.1% (2016 est.)
2.3% (2015 est.)
3% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
$32,200 (2016 est.)
$31,300 (2015 est.)
$30,600 (2014 est.)
note: data are in 2016 dollars
country comparison to the world: 58
23.9% of GDP (2016 est.)
23.7% of GDP (2015 est.)
25.4% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
household consumption: 51.8%
government consumption: 19%
investment in fixed capital: 18.4%
investment in inventories: 1.3%
exports of goods and services: 79.2%
imports of goods and services: -69.6% (2016 est.)
agriculture: 2.3%
industry: 32.4%
services: 65.3% (2016 est.)
hops, wheat, coffee, corn, apples, pears; cattle, sheep, poultry
ferrous metallurgy and aluminum products, lead and zinc smelting; electronics (including military electronics), trucks, automobiles, electric power equipment, wood products, textiles, chemicals, machine tools
2.8% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
920,400 (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
agriculture: 3.7%
industry: 31.7%
services: 64.6% (2015 est.)
8% (2016 est.)
12.3% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
14.3% (2015 est.)
lowest 10%: 3.8%
highest 10%: 20.2% (2012)
24.5 (2015)
25 (2014)
country comparison to the world: 147
revenues: $19.2 billion
expenditures: $20.01 billion (2016 est.)
43.6% of GDP (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
-1.8% of GDP (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
79.7% of GDP (2016 est.)
83.5% of GDP (2015 est.)
note: defined by the EU's Maastricht Treaty as consolidated general government gross debt at nominal value, outstanding at the end of the year in the following categories of government liabilities: currency and deposits, securities other than shares excluding financial derivatives, and loans; general government sector comprises the subsectors: central government, state government, local government, and social security funds
country comparison to the world: 37
calendar year
-0.1% (2016 est.)
-0.7% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
0% (16 March 2016)
0.05% (4 Sept 2014)
note: this is the European Central Bank's rate on the marginal lending facility, which offers overnight credit to banks in the euro area
country comparison to the world: 150
2.81% (31 December 2016 est.)
3.49% (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
$16.54 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$14.39 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
note: see entry for the European Union for money supply for the entire euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 18 members of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own borders
country comparison to the world: 69
$24.3 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$23.31 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 83
$30.23 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$29.96 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
$5.6 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$5.94 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$6.2 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
$2.332 billion (2016 est.)
$1.884 billion (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
$27.65 billion (2016 est.)
$26.67 billion (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
manufactured goods, machinery and transport equipment, chemicals, food
Germany 19.3%, Italy 10.4%, Austria 7.5%, Croatia 7.3%, Hungary 4.4%, France 4.1% (2016)
$25.95 billion (2016 est.)
$25.04 billion (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
machinery and transport equipment, manufactured goods, chemicals, fuels and lubricants, food
Germany 16.8%, Italy 13.5%, Austria 9.9%, Croatia 5.5%, China 4.8%, Turkey 4.4% (2016)
$743.2 million (31 December 2016 est.)
$856.2 million (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
$46.3 billion (31 January 2017 est.)
$48.2 billion (31 January 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
$14.83 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$14.49 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
$7.837 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$7.843 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
euros (EUR) per US dollar -
0.9214 (2016 est.)
0.885 (2015 est.)
0.885 (2014 est.)
0.7634 (2013 est.)
0.7752 (2012 est.)